Cervical vertebrae
The cervical vertebrae (lat. Vertebrae cervicales ) form the head end (cranial) end of the spinal column of vertebrates and particularly the movable swirl between the thoracic spine and the head . This section is known as the cervical spine .
number
Mammals usually have seven cervical vertebrae. This applies to the long neck of the giraffes as well as to whales , but also to small mammals such as the shrews . Humans also have seven cervical vertebrae, which in medicine are abbreviated with the letter C (C1 to C7). Round-tailed sea cows and the Hoffmann two-toed sloth ( Choloepus hoffmanni ) are the only mammals to have only six cervical vertebrae. In three-toed animals three to four thoracic vertebrae are shifted to why long ran up to ten neck vertebrae. In birds , the number of cervical vertebrae varies between ten and 31 (see also bird skeleton ).
The largest cervical vertebra ever found in a terrestrial vertebrate is the eighth cervical vertebra of Sauroposeidon , which is 1.4 m long.
Head joint
The two vertebrae of the cervical spine that are closest to the head differ morphologically from the rest of the cervical vertebrae, which largely correspond to the uniform structure of a vertebra: The top vertebra, the atlas or "Nicker" - has the shape of a ring. Its job is to carry the head. The second cervical vertebra, the axis (also called "Dreher"), together with the atlas, forms the two parts of the lower head joint , the so-called articulationes atlantoaxiales mediana et laterales. When the head is turned sideways, the atlas ring rotates around the axial tooth ( dens axis ).
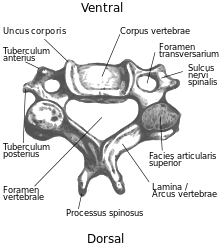
anatomy
The remaining 5 cervical vertebrae have as a special feature in humans hook extensions Unci corporis (singular Uncus corporis , sometimes) as uncinate process referred to, the raise in the first decade of life and leads to formation of a gap between the vertebrae and the Unci, the unkovertebralen columns or Unkovertebralgelenken . With the exception of the first and sometimes second thoracic vertebrae, all other vertebral bodies are nearly planar on the surfaces. In the case of Klippel-Feil syndrome or in advanced age, a disruption of the vertebral system can lead to uncovertebral arthrosis and significant movement restrictions up to nerve or vessel entrapment , as the unci corporis are located directly next to the spinal nerve groove ( sulcus nervi spinalis ).
Another special feature of the cervical vertebrae are the foramina transversaria (singular: foramen transversarium ), which act as the passage point for the arteria vertebralis (from the 6th to the 1st cervical vertebra) upwards and for the venous plexus of the vena vertebralis from the 1st to the 7th vertebra serve below.
The 7th cervical vertebra is the prominent vertebra because it has the most protruding spinous process (towards the back) and is usually easily palpable. On it, as well as on the 6th, there may sometimes still be short ribs, so-called neck ribs, which can lead to difficulties ( neck rib syndrome ).
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ L. Hautier et al.: Skeletal development in sloths and the evolution of mammalian vertebral patterning. In: PNAS. 2010. doi: 10.1073 / pnas.1010335107
- ^ MJ Wedel, RL Cifelli, RK Sanders: Osteology, paleobiology, and relationships of the sauropod dinosaur Sauroposeidon. In: Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 45, 2000, pp. 343-388.
- ^ Alfred Benninghoff, Detlev Drenckhahn, B. Christ: Anatomy: macroscopic anatomy, embryology and human histology . tape 1 . Urban & Schwarzenberg, Munich a. a. 2003, ISBN 3-437-42340-1 .
