Finger length ratio
Finger length ratio describes the ratio of the length of the index finger to the length of the ring finger and is therefore also called 2D: 4D (D for digitus, Latin for finger / toe). The finger length ratio correlates with the ratio of fetal estradiol to fetal testosterone level .
Correlative studies show an association between finger length ratio and fetal growth, handedness , autism , Asperger's syndrome , sperm count , family size , age at heart attack in men and breast cancer in women. It could also be shown that alcohol addiction and dependent video games are associated with a smaller 2D: 4D finger length ratio. A questionnaire study with 134 Austrian professional firefighters stated: "The more masculine the expression of the finger length ratio, [...] the more the firefighter generally strives for risky behavior".
Since a high natural testosterone level is a biomarker of athletic performance and talent in strength / speed strength sports, such individuals are systematically searched for. Most recently it was tennis where it was identified as a talent criterion.
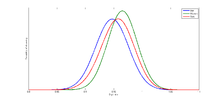
distribution
From a study of 136 men and 137 women at the University of Alberta :
- Men: mean 0.947, standard deviation 0.029
- Women: mean 0.965, standard deviation 0.026
Assuming a normal distribution, this leads to 95% prediction intervals for the 2D: 4D ratio of 0.889–1.005 for men and 0.913–1.017 for women.
From a 2018 study of 249 PhD and undergraduate students from Warwick University, proportionally balanced by gender:
- Men: mean 0.951, standard deviation 0.035
- Women: mean 0.968, standard deviation 0.028
literature
- John T. Manning: Digit ratio: a pointer to fertility, behavior, and health. Rutgers University Press, 2002, ISBN 0-8135-3030-X .
Individual evidence
- ↑ S. Lutchmaya, S. Baron-Cohen, P. Raggatt, R. Knickmeyer, JT Manning: 2nd to 4th digit ratios, fetal testosterone and estradiol. In: Early Human Development. 77, 2004, pp. 23-28, doi: 10.1016 / j.earlhumdev.2003.12.002 .
- ↑ Johannes Kornhuber, Gabriele Erhard u. a .: Low Digit Ratio 2D∶4D in Alcohol Dependent Patients. In: PLoS ONE. 6, 2011, p. E19332, doi: 10.1371 / journal.pone.0019332 .
- ↑ Johannes Kornhuber, Eva-Maria Zenses u. a .: Low 2D: 4D Values Are Associated with Video Game Addiction. In: PLoS ONE. 8, 2013, p. E79539, doi: 10.1371 / journal.pone.0079539 .
- ↑ Ulrike Pum: Test theoretical analysis of the Sensation Seeking scale V and connections with relationship quality, professional commitment and digit ratio (2D: 4D) in firefighters . (PDF) Diploma thesis, October 2008, p. 98 ,; accessed on December 12, 2017
- ^ Arnd Krüger : finger length. In: competitive sport (magazine) 41 (2011), 2, pp. 38–39.
- ↑ CC Hsu, B. Su, NW Kan, SL Lai, TH Fong, CP Chi, CC Chang, MC Hsu: Elite collegiate tennis athletes have lower 2D: 4D ratios than those of nonathlete controls. In: Journal of strength and conditioning research. Volume 29, number 3, March 2015, pp. 822-825, doi: 10.1519 / JSC.0000000000000681 , PMID 25226321 .
- ↑ livescience.com: Finger Length Predicts Aggression in Men
- ↑ frontiersin.org: Self-confidence, Overconfidence and Prenatal Testosterone Exposure: Evidence from the Lab