Forster-Decker reaction
The Forster-Decker reaction is a reaction from the field of organic chemistry . It is also known as the "Forster reaction". It is the representation of secondary amines from primary amines . The reaction was first described in 1899 by the British chemist Martin Onslow Forster (1872-1945) and later developed further by the German chemist Hermann Decker (1869-1939).
Overview reaction
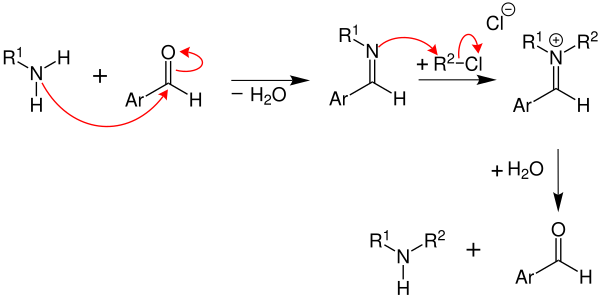
The Forster-decker reaction describes the synthesis of secondary amines by amine - alkylation . These can be prepared by reacting a primary amine with an aromatic aldehyde and a haloalkyl . With the help of this reaction secondary amines are thus synthesized from primary amines.
A primary amine (left) reacts with an aromatic aldehyde ( benzaldehyde ) and a haloalkyl to form a secondary amine (right).
Reaction mechanism
In the first reaction step , an imine , also called Schiff's base , is formed with elimination of water . The alkylation of the Schiff base works best with aliphatic and aromatic-aliphatic imines. However, it is also possible with imines produced from unsaturated amines (R 1 = alkenyl). Imines produced from aromatic amines (R 1 = aryl ), on the other hand, enter into unwanted side reactions and are therefore hardly suitable. The larger the alkyl radical of the haloalkyl (in the example the chloroalkane R 2 -Cl), the worse the result of this amine synthesis . The methyl group has therefore proven to be particularly suitable as an alkyl radical. The following mechanism shows the production of secondary amines from primary amines :
First, the primary amine reacts with an aromatic aldehyde (e.g. benzaldehyde ) to form an imino compound . The addition of a haloalkyl to the carbon-nitrogen double bond of the imino compound produces a quaternary ammonium salt . This gives a secondary amine by hydrolysis .
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ BP Mundy, MG Ellerd, FG Favaloro, Jr .: Name Reactions and Reagents in organic synthesis. 2nd Edition. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ 2005, ISBN 978-0-471-22854-7 , p. 35.
- ↑ Entry on Forster-Decker reaction. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 3, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e H. Krauch, W. Kunz: Name reactions of organic chemistry . Dr. Alfred Hüthig Verlag, Heidelberg 1961, p. 163.