Common night tree snake
| Common night tree snake | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Common night tree snake ( Boiga trigonata ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Boiga trigonata | ||||||||||||
| ( Tailor in Bechstein , 1802) |
The common night tree snake ( Boiga trigonata ), sometimes referred to as the triangular night tree snake , is a species of the snake (Colubridae) and belongs to the genus of the night tree snake ( Boiga ).
features
The Boiga trigonata reaches a total length between 80 and 117 cm, with females mostly becoming larger than males. The body is slim and slightly flattened on the sides. The head is short and set off from the neck, the eye is relatively large and protruding. The pupils are slit vertically when exposed to light. The shields of the upper lip are light. A light, black-rimmed stripe can be seen between the eye and the corner of the mouth. The basic color of the body varies between yellowish-white, gray and brown. The top of the head and back are marked by striking V- or Y-shaped, light and dark-edged spots. The ventral side is light, the ventral shields are dotted black on the edge. The subspecies Boiga trigonata melanocephala differs from the nominate form by a generally darker body color and a black head. Boiga trigonata is a snake and has a venom apparatus with venom glands (specialized salivary glands ) and immobile fangs located in the rear upper jaw ( opistoglyph tooth position).
Pholidosis
The pholidosis (scaling) shows the following characteristics:
- 8 upper lip shields ( supralabials ), of which the 4th and 5th and, if applicable, the 3rd touching the lower edge of the eye,
- 11 lower lip shields ( sublabials ),
-
Scuta ocularia :
- 1 front eye shield (scutum praeoculare)
- 2 posterior shields (Scuta postocularia),
- 1 small, square scutum loreale ,
- 21 rows of smooth trunk scales ( Scuta dorsalia ),
- 106 to 256 abdominal shields ( scuta ventralia ),
- 75 to 96 under tail shields ( Scuta subcaudalia ) and
- 1 undivided anal shield ( scutum anale ).
Systematics
The first description by Schneider was under the name Coluber trigonata . Currently (status: 2018) two subspecies are listed:
- Boiga trigonata trigonata ( Schneider 1802) - nominate form
- Boiga trigonata melanocephala ( Annandale 1904)
distribution
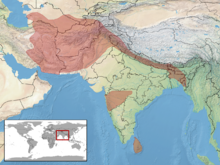
The distribution area includes areas in Sri Lanka , India , Pakistan , Nepal , Bangladesh , Afghanistan , Turkmenistan (south), Uzbekistan (south), Tajikistan (southeast) and Iran . Boiga trigonata melanocephala is found in Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Iran. In the Himalayas , Boiga trigonata can be found at heights of up to 1,500 meters. The populated habitats are extremely diverse and include, among other things, evergreen forests. The species can be observed in both moist and relatively dry habitats. Boiga trigonata can regularly be found near human settlements or in gardens.
Way of life
Boiga trigonata leads a largely nocturnal way of life. It is mainly to be found arboricolous (climbing) in branches of bushes and trees close to the ground, but is also found in almost vegetation-free biotopes. Hollow tree trunks are often used as hiding places, in which she hides with tangled body loops. The range of prey includes small lizards, especially beautiful lizards ( calotes ), as well as small mammals and birds. Prey animals are killed by strangulation and simultaneous application of poison. The propagation is done by oviparity so oviparous. 3 to 11 eggs are laid in September. These measure around 30 × 10 mm. The young snakes measure approx. 26 cm when hatching.
Boiga trigonata shows strong defensive behavior when threatened. In the defensive position, the head and front body are raised. The body is alternately inflated and exhaled by deep breathing. Short, checked sibilants are emitted. The body is laid in around eight loops, while the head is in the middle. Vibrating movements are made with the tip of the tail. When approaching or persistent provocation, multiple bites often occur.
Snake venom
The poison secretion from Boiga trigonata contains neurotoxins , among other things . It is effective against prey. Serious symptoms are not to be expected in the case of bite accidents with humans.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Boiga trigonata in The Reptile Database (accessed on July 9, 2018)
- ↑ Nova Nature Welfare Society: Common Cat Snake, Boiga trigona (accessed July 9, 2018)
- ↑ University of Adelaide, Clinical Toxinology Resources: Boiga trigonata (accessed July 9, 2018)
literature
- Ludwig Trutnau: Snakes in the Terrarium Vol. 1/2: Non-poisonous snakes . Publishing house Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart 2002.