Gemmenich tunnel
| Gemmenich tunnel | ||
|---|---|---|
|
West portal of the Gemmenich tunnel
|
||
| use | Railway tunnel | |
| traffic connection | Montzen route | |
| place | Vaalserberg | |
| length | 870 m | |
| Number of tubes | 1 | |
| Largest coverage | 66 m | |
| construction | ||
| Client | Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company | |
| start of building | 1872 | |
| business | ||
| operator | DB network | |
| location | ||
|
|
||
| Coordinates | ||
| East portal | 50 ° 45 ′ 21 ″ N , 6 ° 1 ′ 46 ″ E | |
| West portal | 50 ° 45 ′ 9 ″ N , 6 ° 1 ′ 5 ″ E | |
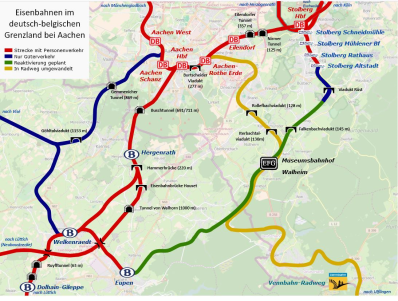
The Gemmenich Tunnel is an 870 m long, double-track railway tunnel near Aachen , which connects the DB route 2552 with the SNCB route Spoorlijn 24 in Belgium on the Montzen route .
The tunnel was built in 1872 by the Bergisch-Märkische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft as part of the Aachen – Bleyberg – Welkenraedt line. The building is named after the village of Gemmenich , now part of Plombières . In Belgium the tunnel is also known as the “Botzelaer Tunnel” (Tunnel de Botselaer) . It is a border tunnel between Germany and Belgium, over a length of 250 m it lies on Belgian territory. The state border running in the tunnel only shifted slightly as a result of the German assignment of territory after the First World War . The tunnel crosses the 322 m high Vaalserberg with the border triangle Germany-Belgium-Netherlands with a maximum overburden of 66 m . For operational reasons, the tunnel has been managed by the German side since its construction, initially by the Bergisch-Märkische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft, then by the Deutsche Reichsbahn , the Deutsche Bundesbahn and, since 1994, by the Deutsche Bahn AG or its subsidiary DB Netz AG .
Between 1989 and 1991 the tunnel was widened and refurbished for later electrification . For this purpose, the up to 77 cm thick masonry vault was partially cut off and replaced by a reinforced, 17 cm thick shotcrete shell. The base vault, which is up to 60 cm thick, was also partially demolished and replaced by a reinforced concrete slab . A fixed track with galvanized Y-thresholds is mounted on the plate . In addition, a third track was laid in the form of a track loop to the center of the tunnel so that trains with excess loading gauge (LÜ) can also use the route. The track can be used in both directions. The tunnel was electrified in 2008 with power rails on the tunnel ceiling. The conductor rail above the right-hand track in the direction of Aachen-West-Montzen was offset towards the tunnel axis in such a way that it can also be reached by pantographs from locomotives on the LÜ track. Train journeys that exceed the loading gauge and must use the track loop can also be carried out with electrical traction.
literature
- Pichier: The tunnel near Aachen on the link between the Bergisch-Märkische Railway and the Belgian State Railway. In: Zeitschrift für Bauwesen , 23rd year 1873, column 511-516.
- Hans Schweers, Henning Wall: Railways around Aachen: 150 years of the international Cologne – Aachen – Antwerp line . Verlag Schweers + Wall, Aachen 1993, ISBN 3-921679-91-5 .
Web links
- Helmut Roel: Gemmenich Tunnel. In: Eisenbahnrelicts - Alles Schnucke ..... Helmut Roel, accessed on January 20, 2016 .
- Lothar Brill: Route 2552: Gemmenich Tunnel. In: eisenbahn-tunnelportale.de. Lothar Brill, January 19, 2012, accessed January 20, 2016 .
- Stefan Jakab: * Lightshow * at the Gemmenich Tunnel near Reinhartzkehl (Aachen). A freight train from Belgium is traveling with high beam. The glaring light gives a deep insight into the tunnel. In: bahnbilder.de. Thomas Wendt, July 21, 2012, accessed January 20, 2016 .
Individual evidence
- ^ Ulrich Simons: Goods faster in Antwerp. In: Aachener Nachrichten . December 27, 2008, accessed January 20, 2016 .