Glutathione reductase
| Glutathione reductase | ||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Ribbon model of the GSR of humans, according to PDB 1GRE | ||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 479 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homodimer | |
| Cofactor | FAD | |
| Precursor | (522 aa) | |
| Isoforms | M, C, 2, 3, 4 | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | GSR | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 1.8.1.7 , oxidoreductase | |
| Response type | Redox reaction | |
| Substrate | GSSG + NADPH / H + | |
| Products | 2 GSH + NADP + | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Animals, fungi, some bacteria | |
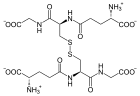
The glutathione reductase (GSR) (more precisely, glutathione reductase ), the enzyme , the glutathione disulfide (GSSG) to glutathione reduced (GSH). A reduction equivalent (NADPH / H + ), which comes from the pentose phosphate route, is used. The reaction takes place in animals, fungi and various bacteria and is used to restore glutathione after it has been oxidized.
When people can from the GSR - Gen several splice variants of the enzyme produced, the (, cytosolic mitochondrial) differ in their localization. Mutations in GSR can lead to inherited decreased enzyme activity with hemolytic anemia .
Catalyzed reaction
One molecule of glutathione disulfide is reduced to two molecules of glutathione.
Individual evidence
- ↑ InterPro : IPR006322 Glutathione reductase, eukaryote / bacterial (English)
- ↑ UniProt P00390
- ↑ Orphanet: Anemia, haemolytic due to glutathione reductase deficiency
Web links
Wikibooks: Biochemistry and Pathobiochemistry: Glutathione Metabolism - Learning and Teaching Materials