Corcovado Gulf
| Corcovado Gulf | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Corcovado Gulf between Chiloe and mainland Chilean |
||
| Waters | Pacific Ocean | |
| Land mass | Mainland South America | |
| Geographical location | 43 ° 22 ′ 0 ″ S , 73 ° 21 ′ 13 ″ W | |
|
|
||
| Tributaries | Moraleda Channel | |
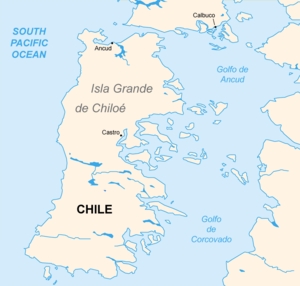
The Gulf of Corcovado is located between the Chilean island of Chiloé and the Chilean mainland.
location

East of the canal is the Chilean Región de los Lagos . There is also the Corcovado volcano , which gave the gulf its name.
West of the Corcovado Gulf is Isla Grande de Chiloe, a popular tourist attraction. The main town of the island, Castro, is located on the Gulf of Corcovado .
In the north, the Gulf of Ancud borders the Gulf of Corcovado.
In the south joins the Moraleda Canal , which separates the Chonos Archipelago from the Chilean mainland.
Salmon fattening
The Gulf of Corcovado has been used for fattening salmon and mussels since the 1980s , so that today around 90% of Chilean salmon and mussels come from the Corcovado Gulf. This means that the region has played a major role in the fact that Chile has become the world's largest salmon producer after Norway.
Whales
The Chiloe-Corcovado region is known for its biodiversity, but the whale populations of the waters are particularly noteworthy. Blue whales were sighted in the Gulf of Corcovado 100 years ago , but the population was not rediscovered until a new sighting in 2003. The life of the blue whales is now more and more in danger, since the aquaculture in the Gulf creates mud from excrement and food residues of the salmon and lowers the oxygen content of the water. Antibiotic pollution of the Gulf is also a growing problem, as Chile uses significantly more antibiotics for salmon fattening than Norway, for example. Researchers assume that antibiotics have negative effects on the reproduction of blue whales, as a similar connection has already been observed in sperm whales . Another burden for the whales is the increasing shipping traffic in the region, which makes it difficult to locate the animals acoustically.
Environmental organizations like WWF Chile try to counteract this development.
Individual evidence
- ↑ 3sat.online: Chile's wild south - The settlers' fjords -. Retrieved on October 16, 2018 (German).
- ↑ Earth Snapshot • Moraleda Channel. Retrieved October 16, 2018 (American English).
- ↑ hermsen: http://mhs.org/stiftung/front_content.php?idcat=82&idart=557. Retrieved October 16, 2018 .
- ↑ Frankfurter Rundschau: Salmon fattening: fish farming beats blue whale on the stomach . In: Frankfurter Rundschau . ( fr.de [accessed on October 16, 2018]).
- ^ Gulf of Corcovado - home to numerous marine mammals . January 4, 2016 ( wwf.de [accessed October 16, 2018]).