Border between Gambia and Senegal
The border between Gambia and Senegal is an international border between the two states.
description
overview
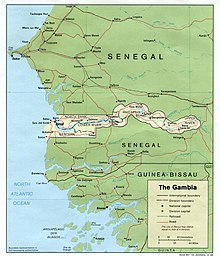
The Gambia is a state in West Africa , almost isolated in Senegal . It stretches on both sides of the Gambia River and is 20 to 50 km wide on each of its banks, over a length of 320 km. Only the Atlantic Ocean allows the Gambia not to be completely isolated on Senegalese territory.
Although the Gambia is the smallest independent state in continental Africa, there are more than 50 smaller international land borders on the African continent as the Gambia is shaped like a thin, long ribbon. For Senegal, it is the second longest international border after the border with Mauritania .
course
Land border
The approximately 740 km long land border between the two countries generally consists of two parts, oriented roughly from west to east, one north of Gambia and the other south, which are connected by an arch at their eastern end. Your physiognomy has two different zones:
- To the west, both north and south, the boundary follows a parallel of latitude (approximately 13 ° 35 '35 "N in the north, 13 ° 9' 52" N in the south), approximately 100 km. The only exception is the western end of the southern part, the approximately twenty kilometers long border along the course of the Allahein to the southwest.
- To the east, the border surrounds the Gambia River roughly on its route. It then consists of a series of arcs.
Maritime border
The approximately 800 km long maritime borders between the two countries consist of two different segments in the Atlantic that are almost completely horizontal, one in the north and the other in the south.
To the north, the boundary is defined by a single segment of latitude 13 ° 35 '35 "N:
- It starts on the east coast, where the land border ends in the direction of 13 ° 35 '35 " N , 16 ° 33' 0" W .
- The western border is not set by treaty, but the two countries claim an exclusive economic zone of 200 nautical miles (370 km). It ends in the west at approximately 13 ° 35 '35 " N , 20 ° 0' 0" W .
In the south the border is defined by several segments:
- It starts east on the coast, again on the edge of the border, at 13 ° 3 '51 " N , 16 ° 44' 49" W .
- It continues in the southwest to 13 ° 1 '21 " N , 16 ° 45' 19" W .
- It tends to the north 13 ° 3 '27 " N , 16 ° 45' 22" W .
- There then follows the latitude 13 ° 03 '27 "N and the western limit is also not determined by the contract, however, the border ends at approximately 13 ° 7' 27" N , 20 ° 10 '48 " W .
history
The land border was established in 1889 by an agreement between France and the United Kingdom on the demarcation between the colonies of Senegal and Gambia. Legend has it that the distance between the border and the Gambia River is the distance a British naval cannon could reach at the time, but no historical evidence supports this view; the border is also precisely delimited by a Franco-British commission.
Senegal became independent from France on June 20, 1960 as a member of the Mali Federation and left it on August 20, 1960, while Gambia gained independence from the United Kingdom on February 18, 1965.
The two countries joined the Senegambia Confederation in 1982 , but this organization was dissolved in 1989.
The maritime borders between the two countries are determined by a treaty signed on June 4, 1975.
See also
Individual evidence
- ^ Donald R. Wright: The World and a Very Small Place: A History of Globalization in Niumi, The Gambia . 3rd edition. ME Sharpe, New York 2004, pp. 151-152 .
- ↑ Craig Emms, Linda Barnett: Brandt Travel Guide for The Gambia . Chalford, 2001.
- ↑ Maritime Boundaries: The Gambia / Senegal, June 4, 1975. United Nations, accessed August 19, 2019 .