Great Mindoro fruit pigeon
| Great Mindoro fruit pigeon | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Great Mindoro fruit pigeon |
||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||
| Ducula mindorensis | ||||||||||
| ( Whitehead , 1896) |
The great Mindoro fruit pigeon ( Ducula mindorensis ) is a very large, monotypical , species of pigeon birds. It occurs exclusively on the Philippine island of Mindoro .
The stock situation of the Great Mindoro pigeon comes with high risk ( endangered specified).
Appearance
The great Mindoro fruit pigeon reaches a body length of about 50 centimeters. It is therefore significantly larger than a wood pigeon . The tail accounts for 15.9 to 17.8 centimeters. The beak has a length of 2.1 to 2.4 centimeters. There is no noticeable gender dimorphism .
Appearance of the males
The forehead and the reins are dull pink and then merge into a blue-gray part. The neck is also grayer, but darker than the top of the head. The feathers around the eye and the back of the ear-covers are blackish. The coat is also blackish and shimmers intensely copper-colored and purple at the lower end. The elytra are green with a bronze tinge. The arms are green with a turquoise sheen. The wings of the hand are blackish with a blue-green tinge on the outer flags.
The back is glossy green, the upper tail-coverts are green with a dark blue sheen. The tail is blackish, the outer flags shine blue-green and purple. A wide, dark gray central band runs across the middle of the tail feathers.
The chin and throat are pale pink with a pale gray neck and a slightly darker chest. The belly is also gray, the under tail-coverts are dark gray. The beak is black. The iris is bright yellow inside and red outside. The dark circles are dark red, the feet are dull brown.
Appearance of the females
The plumage of the female is very similar to that of the male. In the female, only the under tail-coverts have conspicuous chestnut-brown borders. The iris is straw yellow with a golden brown outer ring. The beak is brown with a black tip. The feet and legs are dull red.
Possible confusion
There are two types of fruit pigeon in the distribution area, with which the Great Mindoro fruit pigeon can be confused. The gray-headed fruit pigeon is significantly smaller and the gray central band above the tail feathers is noticeably lighter. The belly is pink and the under tail-coverts are maroon. The top of the gray-headed fruit pigeon is greener and has a less intense shine.
The bronze fruit dove differs significantly from the great Mindoro fruit dove. It has a uniformly soft pink head with a gray tinge. The neck, chest and stomach are also colored in this way. The gray central band over the tail feathers is also missing.
Distribution area
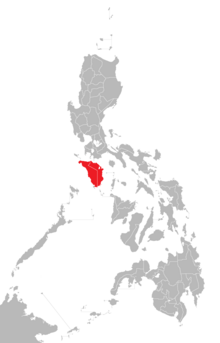
The great Mindoro fruit pigeon is an island endite , which is restricted in its distribution area to the Philippine island of Mindoro. With an area of 9,735 km², Mindoro is the seventh largest island in the Philippines, together with the minor islands it covers 10,244.50 km². The island extends over 110 km in north-south direction and forms a headland to the northwest. It is about 80 km wide in an east-west direction. A ridge that also runs in a north-south direction separates the east and west coast. The highest mountain is the Halcon in the north with 2,582 m, in the south the Baco rises .
The great Mindoro fruit pigeon occurs only in the dense forests of the foothills and mountains of the center of the island. The height distribution ranges from 700 to 1500 meters. It occurs on the Halcon and in Mount Iglit Baco National Park , among others . It is generally rare. Deforestation , among other things, contributes to the population threat , as it is a very large, exclusively forest-dwelling species that depends on large, contiguous forests.
Habits
The great Mindoro fruit pigeon lives solitary or in pairs. It only occurs occasionally in groups of up to four individuals. She spends the night occasionally with the gray-headed fruit pigeon and the white-cheeked pigeon . She seeks these resting places at dusk and leaves them again at dawn. It looks for food in the lower treetop area, only to rest it seeks the upper treetop area.
They eat a wide variety of fruits, ranging from small berries to fruits the size of a pigeon's egg. The reproductive biology of this species has not yet been conclusively investigated.
literature
- David Gibbs, Eustace Barnes and John Cox: Pigeons and Doves - A Guide to the Pigeons and Doves of the World . Pica Press, Sussex 2001, ISBN 90-74345-26-3 .
- Gerhard Rösler: The wild pigeons of the earth - free living, keeping and breeding . M. & H. Schaper Verlag, Alfeld-Hannover 1996, ISBN 3-7944-0184-0 .
Web links
- Ducula mindorensis in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2012. Posted by: BirdLife International, 2012. Accessed November 22, 2016th
- Call of the Great Mindoro Fruit Dove on Xeno-Canto
Individual evidence
- ↑ Ducula mindorensis in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2012. Posted by: BirdLife International, 2012. Accessed November 22, 2016th
- ↑ a b c d Gibbs, Barnes and Cox: Pigeons and Doves , p. 529.
- ↑ a b Gibbs, Barnes and Cox: Pigeons and Doves , p. 530.
- ↑ Rösler: The wild pigeons of the earth , p. 293