Half adder

A half-adder (engl. Half adder ) is a switching network , commonly referred to as digital circuit is realized. It consists of two inputs and two outputs. A half adder can be used to add two single-digit binary numbers . The output s (English sum - "sum") delivers the right and the output c (English carry - "carry") the left digit of the result.
The following truth table shows how a half adder works:
| x | y | Carry over c | Sum s |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
That corresponds to the equations
and
- .
Here, the symbol or the equally common in the literature , the XOR operation ( "exclusive-or"). The XOR link is therefore colloquially referred to as transferless addition .
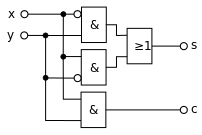
The figure above shows a simpler implementation in which an exclusive-or gate is used for output s . The figure below shows the structure of a half adder using only AND and OR gates . The required XOR link is implemented by interconnecting two AND gates with an OR gate.
Half adders are often part of microprocessors . This logic function can also be implemented in a programmable logic module (PLD), an FPGA or an ASIC as part of an overall circuit. With discrete logic components, this circuit function is hardly realized today, since the required mostly high clock frequencies cannot be achieved with these components and the circuit complexity for the structure and the wiring is far too great.
A full adder can be constructed from two half-adders and an additional OR gate .
The half adder is used in combination with full adders to set up adding networks .
literature
- Ulrich Tietze, Christoph Schenk: Semiconductor circuit technology . 12th edition. Springer, 2002, ISBN 3-540-42849-6 .