Homoallyl position
The term homoallyl position is derived from the syllables homo and allyl . It is with gay in organic chemistry meant often that a methyl group is added to a basic connection. In this case the basic compound is the allyl group , which is indicated by the syllable allyl . So homoallyl means that a methylene group is attached to the allyl group. The constitutional formula of the homoallyl group is therefore: H 2 C = CH – CH 2 –CH 2 -.
A radical R, like a functional group , is therefore in the homoallyl position when it is bonded to the fourth carbon atom after a double bond. The same applies to homoallyl radicals or homoallyl carbenium ions :
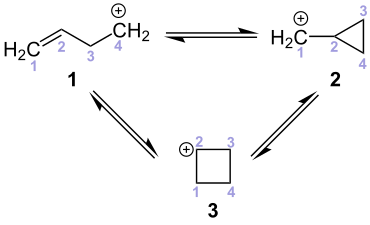
Typical reactions
For Homoallyl carbenium ( 1 ) rearrangement reactions are typical, to cyclopropane -Carbeniumionen ( 2 ) and cyclobutane -Carbeniumionen ( 3 result).
use
Homoallyl alcohols and homoallyl amines are important representatives of chemical compounds which contain functional groups in the homoallyl position. They are often found in the synthesis of pharmaceutically relevant substances. This is partly because they can be produced enantioselectively (see synthesis of homoallyl alcohols with the Roush reaction ) and are thus used to form stereocenters . One example of this is the synthesis of stevastelin B, a depsipeptide with immunosuppressive effects. This connection is made using the Roush reaction.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b S. Kubik: Entry on Homoallyl position. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on August 4, 2017.
- ↑ Entry on Homo .... In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on August 4, 2017.
- ↑ M. Hanack, H.-J. Schneider: Neighboring group effects and rearrangements in reactions of cyclopropylmethyl, cyclobutyl, and homoallyl systems. In: Angewandte Chemie . Volume 79, No. 16, 1967, pp. 709-720, doi: 10.1002 / anie.19670791603 .
- ↑ a b c L. Kürti, B. Czakó: Strategic Applications of Named Reactions in Organic Synthesis. Elsevier Academic Press, Burlington / San Diego / London 2005, ISBN 0-12-369483-3 , pp. 386-387.
- ↑ TR Ramadhar, RA Matey: Allylation of imine and Their Derivatives with Organoboron Reagents: Stereocontrolled Synthesis of Homoallylic Amines. In: Synthesis . Volume 2011, No. 9, 2011, pp. 1321-1346, doi: 10.1055 / s-0030-1258434 .