Allyl group
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is an unsaturated hydrocarbon radical which has the formula H 2 C = CH – CH 2 -, i.e. represents a 2-propenyl group. Formally, it is a vinyl group H 2 C = CH– to which a methylene group –CH 2 - is attached. Allyl cations and radicals are mesomeric stabilized and therefore significantly more stable than the corresponding tert- butyl cation or radical. For example, allyl alcohol has the formula H 2 C = CH-CH 2 -OH.
The name Allyl was coined by Theodor Wertheim in 1844 and is derived from Allium , Latin for garlic , in which a number of allyl compounds such as B. Find allicin .
Properties and use
The allyl group is one of the allylic groups because it is easy to abstract . H. Hydrogen atoms or protons are a reactive functional group in organic molecules on the sp 3 -hybridized carbon atom adjacent to the double bond . If two different further substituents are also bound there, the clear orientation of the groups to one another due to the 1,3- allyl tension can be used in the stereoselective synthesis .
Allyl compounds
There are numerous natural and synthetic organic compounds that contain one or more allyl groups. Technically important allyl compounds are the allyl , the allyl chloride and the allyl amine (with diallyl and triallyl amine ). There are also allyl compounds, which usually occur as intermediates in chemical reactions. These include allyl cation , allyl and allyl radicals . These are very well stabilized due to the mesomerism that occurs .
Allyl cation
The allyl cation represents a positively charged allyl group. The following two equivalent mesomeric boundary structures (resonance formulas) can be formulated:
The positive charge is distributed over the entire molecule, i.e. delocalized .
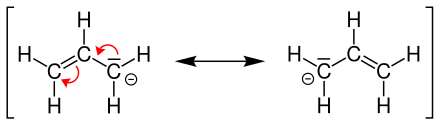
Allyl anion
In contrast to the allyl cation, the allyl anion represents a negatively charged allyl group. Again, two mesomeric boundary structures can be drawn here:
The lone pair of electrons is not localized on the terminal carbon atoms , but rather delocalized mesomerically over the entire molecule.
literature
- K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil E. Schore, Katrin-M. Roy: Organic chemistry . Ed .: Holger Butenschön. 5th edition. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim 2011, ISBN 978-3-527-32754-6 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on Allyl .... In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 14, 2020.