Hurricane Allen
| Hurricane Allen |
|
|---|---|

|
|
| Hurricane Allen on the Yucatán Strait at its peak on August 7, 1980 | |
| Beginning | July 31, 1980 |
| The End | August 11, 1980 |
| area | Northwest Atlantic |
| season | 1980 Atlantic hurricane season |
| maximum wind speed | 165 kn 190 mph 306 km / h (1 min) |
| category | Hurricane level 5 |
| Property damage | $ 1.5 billion |
| Deaths | 290 |
|
|
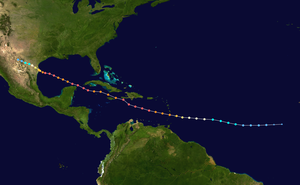
The hurricane Allen was the strongest hurricane of the Atlantic hurricane season in 1980 and one of the strongest hurricanes ever since records began (with wind speeds of up to 305 km / h). It was also one of only a handful of Atlantic cyclones that reached level 5 on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane wind scale in three different places , the others being Hurricane Ivan and Hurricane Isabel . All of them also had the fifth lowest air pressure measured to date of 899 hPa, just behind Rita from 2005 with 895 hPa, the Labor Day hurricane from 1935 (892 hPa), Hurricane Gilbert (888 hPa) from 1988 and Hurricane Wilma from 2005 882 hPa. It is particularly interesting that Allen never pulled the center of his circulation directly over land during his migration through the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico .
The storm front , which was later to form a hurricane, had its origin over the Cape Verde Islands, a rarity for tropical systems in early August. During the move through the Caribbean, the system became the first named storm of the season and rapidly intensified into a Category 5 hurricane on its way west.
After a short weakening, Allen strengthened again at level 5. This powerful cyclone streaked Haiti at level 4 and also caused great damage in Jamaica .
Due to the influence of the mountainous landscape in Jamaica and Haiti, Allen lost some of its strength and weakened at level 3. Due to its enormous extent, Allen also ensured gale-force winds on the island chain of the Florida Keys . Over the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico, Allen increased to the highest level for the third time. Dry mountain air subsequently caused a significant weakening of the powerful storm before it hit the American mainland north of Brownville, Texas. Surprisingly, only wind speeds of 185 km / h occurred. Allen did only limited damage in the United States , as it had weakened and the storm surge that it carried hit largely sparsely populated coastal areas. The storm surge had a height of 3.7 m in Port Mansfield (Texas), although higher values could have occurred in uninhabited areas. A top gust of 209 km / h was also registered in Port Mansfield. The hurricane killed seven in Texas and 17 in Louisiana (most of the casualties in a helicopter crash attempting to evacuate workers from an offshore oil rig).
Allen set off several tornadoes in Texas. One of these caused approximately $ 100 million damage when it hit Austin directly. This makes this the most expensive tornado ever to be triggered by a hurricane .
Allen's arrival nevertheless had a positive side: the precipitation of 200-250 mm that was carried along ended a long-lasting drought caused by the heat wave of 1980.
The name Allen was removed from the list of tropical cyclone names in the spring of 1981 and replaced with Andrew .