Infrastructure management
Infrastructure management is an engineering science that is made up of various fields of construction and economics. It aims to optimally combine both disciplines in the planning, execution and operation of different infrastructures.
Differentiation of infrastructures
Due to the constant change in the area of infrastructure , the term can only be defined more precisely by limiting it to subject areas. The two most important are the social and technical infrastructure. The social infrastructure is primarily concerned with service facilities for the population. These include e.g. B. Education centers (schools, universities), health facilities (hospitals) and leisure facilities (museums, zoos). In contrast to this, the term technical infrastructure is defined by the words communication , traffic and supply and disposal. The infrastructure manager mainly deals with technical infrastructure during his studies . The following descriptions of the sub-areas will show this in more detail.
Word origin
The collective term infrastructure is used in many different areas, but originally it was derived from the Latin infra (below, below). The infrastructure does not only refer to the civil engineering / substructure, but generally refers to all the necessary institutions that contribute to ensuring an economy. A distinction must be made between the existing infrastructure (spatial location, climate, population), the technical infrastructure (supply lines, communication ) and the economic infrastructure created by the state (economic system, state investments and subsidies for infrastructure projects). The term management appears nowadays mostly in connection with leadership or leadership. Originally it is assumed that the word root comes from the Latin "manus agere", "to lead by the hand". The manager is mostly tasked with coordinating projects, buildings and people and his goal is to achieve optimal execution.
Education
The Infrastructure Management course is offered at the Stuttgart University of Applied Sciences . This combines a variety of subjects from the fields of construction and economics. The infrastructure manager should be the interface between the project participants, e.g. B. structurally and commercially. At the same time, the issues of safety, functionality, economic efficiency and the mutual relationship with regard to the population and the environment are taken into account. The municipal infrastructures are becoming more and more complex, both from the technical side and from the administrative side, new infrastructure systems are emerging that can no longer be mastered with the classic methods (e.g. megacities ), for this reason this job description became the Interdisciplinary course in infrastructure management specially designed for the needs of municipal infrastructures.
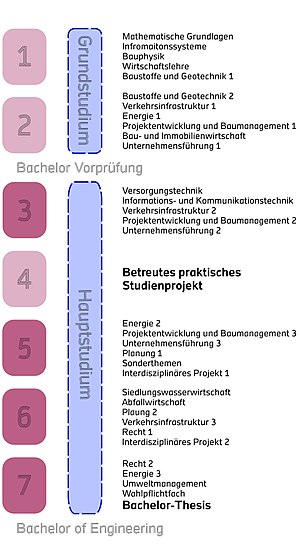
The course is divided into a basic course (semesters 1 and 2) and a main course (semesters 3 to 7). It has a modular structure and comprises a total of 210 credit points. The basic course is completed with the preliminary Bachelor examination. The supervised practical study project should be started in the fourth semester, with the students working at a suitable internship, supervised by the university and gaining professional experience. The modules from the basic course are deepened in the main course. The Bachelor thesis can be written in the 7th semester. The module bachelor thesis (thesis) consists of the written draft and a colloquium. In the colloquium, the student should represent the thesis and the knowledge gained from it. For students of the Bachelor's degree in Infrastructure Management, there are contacts to many partner universities worldwide.
The infrastructure management course was assessed by the ASIIN Accreditation Council in 2007 and successfully accredited in an external audit.
Sub-areas
Transport infrastructure
In order to evaluate the different aspects of the transport infrastructure, the infrastructure manager acquires knowledge during his studies in order to be able to assess and calculate the performance of roads, junctions and public transport systems. In the course of the course, the various traffic systems and the fundamentals of traffic flow on roads and rail lines are considered. The infrastructure manager is able to specifically implement sketched and computer-aided drafts of junctions, systems for stationary traffic and standard cross-sections on the basis of guidelines. In addition, he acquires knowledge of the layout of a road. In addition to the design and planning of traffic, road construction with the technical construction of roads and paths is an essential part of the course. This enables him to make statements about the structure, dimensioning, stress and the resulting requirements for the building materials . In addition, he has the business and technical knowledge to calculate and carry out a construction project. In order to be able to carry out civil engineering transport projects, he has knowledge of geology . This includes building cavities in the rock on the one hand, and soil mechanics on the other. He has the ability to recognize the structure of the subsoil and the associated geological difficulties and to initiate countermeasures.
energy and Environment
Due to the increasing demand for energy, the energy industry is given a special place in the course. The infrastructure manager is provided with in-depth knowledge of the various conventional and alternative energy systems. A distinction is made between power generation in power plants and building energy technology. In the area of energy generation in power plants, the various types of power plants and their advantages and disadvantages are dealt with. Since a lot of unused waste heat is generated during power generation, technologies for waste heat utilization and power plant optimization are discussed. In the building energy sector, the use of solar thermal energy , photovoltaics , geothermal energy and biomass is discussed. Furthermore, the design of the power plants and the resulting economic efficiency of the plant are taught. Since today energy efficiency also has a decisive influence on the profitability of buildings, the infrastructure manager has knowledge after his studies that will help him to use the various construction and insulation materials in a targeted manner. Energy and environmental management illuminates sustainability and environmental protection.
Settlement economy
One of the most important areas of settlement management is the water supply, which includes the dimensioning, construction and calculation of pipeline systems and the construction of water distribution systems. In addition, the infrastructure manager can demonstrate expertise in the operation and technology of storage systems and pipe hydraulics. In addition to water supply, wastewater disposal is an important area that requires fundamental strategic approaches to organize the wastewater conditions in municipal and industrial areas. Here, the infrastructure manager distinguishes himself through specialist knowledge of drainage processes in connection with rainwater management and wastewater treatment. His qualifications include hydraulic calculations of sewers and static calculations of drainage pipes. These topics are supplemented by waste management. The infrastructure manager has the basic knowledge and interrelationships in waste avoidance, recycling and disposal and in waste law. In addition, he knows the individual types of waste and their danger to the environment. Waste management concepts, waste collection and possible waste recycling can be derived from this.
urban planning
The infrastructure manager is familiar with the basics in the context of urban structures and development processes. Building on this, he can examine the public space on the basis of building structures, development and quality features of the room and surface design. The infrastructure manager is particularly trained in the analysis of urban structures. The independent, creative creation of urban planning drafts is just as much part of the skills of an infrastructure manager as the integration of infrastructure and development. This enables him to take a holistic view of the design, supply and disposal systems, parking facilities and route networks. The infrastructure also includes the area of fire protection , which offers constructive fire protection solutions. In order to plan appropriate protective measures, it is necessary to know how a fire develops and how fire and smoke develop. The infrastructure manager is trained in structural fire protection and is familiar with guidelines, fire protection equipment and escape route planning. Another field of activity is the treatment of legal, technical, conceptual and institutional requirements and preventive measures in the field of disaster control.
Project management
Project and construction management always requires a certain amount of basic, organizational, methodological and social competence. The infrastructure manager has this in-depth knowledge of construction project management. The classic areas of activity in project management, such as project organization, contract, schedule, cost and quality management, but also special topics such as project development and facility management , are dealt with using practical examples during the course. In the field of construction organization, the infrastructure manager has a sound basic understanding of the processes involved in planning and executing construction objects. This includes knowledge of the planning techniques used in process, sequence and provision planning. Another area of knowledge is the construction and real estate industry . Here he has know-how that supports him in the recording of boundary conditions, market participants, activities and relationships. Furthermore, the infrastructure manager has basic legal knowledge of public law and construction law. The knowledge of modern and efficient geographic information systems and their handling enable him to deal with these systems.
Economics and business management
The understanding of economic processes is based on the fundamentals of business and economic interrelationships which the infrastructure manager internalized during his studies. This includes knowledge of market processes, market-oriented corporate management and market research. He is able to analyze the external accounting and to carry out calculations in this area independently. It is possible for him to apply methods of corporate management through the different instruments of operational and strategic controlling . Static and dynamic investment calculation models as well as all the basics of mathematics and financial mathematics are part of his repertoire. In order to prepare the infrastructure manager for later working life, key skills such as teamwork, communication and presentation are promoted in addition to economic skills . This also includes technical and commercial English skills, which are taught to him during his studies.
other qualifications
- Technical English
- Business English
- Key qualifications (soft skills: group and project work, presentation and communication)
- Basics of occupational safety
- Practical experience in two interdisciplinary projects
requirements
The course has an economic as well as a scientific focus, so it is necessary to have a wide range of interests in these subject areas. The offer is aimed primarily at prospective students who deal with aspects of the areas of building and planning, energy, transport, project management as well as economic components and want to combine them.
Vocational training in a state-recognized training occupation in the technical or commercial area will be taken into account in the application process, as will long-term employment. We recommend a three-month pre-study internship in the fields of energy, transport, public administration in the technical field, at supply and disposal companies and related subjects in infrastructure-oriented companies and offices. The prerequisite for studying infrastructure manager is a general university entrance qualification or a technical college entrance qualification .
graduation
The job title is engineer or infrastructure manager. The degree in infrastructure management at the Stuttgart University of Applied Sciences (HfT) concludes with the academic degree “ Bachelor of Engineering ”. A subsequent master’s degree , like a subsequent doctorate, is in principle possible, e.g. B. in the subject "Transport Infrastructure Management" at the HfT Stuttgart. See the main article: Bachelor . The 7-semester course with the “Supervised Practical Study Project” guarantees the use of the title “Engineer” and the chamber ability (Chamber of Engineers).
Universities and faculties also offer infrastructure-heavy courses of study in which infrastructure management is a core component, see for example the degree in traffic engineering . In engineering, (technical) universities usually award the academic degree Bachelor or Master of Science, which is equivalent to the Bachelor or Master of Engineering and is also eligible for chambers.
job profile
After completing the Infrastructure Management course, he is able to work in a wide variety of economic areas. This is ensured by the broad diversification of the modules during the course and also enables the infrastructure manager to be very adaptable. An analysis of simple and complex infrastructures and their components in structural, technical and financial terms is possible after graduation. These include the main areas: business administration , energy, finance (financial engineering), real estate, law , urban design and planning , corporate management , transport and water management .
The tasks of the infrastructure manager range from the preparation of tenders , risk analyzes , traffic planning measures and profitability calculations to the most diverse areas of facility and project management . Due to the strong involvement of the energy and supply companies in the course, the infrastructure managers are trained to meet the needs of engineers in the supply and energy sector. Another area in which the infrastructure manager works is the public service or public administration. In particular, admission to the preparatory service for the higher civil engineering service will be given, which is a prerequisite for embarking on a civil service career.
Possible employers:
- Advice / consulting company
- Planning offices for infrastructures
- Service company
- Project developer
- banks and insurance companies
- District offices, regional councils
- Energy and utility companies
- Waste disposal companies
- transport services
- Further training opportunities at colleges and universities