Yermolayev Jer-2
| Yermolayev Jer-2 | |
|---|---|

|
|
| Type: | Bomb plane |
| Design country: | |
| Manufacturer: | |
| First flight: |
June 1940 |
| Production time: |
1940-1944 |
| Number of pieces: |
447 |
The Yermolajew Jer-2 ( Russian Ермолаев Ер-2 ) was one of the few long-range bombers developed and used by the Soviet Union during World War II .
history
Robert L. Bartini , an Italian communist living in the USSR , developed the all-metal Stal-7 passenger aircraft with his colleagues in 1937 , which passed some very successful long -range flight tests . Due to the long range of this type, it was decided to develop a military version. The Aeroflot created specifically for this task a development office, whose leadership Vladimir G. Jermolajew who had been part of the collective of Bartini, took over.
Construction began at the end of 1939, and the first prototype named DB-240 ( D alni B ombardirowschtschik = long-range bomber) with two M-103 engines took off for its maiden flight in June 1940 . In the course of testing, the drives were exchanged for M-105 motors . In October 1940 the model went into series production equipped with the M-105. At the beginning of the Great Patriotic War , two regiments under the command of Novodranov and Gusev were equipped with a total of 128 aircraft and stationed in Smolensk . The crews were made up of members of Aeroflot and other civil aviation organizations.
In the initial phase of the fighting, the machine, renamed Jer-2 at the start of production, was used for long-range attacks on Berlin as well as a tactical front bomber, which operated in support of its own ground forces. Some Jer-2s of the 420th Remote Bombing Regiment (DBAP) flew together with five TB-7s of the 432nd DBAP on the night of August 11, 1941, one of the first Soviet air raids on the German capital . At the end of 1941 the production workshops had to be evacuated from Voronezh to Omsk , by then 144 aircraft had been delivered to the air force.
In 1942, attempts were made to increase the payload by installing more powerful AM-35 , AM-37 and M-120 engines, but this was not very successful. At the end of 1943, a series model equipped with Tscharomski ATsch-30B diesel engines appeared at the front, which finally achieved the desired increase and was built in a number of 300 machines. This model was continuously improved during production until 1944 and was also the last production version of the Jer-2.
When Vladimir Yermolayev died on December 31, 1944, his OKB was dissolved and the employees were transferred to Pavel Sukhoi's design office.
After the war, the aircraft also served as a test vehicle, for example replicas of German pulse jet engines attached to Jer-2 that had been used on the V1 were tested as possible drives.
technical description
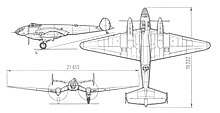
The Jer-2 was an all-metal aircraft in a low- wing configuration ; it was self-supporting and had a gull wing similar to the German Ju 87 . The tail unit was also self-supporting and had two rudder units mounted on end plates. The main landing gear could be retracted into the engine nacelles, the tail wheel was rigidly attached.
Technical specifications
| Parameter | Jer-2 (1940) | Jer-2 (1943) |
|---|---|---|
| crew | 4th | 5 |
| span | 23.00 m | |
| length | 16.40 m | |
| Wing area | 72.0 m² | 73.1 m² |
| Empty mass | 7,200 kg | k. A. |
| Takeoff mass | normal 12,520 kg maximum 14,150 kg |
normal 14,850 kg maximum 18,580 kg |
| drive | two V-engines Klimow M-105 |
two Tscharomsky ATSch-30B diesel engines |
| Starting power | 1,100 PS (809 kW) each | 1,500 PS (1,103 kW) each |
| Top speed | 437 km / h at an altitude of 4,000 m | 420 km / h at an altitude of 6,000 m |
| Cruising speed | 335 km / h at an altitude of 4,650 m | 335 km / h at an altitude of 4,000 m |
| Landing speed | 126 km / h | k. A. |
| Take-off / landing route | 600 m / 750 m | k. A. |
| Summit height | 7,700 m | 7,200 m |
| Range | 4,000 km | 5,000 km |
| Armament | one 12.7 mm machine gun two 7.62 mm machine guns |
a 20-mm-MK SchWAK two 12.7-mm-MG |
| Bomb load | maximum 5,000 kg | normal 3,000 kg maximum 5,000 kg or two FAB-1000 bombs external |
variants
In 1944 a special version for 18 passengers was created under the name Jer-2ON ( O ssobowo N asnatschenija = for special tasks), of which only three were built. A slightly enlarged further development with a symmetrically arranged cabin and larger vertical stabilizer disks appeared in early 1945 under the name Jer-4 or "No.11". It had two ATsch 30BF diesel engines with a modified cooling system and remained a prototype.
See also
literature
- Wilfried Copenhagen : Soviet bomb planes . Transpress, Berlin 1989, ISBN 3-344-00391-7 , pp. 141-143 .
Web links
- Ермолаев Ер-2. Retrieved May 16, 2019 (Russian).