Bartini Stal-7
| Bartini Stal-7 | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Type: | Airliner |
| Design country: | |
| Manufacturer: | |
| First flight: |
1937 |
| Number of pieces: |
1 |
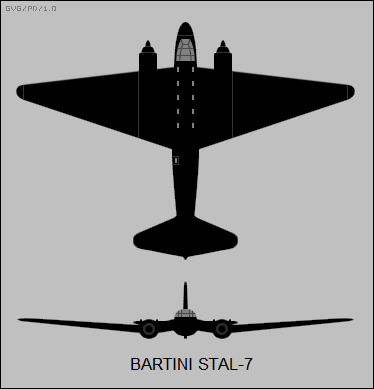
The Bartini Stal-7 (also: Stahl-7, Russian Сталь-7 ) was a Soviet airliner of the 1930s. In contrast to other types, the supporting structure of the “Stal” constructions was made of stainless steel instead of the aluminum that was common at the time .
history
The aircraft was developed by Robert Bartini , an Italian communist who emigrated to the Soviet Union , as a parallel design to the Tupolev PS-35 . This was preceded in 1935 by a tender to create a modern airliner for the Soviet civil air fleet. In the same year, the design work began in the NII GWF . The type was designed as a cantilever middle-decker . The construction consisted of steel alloys with smooth aluminum planking. As a special feature, the wing was given a downward kink , which should protect the cabin from contact with the ground in the event of a belly landing. The main wheels of the tail wheel chassis drove into the rear motor pods of the two Klimow M-100 motors. The Stal-7 should be able to carry eight passengers.
In 1937 the flight test took place, which was successfully completed. Nevertheless, the Stal-7 did not go into series production, like the PS-35 it was probably rejected because of the insufficient passenger capacity. The only copy was used by Aeroflot . On August 28, 1939 it flew with the crew of N. P. Schebanow, W. A. Matvejew and N. A. Baikusow at an average speed of 404.94 km / h on the 5058-kilometer route Moscow - Sverdlovsk - Sevastopol - Moscow, a world record for this aircraft class.
Vladimir Yermolajew , an employee of Robert Bartini, took over the gull wing from the Stal-7 and created the 300-plus long-range Yermolayev Jer-2 bomber by redesigning the fuselage and tail unit .
Technical specifications
| Parameter | Data |
|---|---|
| Conception | Express airliner |
| constructor | Robert Bartini |
| Manufacturer | Scientific research institute of the civil air fleet |
| Years of construction | 1936-1937 |
| crew | 3 |
| Passengers | 8th |
| span | 23.00 m |
| length | 16.00 m |
| Wing area | 72.00 m² |
| Empty mass | 4800 kg |
| Takeoff mass | 7200 kg |
| Engines | two liquid-cooled Klimow M-100 |
| Starting power | 560 kW each (approx. 760 PS) |
| Top speed | 450 km / h |
| Cruising speed | 360 km / h |
| Summit height | 10,000 m |
| Range | Max. 5000 km |