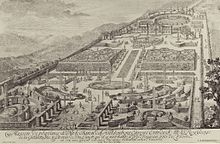
Leather locks
The Ledererschlössel was a historical building near Mühlbergstraße or today's city of children in Vienna-Weidlingau .
Naming
It was named after one of its last owners, the industrialist August Lederer , owner of the Raaber and Jungbunzlauer spirit factories, a well-known art patron and patron of the Vienna Secession , especially Gustav Klimt .
Construction, remodeling, demolition
It was built as the garden palace of the English ambassador Erasmus Freiherr von Huldenberg in 1715 by Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach , which is why the name "Huldenbergschlösschen" appears.
In the 19th century, an extensive redesign in the classical sense took place, through which the central building was given a triangular gable.
In the press releases on the occasion of the demolition in 1971, there is talk of Anton Faistauer's frescoes , which were removed and secured. They depict Diana returning from the hunt and can now be seen in the Faistauersaal of the New Mozarteum in Salzburg .
In addition, the great hall of the Ledererschlössel was adorned with splendid Rococo ornaments, all of which have been lost.
Reuse
Anton Schweighofer , the architect of the City of the Child planned by the municipality of Vienna on the extensive area , would have wanted to preserve the art-historically important object, for example as a management building. However, the Schlössl was torn down in a so-called night-and-fog operation. The building then erected on the site, the City of the Child , a large social institution from around 1970, has since become superfluous and has been sold to a housing developer.
literature
- Dieter Klein , Martin Kupf , Robert Schediwy , Stadtbildverluste Wien - A Review of Five Decades, Vienna 2005, ISBN 3-8258-7754-X
Web links
Coordinates: 48 ° 12 ′ 29 ″ N , 16 ° 12 ′ 42 ″ E