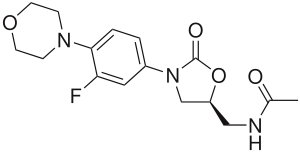
Linezolid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Linezolid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
( S ) - N - ({3- [3-Fluoro-4- (4-morpholinyl) phenyl] -2-oxo-5-oxazolidinyl} methyl) acetamide |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 16 H 20 FN 3 O 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis |
||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 337.35 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Linezolid (trade name Zyvoxid ® , registered trademark of the manufacturing company Pfizer ) is an antibiotic and belongs to the group of oxazolidinones , one of the newest antibiotic groups available.
pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Linezolid works by blocking bacterial protein synthesis on the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome . In contrast to other antibiotics, it hinders the start of protein synthesis.
Area of application and spectrum of activity
In the area of infections caused by gram-positive bacteria, linezolid has quickly become a very important new reserve antibiotic . Linezolid is the only intravenously and orally available MRSA-effective antibiotic. In addition to the MRSA standard antibiotic vancomycin, which was introduced decades ago, it now plays an important role, especially in severe MRSA hospital infections and multi-resistant tuberculosis.
- Spectrum of sensitive germs: staphylococci , including S. aureus including methicillin-resistant strains ( MRSA ), enterococci including vancomycin-resistant strains (VRE), streptococci including penicillin-resistant strains
-
Clinical Use: Linezolid is approved for treatment
- nosocomial and community-acquired pneumonia , as well
- severe skin and soft tissue infections (if microbiological tests show that the infection is caused by linezolid-sensitive Gram-positive pathogens).
Side effects
Side effects are bone marrow suppression and thus thrombocytopenia , anemia, and neutropenia. Headache and gastrointestinal irritation have also been reported.
Interactions
Linezolid increased via inhibition of monoamine oxidase the serotonin levels in the central nervous system. As a result, in co-medication with other drugs that increase serotonin levels, such as the widely used antidepressants of the SSRI type, a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome can occur.
Pharmacokinetics
Linezolid can be given intravenously or orally without dose adjustments and regardless of food intake. It is 100% bioavailable . With the recommended dosage and oral administration, the maximum plasma levels after one to two hours are above the inhibitory concentrations for the most important gram-positive pathogens, with intravenous administration already after 30 minutes. The half-life is about 5 hours.
history
The group of oxazolidinones was developed by researchers at DuPont and published in 1987. The oxazolidinones were originally developed against phytopathogenic bacteria in agriculture. But it soon became apparent that oxazolidinones also have a bacteriostatic effect on human pathogenic staphylococci and enterococci and are bactericidal for streptococci. The pharmaceutical company Upjohn developed the active ingredient linezolid. Upjohn is now part of Pfizer following a number of acquisitions and mergers. The American Food and Drug Administration ( FDA ) approved linezolid in April 2000.
In 2003 Linezolid received the Galenus von Pergamon Prize .
literature
- Trautmann, M., Pharmacodynamics of Linelozid , in Chemotherapie Journal , 13/2004, pp. 218–222 (PDF file; 249 kB)
Web links
- Linezolid inhibits the peptidyl transferase center
- Information about Linezolid (PDF file; 365 kB)
- Warning of increased mortality
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Data sheet Linezolid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 9, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ W. Trattler, M. Gladwin: Clinical Microbiology Made Ridiculously Simple, Edition 3 (2004), p. 171, ISBN 978-0-940780-49-1 .
- ^ Warning from the US Food and Drug Administration dated July 26, 2011; last accessed on July 27, 2011.
- ↑ Linezolid: Complex Interactions with Serotonergic Substances Resulting in Serotonin Syndrome , AKDAE: Drug Safety Mail 2019-39 of July 10, 2019, accessed on July 10, 2019
- ↑ Half-life according to Ruß, Endres, Arzneimittelpocket Plus 2008, 4th edition Oct. 2007, ISBN 978-3-89862-287-5 .
