Search engine spamming
With search engine spamming (Engl. Search Engine Spamming ) (also index spamming , spamdexing , link spamming ) is attempted, the scoring algorithms of over entries in their own or other websites search engines to positively influence. The aim is to appear at the top of the search engine ranking when a search word is entered.
Search engine spamming includes:
- all attempts to list a website under a keyword without the page dealing with the topic in question ( see also Google bomb )
- all attempts to deliberately achieve multiple listings under one search term
- misleading hyperlinks to a website that do not contain any information about the search term entered
This creates a natural-looking visitor flow that enables advertising revenue and / or influences web statistics such as Alexa or Google Analytics .
term
Search engine spamming on Google is also known as Google spamming . The more specific term googleating (read: "Google-ating") is used when websites are only created for the purpose of significantly influencing the link structure in favor of certain web pages in order to achieve a high PageRank .
Methods
Spammers build their optimization methods on the search and evaluation strategies of the successful search engines in order to bring the Internet pages they have created or maintained to the front in the search engine results lists. Most of the spam pages are specifically manipulated for the world's most frequently used search engines Google , Yahoo and Bing .
Keyword density
The search word density and the search word prominence on the target page flow into many evaluation algorithms, albeit not as the only factor.
Methods:
- The inclusion of many keywords in the
altattributes (alternative texts) of the images - the use of multiple title tags to put key terms in prominent positions
- writing text in the background color ( "hidden text" Hidden text ), so that the text just for search engines, but not for Internet surfers on the screen is visible
- The insertion of hidden texts with countless keywords outside of the visible page area, in page areas made invisible by style sheets or in areas below graphics
- with doorway pages (doorway pages) or cloaking search engines other optimized page content is offered than those who get to see a human observer.
- Scraper sites copy the content of other sites
- the use of article directories or content farms
- Sybil Attack is the creation of numerous, reputable pages (discussion forums, blogs, advice pages etc.) on different domains and, after these pages have received a good ranking, use of these unsuspicious pages to promote the actual, commercial website by adding many links or advertising
The meta element keywords was originally introduced specifically for search engines, but has lost its importance due to severe abuse.
Backlinks
Back references (Engl. Backlinks ) and link popularity to be included in the rule of search engines for evaluation. The additional links increase the rating.
Attempts are made to set hyperlinks to the advertised offer on their own link farms or on third-party websites . These links are often hidden, for example with the help of tiny, transparent one-pixel graphics.
Social media also allows unauthorized users to leave content.
- Blogspam
- The comment and trackback functions of blogs and guest books are used to leave links and texts that usually have nothing to do with the actual content, but promote commercial sites.
- Wikispam
- Similar to blog comments, the entire page content of wikis can be changed.
- Social bookmark spam
- Social bookmark services are platforms that enable individual users to save their own favorites online and share them with other users if they wish. Well-known social bookmark platforms are Mister Wong and del.icio.us. Spammers try to get more backlinks for their own projects by adding links (favorites). The exchange of social bookmark links has been observed for some time. With the increase in abuse, most social bookmark platforms have given the outbound links the hyperlink attribute rel = "nofollow" .
- Forum spam
- By setting links in forum posts, an attempt is made to improve one's own ranking.
Negative search engine optimization
Negative search engine optimization (also Google Bowling ) is the attempt to induce the search engines to devalue the respective pages by briefly generating thousands of suspicious links, all of which refer to the same websites of competitors, and thus indirectly to improve your own page.
Countermeasures
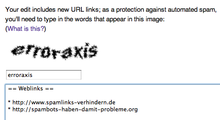
CAPTCHA use to hinder spambots .
With the hyperlink attribute nofollow , which prevents search engines from using such links for evaluation, the German-language Wikipedia , for example, tries to make the setting of such links pointless.
Internal spam filters in blogs and wikis, which recognize and sort out spam via word filters or the IP origin DNS-based blackhole list or suggest it to be moderated. Word filters search for common commercial terms and URLs. Spam filters are also available as external services, such as B. Akismet .
Search engine actions
Quite a few of these manipulation techniques are already recognized by the search engines. If a website that has been massively manipulated in the manner described has been discovered by the search engine operators, the search engine operators have a number of countermeasures at their disposal:
- Adaptation of the sorting algorithm
- Moving the pages in the results list backwards
- Removal of the pages from the index
- Exclusion of individual IP addresses , entire IP ranges or domains from the index
Spam or Optimization?
Any manipulation that is used to force non-relevant results in the search engines is spam . Anyone who links websites with one another with the sole intention of improving the position of a particular website that does not provide any information relevant to the search term is a spammer. The adaptation of pages to the sorting algorithms of search engines with the aim of improving the position in search terms is called search engine optimization - this includes optimization for relevant terms as well as for irrelevant ones.
The transitions from relevant optimization to search engine spamming are often fluid. For Microsoft, it is not possible to draw precise boundaries between search engine optimization techniques and spamming activities. Google noticed a number of SEO service providers whose practices are unacceptable and therefore urges caution.
Professional search engine optimizers try to differentiate between legal (white hat) and illegal (black hat) optimization techniques, i.e. spamming, in order to distinguish themselves from the black sheep in the industry. The users of illegal optimization techniques claim, however, that search engine optimizers do not act ethically, because each of their actions is deliberately aimed at manipulating the search engine results pages. For them, only commercial success counts and this is expressed in whether a side is listed before that of their competitors.
In the chapter on commercial spamdexing, Wally Wang writes that such "consultants" call their work search engine optimization, and a quick search under the search term SEO reveals hundreds of companies that offer paid help in improving the ranking of a customer website in search engine results. There are some who use legal techniques, but also others who use borderline or illegal methods. And Daniel Koch writes: “Most commercially successful websites owe their success solely to a good ranking in the search engines. So it's no wonder that website operators keep trying to improve their ranking using dubious methods. "
Current studies assume that every fourth search hit is a spam page. Erwin Lammenett comments on the industry: “In the absence of sufficiently interesting and up-to-date content, resourceful search engine optimizers have developed methods to fool search engines into the existence of content and its links from other sites. From a legal and moral point of view, these methods are now to be viewed critically and assigned to spamming. ”According to David George, some of the“ unscrupulous ”commercial optimizers even accept that customer pages will be deleted from the search engine index through their“ aggressive ”strategies They also do not shy away from misusing their customers 'pages in order to direct traffic to their own or other customers' pages via hidden links.
Web links
- Google Spam Report
- Yahoo! Spam report
- MSN spam report
- Court: Google filter legally permissible . heise.de
Individual evidence
- ↑ “Any attempt to influence search engine rank via misleading methods is referred to as search engine spamming or spamdexing. The practice of creating a website solely for the purpose of achieving a high PageRank is called Googleating (pronounced 'Google-ating', not 'Google-eating'). ” See Michael Miller: Googlepedia. 2007, p. 634.
- ↑ “… the precise boundary between legitimate SEO techniques and search spam is often subjective and fuzzy…” Spam Double Funnel: Connecting Web Spammers with Advertisers . (PDF; 93 kB).
- ↑ Quotation from the Google page on the subject: “… we've encountered firms calling themselves SEOs who follow practices that are clearly beyond the pale of accepted business behavior. Be careful. "
- ↑ "Black hat SEO optimization techiques are considered 'spamdexing'." Jon Rognerud: Ultimate Guide to Search Engine Optimization . 2008, p. 113.
- ↑ "Black-hatters say did ethics do not come into the SEO as any optimizations made to a website are done as a deliberate effort to manipulate search engine result pages. The point of commercial websites, they say, is to make money and to do this is to rank more highly within search engines than their competition. " David George: The ABC of SEO . 2005, p. 18.
- ↑ See the chapter Spamdexing for hire in: Wally Wang: Steal this Computer Book 4.0 . 2006, p. 284.
- ^ Daniel Koch: Search engine optimization . 2007, p. 37.
- ↑ Koch: Suchmaschinenoptimierung , p. 37, note.
- ^ Erwin Lammenett : TYPO3 online marketing guide . 2007, p. 138.
- ↑ “Working with aggressive SEO businesses can lead to a ban for clients. Some unscrupulous SEO operators also use their client's sites to redirect traffic to their own website or to other clients. " George: The ABC of SEO , p. 18.