Mesh flow method
The mesh flow method is a method used in electrical engineering for network analysis . This method can be used to determine the branch currents . Because every electrical network can be described and calculated in this way by a linear system of equations (in the steady state with linear components ) or by a differential equation system (in the case of in-stationary processes with capacitors and inductances). A network that can be represented by a planar graph , that is to say has no line crossings, is advantageous for a calculation using the mesh flow method . The calculation of non-planar networks is also possible, but less suitable for manual calculation. Alternatively, the node potential method can be used.
Action
- Choose tree
- Simplify the network, i. H. Unite parallel connections.
- Select ideal power sources as the chord, this simplifies the system of equations.
- Convert non-ideal current sources into equivalent voltage sources .
- Mark the tree .
- Set stitches
- Each stitch (M) runs over only one tendon, otherwise it closes over the branches of the tree
- The direction of rotation must be determined for each stitch. The choice of sign depends on the direction of rotation .
- Set up the matrix
- , with complex sizes
The sum of all resistances over which the respective mesh is closed is entered in the main diagonal of the resistance matrix . The dimension of the matrix is the number of meshes minus the ideal power sources in the network.
In the other fields you enter the sums of the resistances with which the meshes intersect. If the direction of rotation is opposite, the sum has a negative sign.
The sum of all voltage sources located in the respective mesh is entered in the source voltage matrix. The sign is positive if the direction of rotation is not the same as the voltage arrow .
Ideal current sources (I q ) must be treated differently. The associated mesh (M Iq ) is not included in the matrix, both row and column are omitted. The solution of the mesh current is already given, I Mi = I q . The overlap with the other meshes is taken into account in that the voltage drop on the common resistors through the ideal current source also flows into the source voltage matrix.
- Solve system of equations
The equations established form a linear system of equations for which there are a large number of solution methods .
- Calculate branch currents
According to the superposition principle, the current in a branch is calculated (with the correct sign) from the sum of the mesh currents that pass through it.
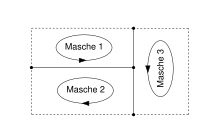
Example:
literature
- Oliver Haas, Christian Spieker: Electrical engineering tasks 1 . Oldenbourg, Munich 2012, ISBN 3-486-71680-8 , p. 81–103 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
Individual evidence
- ↑ www.icie.jku.at/files/KknotenpotMaschenstrom.pdf ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.



![[R] \ cdot [I_M] = [U_ {qM}]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/81f2fcc80371c78da82cbc929b89d4c74f7f8f63)
![[\ underline Z] \ cdot [\ underline {I} _M] = [\ underline {U} _ {qM}]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/60431b1d1e96e3af3ba4af688377e65bdbf16810)


![r_ {ij} = r_ {ji} = \ sum [R \ \ mathrm {in} \ M_i \ \ mathrm {and} \ M_j \ cdot \ mathrm {sense of circulation} (M_i, M_j)]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d6039adcc0f6d752cab6ce5ac80903f3d9d76be8)
![u_ {qMi} = \ sum [U_q \ \ mathrm {in} \ M_i \ cdot (-1) \ cdot \ mathrm {arrow} (U_q, M_i)]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/82c719a99ab0ebde1a30a01c4de292e627aad979)
![u_ {qMi} = \ sum [U_q \ \ mathrm {in} \ M_i \ cdot (-1) \ cdot \ mathrm {arrow} (U_q, M_i)] - I_q \ cdot \ sum [R \ \ mathrm {in} \ M_i \ \ mathrm {and} \ M_ {Iq} \ cdot \ mathrm {sense of rotation} (M_i, M_ {Iq})]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1f304a06d0ff9eeb18e8ea68aaae81ee16b8fdc5)
