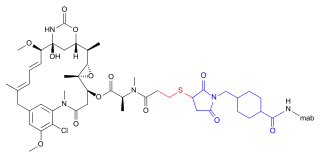
Maytansinoids
Maytansinoids is the name of a group of natural substances with high cytotoxic effects. The maytansinoids were first isolated in 1972 from the shrub Maytenus serrata, which is native to Ethiopia .
description
Maytansinoids are 19-membered lactams that have a structural similarity to rifamycins , geldanamycin and ansatrienin (mycotrienin). Since these related compounds, in contrast to the maytansinoids , are formed by microorganisms , the suspicion arose early on that the maytansinoids are also formed by microorganisms. With the bacterium Actinosynnema pretiosum , an organism was found that is able to produce maytansinoids. As a result, various plants containing maytansinoids were discovered, such as Colubrina texensis and Trewia nudiflora (Gutelbaum). Plant production is either due to a horizontal gene transfer or a plant-microbial interaction. The concentration of maytansine in dried Maytenus serrata is only about 2 × 10 −5 percent. The compound is highly toxic to KB cells ( malignant human epithelial cells ). The ED 50 (effective dose) is between 10 −4 and 10 −5 µg / ml.
A number of natural maytansinoid derivatives have been isolated over time. They differ mainly in the ester side chain (in the C-3 position), which can contain fatty acids or L - alanine , among other things . Also N -demethylierte, deepoxidierte and C-10 epimers were isolated and characterized.
Maytansine, which gave this family of compounds its name, was first isolated from Maytenus serrata in 1972 by S. Morris Kupchan and colleagues at the National Cancer Institute , and the structure was clarified a short time later by means of X-ray structure analysis .
Therapeutic meaning
The highly cytotoxic biogenic maytansine failed as an anticancer agent in clinical studies due to an unacceptable systemic toxicity. However, cytotoxicity can be used in conjunction with a concept of targeted delivery to selectively destroy cancer cells. The cytostatic maytansine derivative DM1, for example, can be conjugated to the monoclonal antibody trastuzumab to target tumor cells, where it binds to the microtubules and triggers apoptosis . The organism is not exposed to such high doses of highly toxic free DM1, so that systemic side effects can be reduced. The antibody-drug conjugate T-DM1 (trastuzumab emtansine) is approved for the treatment of HER2 / neu -positive breast cancer .
literature
- T. Boettcher: Kitasatospora putterlickiae F18-98, a newly isolated bacterial strain from the rhizosphere of Putterlickia verrucosa - Molecular biological and biochemical studies on aminohydroxybenzoic acid biosynthesis. Dissertation, University of Bonn, 2008.
- M. Hesse: Alkaloids. Helvetica Chimica Acta, Wiley-VCH, 2000, ISBN 3-906390-19-5 , pp. 216-217.
Web links
- Biosynthesis of Maytansinoids (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b T. Frenzel: Studies on the chemoenzymatic synthesis of maytansinoid analogues: synthesis of seco-proansamitocin. Dissertation, University of Hanover, 2005.
- ^ A b J. M. Cassady et al: Recent developments in the maytansinoid antitumor agents. In: Chem Pharm Bull 52, 2004, pp. 1-26, PMID 14709862 .
- ↑ SM Kupchan et al: Maytansine, a novel antileukemic ansa macrolide from Maytenus ovatus. In: J Am Chem Soc 94, 1972, pp. 1354-136, PMID 5062169 .
- ↑ SM Kupchan et al: The maytansinoids. Isolation, structural elucidation, and chemical interrelation of novel ansa macrolides. In: J Org Chem 42, 1977, pp. 2349-2357, PMID 874612 .
- ↑ toilet Widdison include: Semisynthetic maytansine analogues for the targeted treatment of cancer. In: J Med Chem 49, 2006, pp. 4392-4408, PMID 16821799 .
- ↑ I. Krop, EP Winer: Trastuzumab Emtansine: A Novel Antibody-Drug Conjugate for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. In: Clinical Cancer Research. 20, 2014, p. 15, doi : 10.1158 / 1078-0432.CCR-13-0541 .