Minkowski sum
The Minkowski sum (after Hermann Minkowski ) of two subsets and a vector space is the set whose elements are sums of one element from and one element from .
definition
Let be two subsets of a vector space. Then the Minkowski sum is defined by
- .
Sometimes the Minkowski sum is also noted with the sign instead of the normal plus sign. In the area of linear algebra and functional analysis , however, this can lead to confusion with the direct sum .
Applications finds the Minkowski sum, for example, in 2D and 3D computer graphics and image processing (especially morphology , will though there usually binary dilation or dilatation called The counterpart is the. Erosion ) in the linear optimization (for example, Minkowski sum of a Polytops and a polyhedron cone ), in functional analysis and in robot control .
properties
The Minkowski sum is associative , commutative and distributive with respect to the union of sets, that is .
The following applies to the power of the Minkowski sum , because each element is added to each and multiple sums are only found once in the set.
The Minkowski sum of convex sets is again a convex set. In the case of convex sets, the calculation of the Minkowski sum can also be done very easily graphically: You slide one polytope along the edge of the other and the area covered is the Minkowski sum.
example
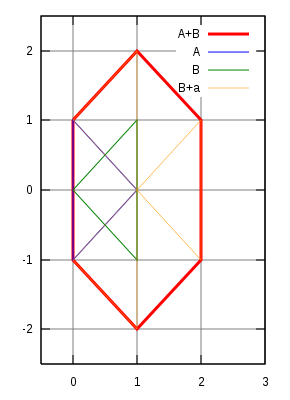
Given A and B with elements from :
Then the Minkowski sum of A and B is:
The point (1,0) occurs three times, i.e. H.
A and B represent isosceles triangles (convex). The Minkowski sum results in a convex hexagon, which can be understood as having been created by driving along B on the edge of A, as the illustration shows.
Web links
- Demonstration of the Minkowski sum (English)
- Applet to demonstrate the Minkowski sum (English)
Individual evidence
- ^ Mark de Berg, Marc van Kreveld, Mark Overmars, and Otfried Schwarzkopf: Computational Geometry: Algorithms and Applications. Springer publishing house.