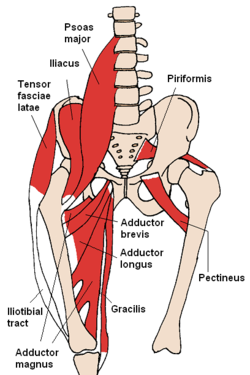
Iliacus muscle
| Iliacus muscle |
|---|
|
| anterior hip muscles |
| origin |
| The iliac fossa and the anterior inferior iliac spine of the iliac bone |
| approach |
| via the iliac fascia to the lesser trochanter of the femur |
| function |
| Acetabular : diffraction ( flexion ) and supination ( outward rotation ); Spine : Flexion ( inclination ) and sideways inclination ( lateral flexion ) |
| Innervation |
| Lumbar plexus and femoral nerve |
| Spinal segments |
| L2-L4 |
The iliacus muscle ( Latin for "iliac muscle ") is a skeletal muscle of the lower extremity in mammals, more precisely the abdominal (ventral) lumbar muscles. It is functionally combined with the large lumbar muscle ( psoas major muscle ) - in humans also with the not always present small lumbar muscle ( psoas minor muscle ) - to form the lumbar iliac muscle ( iliopsoas muscle ). The iliacus muscle forms the "head" of the fillet in slaughtered animals .
anatomy
The iliacus muscle arises from the pit ( iliac fossa ) of the iliac bone ( os ilium ) and the anterior lower iliac spine ( spina iliaca anterior inferior ).
It unites with the lumbar muscles and, enveloped by their muscular ligament ( fascia iliaca ) as a lumbar iliac muscle, passes through the muscular portal ( lacuna musculorum ) to the small rolling hillock ( trochanter lesser ) of the thigh bone , where it attaches. In dogs and cattle is one approach under the bursa , the bursa subtendinea iliac .
Together with the adductor longus and pectineus muscles , the iliopsoas muscle forms the bottom of the thigh triangle . The femoral nerve runs between the iliacus muscle and the psoas major muscle and , together with direct branches from the lumbar plexus, innervates the iliacus muscle.
function
In the hip joint , the muscle causes flexion ; it is the strongest human hip flexor. In the sacroiliac joint , it causes the counter-nutation . In addition, it causes the hip joint depending on the starting position of the joint an outward or inward rotation . Furthermore, it causes a sideways inclination ( lateral flexion ) when tensioned on one side and a flexion ( inclination ) of the spine when tensioned on both sides , thus causing the trunk to straighten up from the supine position.
Targeted training of the iliacus muscle can be done by lifting the legs in a sitting position so that the upper body and legs form a 'V'.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Michael Schünke: Functional Anatomy - Topography and Function of the Movement System . Georg Thieme, Stuttgart 2000, ISBN 978-3-13-118571-6 , p. 337 .
- ^ Richard Nickel, August Schummer, Eugen Seiferle: Textbook of the anatomy of domestic animals: the musculoskeletal system . 4th edition. tape 1 . Paul Parey, 1977, ISBN 978-3-489-72416-2 , pp. 429 .
- ↑ a b c Dirk Ehrhardt: Practical handbook functional training . Georg Thieme, 2012, ISBN 978-3-13-162531-1 , p. 77 .
- ^ Franz-Viktor Salomon et al .: Anatomy for veterinary medicine . 3. Edition. Enke, Stuttgart 2015, ISBN 978-3-8304-1288-5 , pp. 199 .
- ^ Robert H. Whitaker, Neil R. Borley: Anatomiekompass: Pocket Atlas of the anatomical pathways . Georg Thieme, Stuttgart 2003, ISBN 978-3-13-108772-0 , p. 217 .
- ^ Robert H. Whitaker, Neil R. Borley: Anatomiekompass: Pocket Atlas of the anatomical pathways . Georg Thieme, Stuttgart 2003, ISBN 978-3-13-108772-0 , p. 142 .
- ↑ Jo Ann Staugaard-Jones: Psoas training: The large lumbar muscle as the key to physical, mental and emotional well-being . Stiebner, Grünwald 2014, ISBN 978-3-7679-2017-0 , p. 13 .