N 6 adenosine methyl transferase
| N 6 adenosine methyl transferase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 580 amino acids | |
| Isoforms | 2 | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | METTL3 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 2.1.1.62 , methyltransferase | |
| Response type | Methylation | |
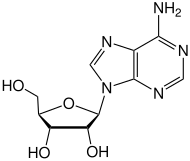
| Substrate | S-adenosyl-L-methionine + m 7 G (5 ') pppAm | |
| Products | S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + m 7 G (5 ') pppm 6 Am | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | mRNA methyltransferase | |
| Parent taxon | Eukaryotes | |
N 6 adenosine methyl transferase (MT-A70) is an enzyme in the nucleus of all eukaryotes that methylates the resulting mRNA at sporadic positions during transcription . The exact meaning of this reaction is still unclear; it is assumed that there is a connection with the subsequent processes of splicing , transport from the nucleus or translation . In humans, MT-A70 is low expressed in many tissue types.
The reaction is non-stoichiometric. Adenosine residues are preferably methylated. The normal course of sporulation in brewer's yeast ( Saccharomyces cerevsiae ) depends on a functioning MT-A70. In one study, METTL3 was one of the genes that was expressed in a particular cell line after a 50 Hz magnetic field was applied.
- Methylation of adenosine to N 6 -methyladenosine
Individual evidence
- ↑ UniProt Q86U44
- ↑ Ludmilla Lokmane, Cecile Haumaitre, Pilar Garcia-Villalba, Isabelle Anselme, Sylvie Schneider-Maunoury, Silvia Cereghini: Crucial role of vHNF1 in vertebrate hepatic specification . In: Development . 135, No. 16, 2008, pp. 2777-2786. PMID 12384598 .
- ^ Chen GD, Lu DQ, Jiang H, Xu ZP: [Effects of 50 Hz magnetic fields on gene expression in MCF-7 cells] . PMID 18275114 .
Web links
- reactome: Internal Methylation of mRNA