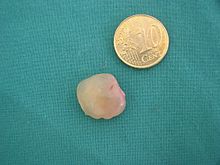
Nasal polyp
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| J33 | Nasal polyp |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
Nasal polyps are protuberances of chronically inflamed and edematous mucous membrane in the nasal cavity . These protuberances consist of mucous membrane which comes from the ethmoid cells or from the maxillary sinuses . They can lead to obstruction of nasal breathing, loss of sense of smell and other diseases of the sinuses . Real nasal polyps have nothing to do with the pharyngeal tonsils ( adenoid vegetations ), which are colloquially also referred to as "polyps".
Mild diseases can be treated by taking glucocorticoids ( mometasone furoate , nasal sprays containing cortisone, corticosteroid tablets , etc.). Most often, however, surgical therapy (e.g., an infundibulotomy ) is required to effectively treat nasal obstruction and odor loss. The operations are carried out endonasally (through the nasal cavities) and under general anesthesia in a minimally invasive manner and achieve healing rates of around 50% and an improvement in symptoms in 90% of cases. Nasal polyps and chronic polypoid sinus diseases tend to recur . Several operations are often required as the disease progresses. A newer method in which the polyps are removed by laser is said to have lower recurrence rates. Minimally invasive sinus operations are among the most demanding procedures in the ENT area and are often associated with a hospital stay of several days and intensive follow-up treatment for patients.
See also
- Rhinolite
- Tonsil stone (sometimes gets into the nasal cavity)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Guideline Polyposis nasi et sinuum at AWMF online
- ↑ Bernhard Schick, Peter Karl Plinkert, Hans Peter Zenner: Minimally invasive endonasal surgery: variety of therapy options . In: Dtsch Arztebl. 2004; 101 (8), pp. A-496 / B-415 / C-407.