Ornithuric acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
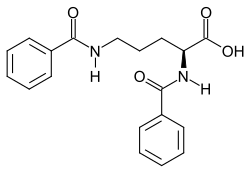
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Ornithuric acid | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 20 N 2 O 4 | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless needles |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 340.37 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
189 ° C |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
poorly soluble in water |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Ornithuric acid , also known as dibenzoylornithine, is an excretion product in birds that is used to detoxify benzoic acid . It is synthesized from the amino acid L - ornithine and two molecules of benzoic acid.
history
The compound was discovered by Charles Upham Shepard in the mid-19th century , but mistaken for a different acid. In 1877 it was examined more closely by Max Jaffé .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d August Kekulé, Richard Anschütz, Gustav Schultz, Wilhelm LaCoste: Textbook of organic chemistry . 1867, p. 447 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Entry on l-ornithine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 20, 2014.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ Heinz Penzlin: Textbook of Animal Physiology. 5th edition. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena 1991, ISBN 3-334-60363-6 .
- ↑ Zeitschrift für rational Medicin, Volume 3, 1868, limited preview in the Google book search.