Peripatos (Acropolis)
The Peripatos ( Greek περίπατος, promenade ') is a path below the Acropolis of Athens , which today leads from the ascent to the Acropolis north around the hill to the Odeon des Perikles . It forms the border to the sanctuaries on the slope above.
On the east side of the Acropolis on the side of the road there is an inscription from the 4th century BC. BC, which gives the name of the path and its length as five stages and eighteen feet, i.e. about 1100 m:
- [Τ] ΟΥΠΕΡΙΠΑΤΟ
- ΠΕΡΙΟΔΟΣ
- Π Σ ΠΟΔΕΣ
- Δ Π ΙΙΙ
- [τ] οῦ περιπάτο
- περίοδος
- π (έντε) σ (τάδια) πόδες
- Δ?ΙΙΙ.
- “Of the Peripatos
- Circulation (amounts)
- five stages (and) feet
- eighteen"
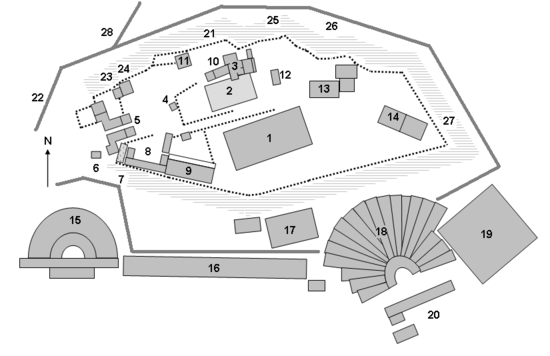
Below the Propylaea , where the Panathenaic Path (28) meets the Peripatos (22) , is the Klepsydra spring (23) . If you go east from there, follow:
24 Cave of Apollon Hypokraios
24 Cave of Olympian Zeus
24 Pan Cave
21 Aglaureion (Cave of Aglauros )
25 Sanctuary for Aphrodite and Eros
26 Peripatosin inscription
27 Another cave of Aglauros
According to the inscription, the Peripatos reached in the 4th century BC. Around the Acropolis. A length of 1.1 km also fits this very well. It ran above the Odeon of Pericles (19) and the Dionysostheater (18) , which, however, was built around 330 BC. Then passed the Asklepion (17) and the Odeon of Herodes Atticus (15) (which was not built until the 2nd century AD ) and finally ended at the starting point.
Another footpath was opened called Peripatos , which leads south around the Acropolis along Dionissiou Aeropagitou Street. There you will pass the Odeon of Herodes Atticus to the south and the Acropolis Museum to the north.
See also
- Peripatos (the philosophical school of Aristotle)
Individual evidence
- ^ Inscriptiones Graecae II² 2639 .
- ↑ Marianne Mehling (Ed.): Knaurs Kulturführer in Farbe, Athens and Attica . Weltbild, 1998, pp. 78-79.
- ↑ Baedeker Alliance Travel Guide: Athens . 8th edition. Karl Baedeker, Ostfildern 2002, ISBN 3-87504-133-X , pp. 8–83.
- ^ Hans Rupprecht Goette , Jürgen Hammerstaedt : The ancient Athens. A literary city guide , CH Beck, 2004, pp. 26–27.
Coordinates: 37 ° 58 ′ 18 ″ N , 23 ° 43 ′ 43 ″ E