Phase noise
Phase noise ( English Phase Noise ) is viewed over time the difference between the theoretical and the actual phase position and the corresponding zero crossings of a harmonic oscillation or a periodic signal. It is used for observations in the frequency domain in order to evaluate the noise power density of an oscillator .
In contrast, the jitter is considered in the time domain , which indicates the time discrepancy in the period of the oscillator signal. Phase noise and jitter are different ways of describing the same physical phenomenon.
The concept of phase noise should not be confused with phase shift .
Emergence
Phase noise means that an oscillator has other, neighboring spectral components in addition to the intended frequency . The phase noise is a characteristic of all oscillators and depends largely on the quality factor Q : Oscillators with a high quality factor usually have less phase noise than those with a low quality factor.
Mathematical representation
In the case of no phase noise, a sinusoidal frequency with additive noise floor can be expressed as:
Here the term describes the noise floor, which, like phase noise , is caused by thermal noise .
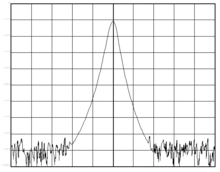
The sine frequency is spectrally expanded by phase noise (“ skirt formation ”), as shown in the adjacent figure in the form of a power density spectrum (PSD).
The phase noise is described by the term . This represents a random change in the phase position of the sine wave and thus a deviation from the ideal single-frequency oscillation.
If the amplitude is also subject to a temporal fluctuation, one speaks of amplitude noise . As a rule, the phase noise is the dominant noise effect in oscillator circuits.
Measurement
The phase noise can be measured with a spectrum analyzer if the phase noise of its local oscillator is significantly smaller than the phase noise to be measured.
It is specified in dBc / Hz (dB Carrier / Hz) at a certain distance (frequency offset or offset frequency) from the oscillator frequency. Since phase noise is a noise power density, the noise power density must be related to a certain bandwidth in order to specify a noise power .
For example, if the output power of an oscillator at its frequency is 5 dBm , the noise power is measured with a bandwidth of 1 Hz, and if a power of −110 dBm is measured in addition to the oscillator frequency with a frequency offset of 100 kHz, this results in a phase noise of −115 dBc / Hz.
Phase noise and jitter
Phase noise can be roughly related to cycle-to-cycle jitter in the areas of the power density spectrum without 1 / f noise and when a uniform rate of change of −20 dBc / Hz per decade occurs using the following equation :
With
- the phase noise
- the offset frequency
- the oscillator frequency .
For example, an oscillator with the specified oscillator frequency of 150 MHz and a phase noise of −55 dBc / Hz, at an offset frequency of 1 kHz, corresponds approximately to a cycle-to-cycle jitter of 0.97 p s .
The restriction to missing 1 / f noise is related to the type of distribution function : in the spectral range where 1 / f noise occurs, the approximation formula cannot be used, here the relationships between phase noise and jitter are more complex.
consequences
In communication technology, phase noise has the consequence that the selectivity decreases or sampling errors occur, which in turn cause a higher bit error rate . In order to be able to achieve high data transmission rates even over long distances, oscillators with very low phase noise are necessary.
In high frequency technology , phase noise is often limited by the accuracy of the measuring systems.
literature
- Enrico Rubiola: Phase Noise and Frequency Stability in Oscillators . 1st edition. Cambridge University Press, 2008, ISBN 978-0-521-88677-2 .
- Rethnakaran Pulikkoonattu: Oscillator Phase Noise and Sampling Clock Jitter . ST Microelectronics Technical Note, 2007 ( Online (PDF; 147 kB)).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Overview on Phase Noise and Jitter. (PDF; 161 kB) Agilent EEsof EDA, accessed on August 1, 2013 .
- ^ GV Klimovitch: Near-Carrier Oscillator Spectrum Due to Flicker and White Noise . Ed .: Proceedings of ISCAS 2000. Vol. 1. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Geneva 2000, p. 703-706 , doi : 10.1109 / ISCAS.2000.857192 .
Web links
- Application Note on Phase Noise (PDF) English article by Telefilter
- Phase noise measurement method (PDF) 3.53 MB ( Memento from January 12, 2006 in the Internet Archive )