Plasma cutter
A plasma cutter or torch cuts metals using a plasma created by an electric arc .
functionality
The plasma cutter consists of a power source , handpiece, earth cable , power supply and compressed air supply . A plasma cutter creates an arc between an electrode and the workpiece. A plasma is an electrically conductive gas with a temperature of around 30,000 ° C. The arc is usually ignited with a high-frequency ignition and constricted at the outlet by an insulated, usually water-cooled copper nozzle. Some systems also use lift-arc ignition, which is also used in TIG welding machines. With these devices, the torch is placed on the workpiece at the interface, and a small current flows that is insufficient to damage the torch. The gas flow pushes the torch away from the workpiece surface, the arc ignites and the electronics of the welding power source increase the current to the strength required for the cut. Due to the high energy density of the arc, the metal melts and is blown away by a gas jet, creating the kerf. Compressed air is often used as the gas for blowing out. For a better kerf, protective gas mixtures are also used, which prevent or weaken oxidation. A rounding of the edge at the entry point is characteristic of plasma cutting joints.
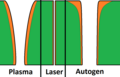
Cross-sections of the kerfs in plasma fusion cutting, laser cutting and oxy-fuel cutting
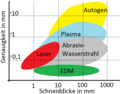
Accuracies for different sheet thicknesses in oxy-fuel cutting , plasma fusion cutting, water jet cutting , laser cutting and spark erosion (EDM)
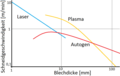
Cutting speeds for oxy-fuel cutting , laser cutting and plasma fusion cutting
Application in industry
Hand-operated or machine-operated plasma cutters are used in metal processing. Depending on the current strength, electrically conductive materials with a workpiece thickness of up to 200 mm can be cut. Current hand plasma systems have an amperage of up to 120 amps, while the more powerful machine-operated plasma cutting systems can have an amperage of up to ten times this value. Conventional systems work with around 300 amps and can pierce 70 mm black plate with it. In today's plasma technology, a distinction is made between conventional plasma fusion cutting and precision plasma cutting. Precision plasma cutting uses burr-free cutting lines, angularity of the cut or a bare metal surface as criteria. Here, instead of compressed air, technical gas is used in order to achieve a better cutting quality that comes close to the quality of laser cutting . The advantages compared to oxy-fuel cutting with CNC plasma cutting systems are mainly the roughly four times higher cutting speed and the lower heat distortion due to the high energy density . In addition, plasma cutters can cut practically all metals, while oxy-fuel cutting is largely limited to structural steels.
Application in rescue services
The plasma cutter originally developed for industrial use is also used in a mobile version in technical emergency aid , for example by the fire brigade and the THW . If a hydraulic rescue set with spreader and cutting device cannot be used due to lack of space or if the use of a cutting torch is impossible due to its difficult handling and considerable thermal expansion, the plasma cutter is an ideal alternative. The lower thermal expansion enables you to work closer to people. It is not possible to use a hydraulic cutter on hardened steel like the one used in the steering column and wishbone. That is why the plasma cutter is often used there. The devices used generally achieve a current strength of up to 60 A.
Individual evidence
- ↑ plasma cutting vs. Laser cutting. (No longer available online.) In: weber-stempel.de (formerly trotec-leipzig.de). Archived from the original on January 10, 2018 ; accessed on February 1, 2016 .
- ↑ Plasma cutter. (No longer available online.) In: itheine.de. Archived from the original on March 2, 2014 ; accessed on February 4, 2014 .
- ↑ Cimolino Heck: Technical assistance in case of truck accidents: Technical and medical rescue of trapped people, handling of heavy road vehicles involved in an accident. , 1st edition, Ecomed Sicherheit, Landsberg 2003, ISBN 9783609686615 . , Preview online