Plastoquinone
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Plastoquinone | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 53 H 80 O 2 | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light yellow leaves |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 749.20 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Plastoquinone (abbreviated PQ from English plastoquinone ) is a chemical compound belonging to the group of quinones that occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts . Here it is involved in the light reaction of photosynthesis by transporting electrons from photosystem II to the cytochrome b 6 f complex as a link in an electron transport chain .
Molecular structure
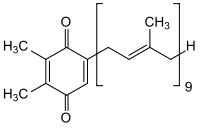
The main body of the plastoquinone is 1,4-benzoquinone , which belongs to the quinone group and contains a methyl group in positions 2 and 3 and an isoprenoid side chain in position 5 . Plastoquinone is also referred to as PQ-9 based on the number of isoprene units in the side chain. This hydrophobic side chain enables the connection to be anchored in the likewise hydrophobic area of the thylakoid biomembrane .
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on Plastoquinones. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 28, 2014.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
