Porphobilinogen deaminase
| Porphobilinogen deaminase | ||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Porphobilinogen deaminase monomeric, human | ||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 361 amino acids | |
| Cofactor | Dipyrromethane | |
| Isoforms | 2 | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | HMBS | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 2.5.1.61 , transferase | |
| Substrate | 4 porphobilinogen + H 2 O | |
| Products | Hydroxymethylbilane + 4 NH 3 | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | PBG-D | |
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
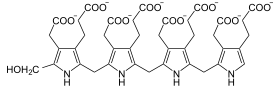
Porphobilinogen deaminase (PBG-D) (also: hydroxymethylbilane synthase , HMBS ) is the enzyme that in all living things, the elimination reaction and subsequent polymerization of four porphobilinogen molecules to hydroxymethylbilane catalyzed . PBG-D is therefore necessary for porphyrin biosynthesis. Mutations at HMBS - gene of people with the following lack of PBG-D can for acute intermittent porphyria lead.
There are two isoforms of PBG-D in humans , one found only in erythrocytes , the other is expressed in the remaining tissue types.
Catalyzed reaction
Four molecules of porphobilinogen polymerize to one molecule of hydroxymethylbilane, consuming water and producing ammonia. As cofactor is dipyrromethane necessary, the bound and to which the individual porphobilinogen molecules are first added gradually.
Individual evidence
Web links
- Jassal, D'Eustachio / reactome: Four PBGs combine through deamination to form hydroxymethylbilane (HMB)
- OMA: PBG-D homologues