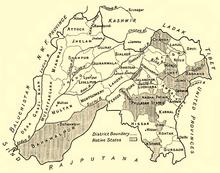
Shimla Hill States
The Shimla Hill States (from 1901 Punjab Hill States ), named after the capital Shimla , which was also the summer capital of British India , were an administrative group at the time of colonial rule. They originally comprised 19 or 28 princely states if you count the vassals. Together they had a size of 16,400 km².
history
The states, whose ruling houses are all of Rajput origin, came under British "protection" as a result of the war to expel the Gurkhas , which in 1815 was under the command of General David Ochterlony . The state of Tehri-Garhwal , which was originally also included in the region, was added to the Central India Agency .
From the states of this agency , the Punjab Hills States Agency was created in 1901 with other states , which was merged into the Punjab States Agency in 1936 . The total tax revenue in 1911 was about £ 660000 out of a population of 410,000 souls.
organization
The British Deputy Commissioner of Shimla District, which was divided into nine areas by the princely states, was the responsible colonial officer as superintendent . He was subordinate to the governor of the Punjab in Lahore .
Only the more important states were granted the right to their own higher jurisdiction. The Rajas of Sirmur and Bilaspur were entitled to salute and were thus entitled to a seat in the Chamber of Princes created in 1921 .
Shimla Hill States
| country | Population (thousand) | Area (km²) | Tax revenue ( Rs. ) | Ruler title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baghal | 1891: 20.6 | 319 | Raja (from 1875) | |
| Baghat | 1891: 8.3, 1941: 9.7 | 155 | 1941: 150000 | Rana |
| Balsan | 1891: 5.2 | 131 | Rana | |
| Bhajji | 1891: 12 | 242 | Rana | |
| Bija | 1891: 1.1 | 10.3 | Thākur | |
| Kahlur (= Bilaspur) | 1891: 86, 1941: 101 | 1155 | 1911: 190000, 1941: approx. 300000 | Raja |
| Bashahr | 1891: 64, 1911: 93 | 10,000 | 1911: 95000 | Raja |
| Darkuti | 1891: 0.59 | 10 | Rana | |
| Dhami | 1891: 3.3, 1941: 5.2 | 75 | 1941: 50000 | Rana |
| Hindur (= Nalagarh) | 1941: 50 | 660 | 1941: 216000 | Raja |
| Jubbal | 1891: 19, 1941: 27 | 825 | 1941: 850000 | Rana |
| Keonthal | 289 (with vassals 926) | |||
| Kumharsain | 1891: 9.5 | 242 | Rana | |
| Kunhiar | 1891: 1.9 | 23 | Thākur | |
| Kuthar | 1891: 3.6, 1941: 3.7 | 49 | 1941: 42000 | Rana |
| Mahlog | 1891: 9.1 | 137 | Thākur | |
| Mangal | 1891: 1 | 33.5 | 1911: 0.9 | Rana |
| Sāngri | 1891: 2.6 | 41 | 1901: 2400 | Mian (Protectorate 1846) |
| Sirmur (= Sirmaur, Sirmour) | 1891: 112, 1901: 135, 1941: 148 | 2700 | 1901: 600000, 1935–40: ø 867000 | Raja (Maharaja 1918) |
| Taroch | 1891: 3.2 | 193 | Thākur |
Vassals
- from Bashhar: Khaneti and Delath.
- from Jubbal: Rawin (Rawingarh) and Dhadi (originally Tharoch was tributary, then Bashahr, from 1896 Jubbal).
- from Keonthal: Thiog (= Theog), Koti, Ghund, Kheri, Madhan (= Kiari) and Ratesh (= Kot); the first four of these zaildars had to pay tribute.
Punjab Hill States
During the administrative reorganization, the following additional, comparatively important states became part of this new administrative unit:
Except for Siba, all these princes were entitled to salute.
literature
- Thomas H. Holland (Ed.): Provincial Geographies of India. 4 volumes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1913-1923.
- Lethbridge, Sir Roper; The Golden Book of India; London 1893
- Imperial Gazetteer of India; Vol. XXVII Samadhiala to Singhana; Oxford 1908
- Individual evidence
- ↑ 1891 census, or 1901. additionally different years of the Imperial Gazetteer
- ↑ Conversion factor 2.58 per mile². According to Golden Book, 1893, not always reliable due to a lack of sufficient cadastral data
- ↑ according to the Golden Book of India; 1893