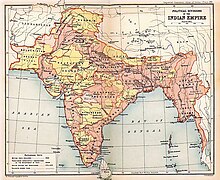
List of Indian princely states
This list of Indian princely states reflects the more important state structures that existed on the subcontinent (excluding Burma) at the time of British colonial rule . "Significant" are those whose rulers had been granted the right to a gun salute . In terms of area, they can be very small. Coin shelf and post office sovereignty are mentioned as they are an important feature of sovereignty. Overall, it is assumed that there were 565 states that existed on August 15, 1947, the Indo-Pakistani Independence Day. The “diplomatic yearbook” spoke of 617 in the 1920s. About 400 of these were smaller than 50 km². Especially on the Kathiawar peninsula (Bombay) there were little lands that were inferior in size to the German Duodez principalities . The Salut criterion means that some countries with a large area, such as Bastar , which was larger than Belgium, are not included in the list.
It should be noted that several more important states (including Arcot , Assam , Oudh ( Awadh ), Coorg , several Marathas , Punjab , Utkala ) in the provinces of British India were still in the 19th century , and that its greatest expansion was only under George Curzon reached, rose. The conquests lasted until 1907, especially in the north-west and north-east. The total area of the princely states ( princely states ) was 40% less than their proportion in the population and economic power was lower. The princes were controlled by residencies and agencies. About 300 smaller states did not have the right of higher jurisdiction and in most cases no treaties regulating their relationship with the colonial power.
The relationship between states and the British crown was governed by the Interpretation Act 1889 and, to a certain extent, the Royal Titles Act 1876. The rulers' rights and tribute obligations were usually repeated in the viceroy's sanad when a new ruler was enthroned . The Rajas of the states, who were allowed eleven or more rounds of salute, had a seat in the Chamber of Princes from 1921 . Another 12 members were elected from among 127 smaller princes.
A – K
| country | Title , salute | Area population (thousand) |
Tax revenue (thousand Rs. ) | military | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Amir , 21 (local 31) | 652,000 km² 4.9 million |
19,500 K, 40,408 I, 210 G | after the Russo-British agreement a neutral, independent buffer state. (see: History of Afghanistan: 19th and early 20th centuries ) | |
|
|
Raja (from 1877: Sawai Maharaja), 11 | 2069 km² 1881: 81, 1891: 93, 1901: 78 |
225,000 | 77 K, 544 I, 13 G | Gegr. 1731. Occupied by the British from 1855–1859. |
|
|
Rana , 9 | 2165 km² 57 |
11 K, 169 I, 7 G | Bev. Also 19,000 Bhil | |
|
|
Rao Raja (until 1826), Maharaja Sawai, 15 | 7802 km² 682 |
2.6 million | 2189 K, 3676 I, 351 K | Nov. 1775 from parts of Jaipur . Protectorate since November 14, 1803. Part of the Rajputana Agency , coin rack until 1893, postal sovereignty until 1902 |
|
|
Nawab , 17 (1966: 21) | 44,600 km² 1891: 573, 1901: 720, 1941: 984 |
1911: 3.5 million, 1941: 12 million | 443 K, 1352 I, 11 G. | Largest state in Punjab . Protectorate 1838. Coin shelf, occasional copper coins. |
|
|
Babi, 7 | 488 km² 46 |
1903: Rs. 99543, Baroda tribute: 3000, British: 9766 | 60 K 177 I, 5 G | Coin shelf until 1885. |
|
|
Nawab (from 1871), 6 (later 9) | 428 (later 709) km² 31, 1941: 39 |
founded in 1761; After 1900 temporarily under compulsory administration. The only Muslim state in Madras Province . | ||
|
|
Kiladar (from 1876: Nawab ), 9 | 554 km² 1891: 35, 1941: 49 |
Tribute: Rs 7351½ (+ 1500 from 1858). Since 1873 subsidy 8698, remaining Rs. 153½ net | Gegr. as domain 1665. Occupied by Mysore from 1783–90 , then independent rule. Protectorate from 1818. 1831–48 annexed by Hyderabad , but under British administration. | |
|
|
Maharawal, 15 | approx. 3870 km² 1891: 175 (decrease up to 1901: <20%) |
640 K, 783 I, 14 G | Protectorate from 1818. Shelter from the political agent in Udaipur (= Mewar). | |
|
|
Nawab Bahadur, 11th | 300 km² 1891: 17, 1941: 19 |
1941: 180,000 Rs. | 9 K, 185 I, 2 G | Gegr. 1784 by descendants of Nizam-ul-Mulk Asaf Jah I. After exchanging official letters (instead of contracts) on December 24, 1806 under British protectorate, part of the Central India Agency . |
| Baraundha | Raja (Bahadur, since 1877), 9 | 611 km² 17 |
15 K, 75 I, 6 G | 34 generations of this Rajput dynasty are said to have ruled in Rusin ( Banda district ) before they went to Baraundha. Protectorate 1807. Temporary residence in Paturkuchar . | |
|
|
Maharawal, 11 | 2097 km² 1941: 160 |
1941: 1.1 million | ||
|
|
Maharaja Gaekwar , 21 | 22110 km² (1943: 35774 km²) 1891: 2.185; 1901: 1.95 million |
£ 1.53m | 3562 K, 4988 I, 38 G. | First alliance treaty Jan. 26, 1780. Protectorate June 6, 1802. Territory ceded to the British for defense 1805, 1808, 1817. In 1940-3 absorbed numerous dwarf states in the region. Coin shelf until 1947. |
|
|
Rana, 9 (later 11) | 3513 km² 56 |
17 K, 225 I, 9 G | from 1921 own stamps 
|
|
|
|
Raja (from 1859: Maharaja Bahadur), 13 (locally 15) |
|
for defense: Rs 219000 | Old state tradition as Kashi. 1194 to Oudh . 1790 independent. At the moment Warren Hastings placed under direct control, in 1860 again as a separate state, which from 1911 was considered completely independent internally. (The capital has been called Varanasi since 1947 ). | |
|
|
Maharaja , 15 (later 19) | 5092 km² 1891: 645, 1941: 487 |
1941: 3.15 million | 1647 K, 8207 I, 54 G. | Gegr. 1752. Protectorate 1803, treaty of 1805, final treaty January 18, 1828. 1,600 soldiers in East Africa during the First World War . |
|
|
Thakur Sahib, 13 | 7639 km² 1941: 500 |
1941: 10.8 million | ||
|
|
Begum (Nawab), 19 (local 21) | 17729 km² approx. 1 million; 1931: 730 |
1941: approx. 8 million |
Protectorate since December 1817. From 1844–1926, it was ruled by women for several generations. Coin rack; Post sovereignty until 1908. Annexed by India on May 1, 1949. |
|
|
|
Pant Sachiv, 9 | 1891: 3846, 1941: 2347 km² 1891: 145, 1941: 141 |
The Pant Sachiv were one of eight ministers who held hereditary ministerial offices at the Mughal court . | ||
| Bijawar | Maharaja, 11 | 2512 km² 113 |
1941: 360000 | 100 K, 1000 I, 13 G | Protectorate 1807. |
|
|
Maharaja, 17 (1921: 19) | 57-60,000 km² 1891: 510, 1941: 936 |
1941: 12.7 million | 400 K, 564 I, 91 G | Title founded in 1456, completely Maharajadhiraj Narendra Maharaja, bestowed by Ahmad Shah Durrani in 1752. Protectorate March 9, 1818, with the obligation to provide the British with troops in the event of war. |
|
|
Maharao Raja | ??? km² 254; until 1901> -40% (starvation) |
Tribute: 40000 Rs | 446 K, 1835 I, 144 G. | Gegr. 1342. Protectorate Feb. 10, 1818. Postal sovereignty, coin shelf, but only a few coins |
| Burdwan | Maharaja Adhiraj Bahadur, since 1877: 13 | - |
(in the 18th century up to 2000 K) | Not really a ruler, but a zamindar . As such, the Empire's greatest taxpayer. Supported the suppression of the Santal uprising in 1855. | |
|
|
Nawab, 11th | 903 km² 1891: 86, 1941: 89 |
1941: <1 million | 36 K, 498 I, 12 G | One of the first places of entry for the Portuguese. Defense treaty against pirates April 23, 1773. Brit. Protectorate June 6, 1802. Salt tax to the British instead of a tribute. Own 13½ mile railroad ( Tarapur to Cambay ). |
|
|
Raja Sri | 7,977 km² 1891: 115, 1931: 147 |
1941: 981000 | 12 K, 200 I, 3 G | Gegr. 550. 1809–46 Jammu subject to tribute. Protectorate March 9, 1846. Title of ruler Paramanabhattaraka Maharajadhiraja until 1808. In the 19th century, tribute 10,000, reduced to Rs. 3,800 against land cession. Post sovereignty. |
|
|
Raja; Maharaja (from 1877, also Sipadar-ul-Mulk ), 11 | 2033 km² 143 |
188 K, 1552 I, 42 G. | Gegr. 1765 Protectorate 1803 | |
|
|
Raja; Maharaja from 1919 | 3,013 km² 1891: 167; 1901: 156 |
1941: 755 | 39 K, 814 I, 39 G | A jagir who only rose to raja in 1806 when he signed a protectorate treaty. The last Maharaja was Dīwān of Hyderabad in the 1940s . |
|
|
Raja, 9 | 2252 km² 1891: 71, 1941: 145 |
1904: 215391. Tribute to Baroda 7806 Rs., 1941: 1.1 million | 50 K, 256 I, 4 G | Gegr. 1743. Submission in 1822. Population mainly tribals : Bhil and Koli . |
|
|
Raja | 3511 km² 1891: 600; 1901: 812, 1941: 1.2 million |
1891: 200,000 for defense, 1941: 940,000 | 16 K, 324 I, 4 G | Dependent on the Portuguese in the 16th century, then close ties to the VOC. Protection treaties with British 1791, 1809. Office of Divan 1632–1809 hereditary in the Paliat Achan family. Full title from 1895: Maharaja Gangadhara Koviladhi Karikal Sri. Historically good own postal system that continued to exist. Different currency denominations until 1911: 6 putnams = 5 annas. Elected parliament from 1930 (with high retention of title). Merged with Travancore in 1948, with postage stamps being issued again until 1950. |
|
|
Maharana, 9th | 5934 km² 18 |
70 K, 67 I. | ||
| Datia (= Duttia; Bundelkhand) | Rao (until 1820s), Raja until 1865, Maharaja, 15 (from 1906: 17) | 2156 km² 1891: 183, 1931: 159 |
1941: approx. 120000 | 945 K, 5203 I, 124 G. | Additional title of the ruler: Lokendra ("world protector"). Protectorate March 15, 1801, enlargement of the country in 1817, new treaty in 1818. Post sovereignty until 1921. 1941: Two companies of Govind Infantry, plus a further 1200 soldiers. |
|
|
Raja Baba Sahib (older line, 1728), 15th century Raja Dada Sahib (jgr.line), 15 |
Baba: 400, Dada: 145 km² Baba: 73, Dada: 66, 1941: 70 |
Baba 1941: 650,000 km² Dada 1941: 900,000 |
Baba: 70 K, 594 I, 14 G km² Dada: 79 K, 176 I, 6G |
Marathas state with two-part rule, part of the Central India Agency. Both Rajas resided in Dewas. Protectorate and opium cultivation contract Dec. 1818. Both rulers increased to Maharaja in 1918. Area expansion at the beginning of the 20th century |
|
|
Raja, 15th | 4490 km² 1891: 148, 1901: 142, 1941: 243 |
1941: 1.75 million | 367 K, 1249 I, 5 G | Gegr. 1762. Protectorate Jan. 10, 1819, sided with the rebels in 1857, therefore confiscated, but reconstituted in 1864 without the Bairsia district, which went to Bhopal. Numerous smaller states had to pay tribute. Annual contribution of Rs 12,000 to the Malwa Corps in 1880 replaced by a one-off payment of Rs 300,000. Post sovereignty until March 31, 1901. 1 Anna = 4 Dabel. Coin shelf until 1893 (?) |
|
|
Raja, 9 (later 11) | 2048 km² 102 |
Tribute (from 1870): Rs 9,000; 1941: 856000 | 40 K, 171 I, 4 G | Ancient Rajput dynasty (since 1262?). Protectorate Dec. 31, 1802. |
|
|
Gohad: Rana Shri; united from 1806: Maharaj Rana, 15 | approx. 3100 km² 250; 1901: 270 |
1941, 1.6 million | 139 K, 1588 I, 32 G; 1941: 1058 | Dholpur founded approx. 770 (= Dhavalapura). Gohad (= Gohud) founded in 1505, the 1740–56 and 1782-Dec. 1805 was occupied by Gwalior. Bahratpur occupied Dholpur from 1761–75. British Protectorate ("Eternal Treaty of Friendship") December 2, 1779. The ruler of Gohad united Dholpur and Gohad in 1806, at the same time a new treaty with the British. |
|
|
Raj Sahib (from 1918: Maharaja), 11 (from 1877: 15) | 3010 km² (1943: 4780) approx. 100 |
103 K, 470 I, 9 G | State of Jhalawad founded in 1190 (alternatively: Kuwa, Halwad, Halwad-Dhrangadhra). Renamed Dhrangadhra to establish the new capital in 1735.
|
|
|
|
Thakur Sahib, 9 | 730 km² 22 |
25 K, 285 I, 6 G | Gegr. 1595. | |
|
|
Rawal (until 1808), Maharawal, 15 | approx. 2500 km² 154, 1901: 167 1941: 227 |
Tribute: Rs 17,500; 1941: approx. 750,000 | 251 K, 535 I, 8 G | State founded in 1197. Protectorate Treaty on December 11, 1818 negotiated by Sir John Malcolm (1769–1833). Approximately 35% of the population of the indigenous Bhils around 1900. |
|
|
Sardar (1643-1843); Raja Bahadur, 11th | 1578 km² 1891: 97, 1941: 170 |
1941: 180000 | 70 K, 300 I, 6 G | Founding of Kot Kapura in 1643. 1763 Division into Kot Kapura and Faridkot. Occupied by Punjab from 1807-09. From April 3, 1809 independent again under British protectorate. Was on the British side in the First Sikh War , which led to territorial gains. Loyal in 1857, therefore increased rank. Post sovereignty until December 31, 1886, own stamps until March 31, 1901. Coin denominations: 8 Fulus = 4 Paisa = 1 Anna. |
| Gondal (Kathiawar) | Thakur Sahib, 11 | 2641 km² 1941: 205 |
1941: State revenue ½ million (no taxes!) | Dynasty of the same name founded by Kumbhoji I in 1634. The state was free from taxes, duties, customs duties and excise duties. One financed oneself from plants. School attendance is also compulsory for girls. | |
|
|
Maharaja, 19 (local: 21) | 74,980 km² 1891: 3 million, 1901: 2.9 million, 1941: 3.52 |
1941: 24 million | 5504 K, 11040 I, 48 G. | First peace and friendship treaty October 13, 1781, protectorate December 30, 1803 (Treaty of Sarje Anjenagon). The ruler was known as Scindia . Post sovereignty, whereby the stamps were valid for all Indian traffic. Coin shelf with regular issues until 1947. |
|
|
Nizam, Jan. | 252840 km² 1891: 13 million, 1901: 11.1 million 1941: 16.3 million |
1903: 4.17 million (without Jagir , this approx. ⅓), 1941: 91 million | 6228 K, 24068 I, 35 G (1901: total 24012, of which 3594 K) |
The "first" prince of India. Full title: "His Highness Asaf Jah, Muzaffar-ul-Mamalik, Rustam-i-Dauran, Arastu-i-Zaman, Nizam-ul-Mulk, Nizam-ud-daula, Nawab Mir Sir Mahbub Ali Khan Bahadur, Fath Jang. " The Crown Prince was "HH the Prince of Berar." See also: Category: Hyderabad (State) |
|
|
Raja (until 1843), Maharaja, 15 | 1891: 6450, 1941: 4306 km² 1891: 258, 1941: 308 |
Baroda pay tribute. 1941: 210000 | 54 K, 100 I, 15 G | Made around 1200. 1791–1843 divided into up to five states. |
|
|
Maharaja, 19 (local 21) | 21,600 km² 1.05 million (approx. 10% tribals), 1901: 850,000 |
1941: 13 million | 3231 K, 6128 I, 65 G | First Protectorate Treaty Dec. 24, 1805, imposed by Lord Lake , new treaty in 1818, which envisaged major land cessions to the British.
|
|
|
Maharaja, 19 (on site 21) | 1891: 37320, 1941: 43,000 km² 2.5 million, 1901: 2.65 (> 6% starvation), 1931: 2.6 million |
Tribute: Rs 400,000; 1941: 14.3 million | 3578 K, 16099 I, 281 G. | Protectorate April 25, 1818. Spelling until 1860 Jeypore. New protectorate treaty 1871, including assignment of the salt tax. Full title from 1880: Saramand-i-Rajha-i-Hindustan Raj Rajindra Sri Maharajadhiraj. Post sovereignty. Coin shelf for silver and copper until 1947. |
|
|
Maharawal (from 1891: Maharajadhiraj Maharawal), 15 | 41,433 km² 1891: 109, 1941: 76 |
1941: 420000 | 140 K, 353 I 25 G | Gegr. as Deogarh 731. New capital Jaisalmer 1156. Protectorate December 11, 1856. ( Jessulmere ). Coin shelf, but no embossing. |
|
|
Maharaja, 19 (from 1877 local: 21) | 206,000 km² 1891: approx. 1.5 million, 1931: 3.6 million |
8000 K and I, 288 G; 1941: 8900 (on site) | The Raja of Jammu bought Kashmir after the First Sikh War for Rs 750,000. 31,000 soldiers in the First World War. | |
|
|
Nawab, 9 (from 1919: local 13) | 836 km² 1891: 77, 1941: 110 |
1941: 1.1 million | 310 I, 179 G. | First defense agreement (anti-piracy) Dec. 6, 1733. 1753 Union with Jafarabad (97 km²), which was nominally a dependent Giet. Since the mint produced counterfeit money for the nearby trading center of Bombay, it was destroyed in 1834 and the little land became a protectorate. No tribute to the British, however. |
|
|
Nawab, Jan. | approx. 1500 km² 1891: 120, 1941: 100 |
Rs. 160000 for defense | 13 K, 167 I, 15 G | Protection treaty 1818. 1857 loyal. Panth-Piploda was separated in 1942. |
|
|
Raja, 9 | 794 km² 1941: 57 (mostly tribals) |
1941: approx. 500,000 | No obligation to pay tribute. Absolutist ruler until 1947. | |
|
|
Raja, 11th | 3446 km² |
Rs 1672 for defense | 64 K, 253 I, 4 G | Originally Indore tribute. Established as a separate state when the Protectorate Treaty was signed on Jan. 18, 1818. Over 55% Bhil. |
|
|
Maharaja Rana, 13th | 1891: 6950, 1941: 2097 km² 1891: 340, 1941: 108 |
Tribute 80,000, from 1899 30,000 Rs; 1941: 711000 | 403 K, 3873 I, 94 G | Created in 1838 from part of Kota State . Part of the area was returned in 1899. Post sovereignty until October 31, 1900. Coin shelf until 1893. Decline in rural population 1891–1901: 22.7%.
|
| Jind (1886–1914: Jhind) | Raja Bahdur (from 1881: Raja-i Rajgan), 11 | 3248 km² 1891: 250, 1941: 324 |
1911: £ 127,600; 1941: approx. Rs. 260,000 | 379 K, 1571 I, 12 G. | By proclamation under British protection in 1809. Area enlargement and new protection treaty in 1847 (see First Sikh War ). Loyal 1857 with area increase in 1860 (tax revenue Rs 116813). Post sovereignty in cooperation with the Imperial Indian. |
|
|
Maharaja, 17 (local 21) | approx. 95,000 km² 1891: 1.75 million, 1901: 1.9, 1941: 2.1 |
115000 Rs for Erinpura Regiment | 3162 K, 3653 I, 121 G Life Guards Jodhpur Sardar Risala and 1st Infantry Battalion assigned to overseas service during World War II . |
The state of Marwar was founded around 1250. About 200 years later it was renamed when the new capital Jodhpur was founded. Full title from 1751: Raj Rajeshwar Saramad-i-Rajha-i-Hindustan Maharajadhiraja Maharaja. Protectorate Jan. 6, 1818. Interventions 1824, 1839, and 1870. Part of the Western Rajputana States Agency. Post sovereignty until 1927. Regular coinage until 1948. Part of the Indian Union March 9, 1949. |
|
|
Nawab, 11th | 8,460 km² 1891: 388; 1947: 545 |
1941: approx. 10 million | 251 K, 1972 I, 66 G. | Gegr. 1748, Protectorate 1807. Post sovereignty. Coin shelf, occasional copper embossing. Last refuge of the Indian lion. Aug. 15, 1947 Accession to Pakistan, annexed by India on Nov. 7, 1947, referendum on Feb. 20, 1948 for India, official affiliation on 25. 91 voters had voted for Pakistan. |
|
|
Raja, 11th | 1155 km² 1891: 86, 1941: 101 |
1911: 190000, 1941: approx. 300000 | 40 K, 620 I, 11 G | Gegr. around 880. One of the Shimla Hill States. Under British protection from 1815 after the Gurkha occupiers (since 1803) were driven out. |
|
|
Wali, 19th | 1891: approx. 234,000, 1941: 141,000 km² 1891:? 150; 1901:? 372 (improved methodology), 1941: 319 |
1941: 1.5 million | 300 K, 1500 I, 6 G | Gegr. End of the 16th century. Further titles Begar Beli, awarded in 1739 by Nadir Shah . In the border area with Afghanistan, this temporarily subject to tribute. Protectorate 1875. Various assignments of territory, u. a. the Tehsils Quetta, Bolan, Nushki, Nasirabad. Kharan is considered part of the state. One of three states in the Baluchistan Agency. Extensive destruction in the 1935 earthquake. |
|
|
Raja, 11th | 1542 km² 1891: 253, 1941: 316 |
1941: approx. 400,000 | 197 C, 829 I, 13 G. | Under British control in 1846, soon reconstituted. Protection treaty 1854, loyalty rewarded with gains in territory in 1857, treaty renewed in 1876. The Raja owned a further 1806 km² of country estates in British territory, which Randhir Singh received as a gift in 1857 for his loyalty. Maharaja Jagatjit Singh married the Spanish "dancer," Anita Delgrada, in 1910, who was not recognized by the British as a legal wife. (Life story filmed in 2006: La princesa de Kapurthala ). Captured by Pakistan on March 15, 1948. |
|
|
Maharaja, 17 | 3116 km² 1891: 150, 1931: 140 |
1875: 300000, ø 1935–40: 671000 | 281 K, 1640 I, 56 G | Gegr. 11th century alliance and protection treaty June 13, 1817. After succession disputes had already broken out in 1838–40 and 1848, the country was to be annexed in 1852 under the Doctrine of Lapse , which was prevented in London. Loyal in 1857, at times under administration due to debts until the 1860s. Absolutist ruler with a divan.
|
|
|
Raja (Bahadur, 1877), 9 | 9,662 km² 1891: 224, 1941: 513 |
Tribute from 1905: 12,000; 1941: 650000 | no | Originally due to the Maharaja of Nagpur, after whose takeover in 1853 a feudatory state. Population mostly Gond . There are five large zamindars in the country. Main town Bhawanipatna (19 ° 54 'N, 83 ° 10' E). From 1938 to the Eastern States Agency. |
|
|
Me | 15760 km² 129 |
700 K, 774 I, 32 G | Protectorate 1838. 1947 to Pakistan. 1955 absorbed in the Western Province, today Province of Sindh. | |
| Khilchipur (Bhopal) | Rao Bahadur, 9 | 700 km² 36 |
Rs 83317; Tribute to Sindh 13183 Hali-Rs. | 44K, 202 I, 2 G | Rajput ruler tributary to Scindia . Area in 1881: approx. 407 km². Location: 23 ° 52 'to 24 ° 14' N, 76 ° 28 'to 76 ° 45' E |
|
|
Maharaja, 15 | 1891: 1867, 1941: 2213 km² 1891: 113, 1941: 86 |
1941: 750000 | 499 K, 2000 I, 51 G | Post sovereignty until around 1930. Coin shelf, which was not exercised. |
|
|
Raja Chhatrapati (Maharaja from 1900), 19th century | 7268 km² 1891: 800, 1941: 957 |
1941: approx. 510000 | 255 K, 1902 I, 67 G. | Gegr. 1710 by Shivaji II , the former ruler of Satara . Protectorate Treaty October 1, 1812, in which some forts and the port of Malwan were ceded. 11 vassal states u. a .: Vithalgarh, Bavda, Kapshi, Kagal, Ichalkaranji Torgal, Datva. From 1933 part of the Kolhapur Residency & Deccan States Agency formed from 17 states . Maharaja Vikramsinhrao, of the older line of Dewas, was adopted in 1947 and ruled until 1949. |
|
|
Maharao, 17th | 9796; 1893: 14684 km² 1891: 517 (1891–1901: −34.6%), 1901: 544 (enlarged), 1941: 985 |
Tribute 1830: 102,000; 1838: 200000, 1941: 500000 | 949 K, 5756 I, 148 G. | Not to be confused with the Kohat District ( NWFP ). Secession of Bundi 1631. Protectorate Treaty December 26, 1817, amended in 1838. Increase in territory from the territories of Jhalawar (1892). In 1942, the internment camp Camp 17 (Deoli) was located near the main town for German men who had been deported from the Dutch East Indies . |
|
|
Maharaja (since 1884), 13 | 3372 km² 1891: 602; 1901: 566; 1941: 590 |
1871: 700,000 Rs, of which 50% to the British; 1941: 3 million | 9 K, 176 I, 4 G | Founding of the state of Kamata, since 1510/5 under the dynasty of the "Koch". Won by Bhutan through the 1783 campaign . The love marriage of the second-born Prince Jitendra (r. 1913-22) with Indira Devi von Baroda in 1913 was considered scandalous. The Maharani then ruled during the minority of their son, the last Raja Jagaddipendra Narayan , who served in the British Army during World War II. |
|
|
Rao (from 1885: Sawai Bahadur), 17 (on site: 19) | Approx. 15500 km² habitable, plus ~ 23000 km² salt steppe in the Rann von Kachchh 1891: 512, 1901: 488, 1941: 500+ |
Tribute (Anjer-Fort) Rs 88,000; 1929: 186000, 1941: 320000 | 354 K, 1412 I, 164 G. | Gegr. 1320, further conquests, capital since 1548 Bhuj . Agreement with the British in 1809, 1813 and after intervention in the follow -up dispute on October 13, 1819, taking into account certain rights of the Jareja aristocrats, which led to disputes lasting for decades. Advanced administration in the 19th century. Since 1933 under the Mahi Kantha Agency , to which 16 salute states and 236 smaller states belonged. Coin shelf with regular coinage until 1947, including those with the name Edward VIII in 1936 . |
L-Z
| country | Title, salute | Area population (thousand) |
Taxes (thousand Rs. ) | military | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Jam, 9 | 21930 km² 1901: 56 |
33 K, 276 I, 4 G | Formerly a vassal of Kalat. Under the Baluchistan Agency. Post-sovereignty until March 1907. Main place burial place of Muhammed bin Harun († 712) and Sir Robert Groves Sandeman († 1892). | |
| Limbdi (= Limri) | Thakur Sahib, 9 | 887 km² 43 (10% Muslims) |
approx. 160,000 Rs, of which 51,396 tribute | 35 K, 174 I, 28 G | |
|
|
Nawab, Jan. | 583 km² 1941: 23 |
1941: approx. 137,000 | ||
|
|
Rana (1867: Maharana), 9 | 1001 km² 1891: 76, 1901: 64, 1941: 95 |
Rs 176,000 Tribute to Baroda 5001, British: 9231 | 201 K, 295 I, 40 G | Gegr. 1225 in Virpur, since 1434 in Lunawara. Protectorate 1819, from 1826 under Rewa Kantha Agency . Tribute to Baroda and Gwalior, whose claims the British took over in 1861. Loyal 1857. |
| Maihar | Thakur, from 1869: Raja, 9 | approx. 1000 km² 71 (thereof 15% tribals) |
8 K, 227 I, 7 G | Gegr. 1778, 1788–90 occupied by Banda. Under protectorate since 1806. | |
| Malerkotla (= painter Kotla; Punjab) | Nawab Bahadur, 11th | 460 km² 1891: 71, 1941: 84 |
1941: 805,000 | 60 K, 228 I, 6 G | Founding of Malerkotla by Bazid Khan in 1657. From May 3, 1809 by proclamation under British protection. |
|
|
Raja Bahadur, 11th | 3150 km² 1891: 140, 1901: 174, 1941: 207 |
1941: 1.26 million | 25 K, 1600 I, 10 G | Secession of Suket approx. 1290. New capital and renaming in 1527. Under Gurkha rule 1803–15. Then under the superintendent of the Hill States. 1839 invasion of the Sikhs. Raja Balbir Sain submitted to the British in February 1846, who installed him as ruler in October. |
|
|
Maharaja, 9 | 10989 km² 1901: 610 |
|||
|
|
Thakur Sahib, 11 | 2118 km² (1943: 2430 km²) 1891: 90, 1941: 123, 1943: 154 |
1891: 80000, 1941: 580000 | 121 K, 1155 I, 7 G | Post sovereignty with own stamps 1931–35. |
|
|
Raja, 9 | 949 km² 1941: 63 |
1935–40: ø 318,000 | The oldest surviving Marathas state. | |
|
|
Maharaja, 21 | 158,400 km² 1901: 5.5 million, 1941: 6.56 million |
Tribute: 35 million, from 1926: 25 million | 1173 K, 3425 I, 21 G (see Imperial Service Corps ) | See also: Hyder Ali and Tipu Sultan . Under direct British control since 1831. Reconstituted in 1868, but under the Court of Wards until 1881 because the adopted Raja was a minor . Massive famine in 1877/78. In 1881, Coorg, occupied in 1834, was split off again. No coin shelf. Arms imports, employment of foreigners in the civil service and changes in the law (!) Required British approval. Progressive administration, considered to be on par with Italy in the 1930s. |
|
|
Raja (from 1911: Maharaja), 11 | 2394 km² 1891: 261, 1901: 297, 1911: 248 (51% Hindus), 1931: 288 |
1911: 1.7 million, 1941: 2.3 | 366 K, 1253 I, 18 G | Founded in 1652. Expansion under Jaswat Singh (r. 1783–1840). Protectorate 1809. Own coins still in 1846. Post as convention state with overprint marks. 14 smaller non-contiguous areas. Backward, no paved road until 1924, but railroad. |
|
|
Raja, 9 | 1161 km² 1891: 79 (10% tribals), 1941: 75 |
1891: 72,400 Rs., 1941: almost 300,000 | 6 K, 116 I, 4 G | Gegr. 1344 as Unchehara . 1809 protectorate. Loyal in 1857, for a district gain of territory; until 1865 under compulsory administration due to indebtedness. |
|
|
Raja, 11th | 1607 km² 1891: 112, 1941: 114 |
1941: 950000 | 318 K, 450 K, 16 G | The domain founded by the Diwan of Rajgarh in 1681 was recognized as a state in 1872. From October 1929 abolition of child marriage, forced labor ( begar ) and the divan, which was replaced by an executive committee with specialist ministers. |
|
|
Jam Sahib, Jan. | 9780 km² 1891: 316, 1941: 409 |
1941: 9.7 million | 191 K, 3060 I, 117 G. | 1812 submission. |
|
|
Maharaja, 17 (local: 19) | 5366 km² 1891: 311, 1911: 321 |
1945: approx. 150,000 | 50 K, 4400 I, 90 | Gegr. 1532 by Rudra Pratap. Protectorate 1812. Additional titles from 1882: Sawai Mahendra Maharaja and Saramad-i-Rajaha-i-Bundelkhand. Post sovereignty until 1939. Coin shelf, but no coinage. |
|
|
Diwan (from 1910: Nawab Sahib), 11 | 8127 km² 1891: 236, 1901: 223 |
294 K, 697 I, 80 G. | Founded in 1594 by the originally Afghan Lohani dynasty, in 1947 in the 30th generation. Treaties with the British in 1809, 1813 and protectorate from 1817. Palanpur Agency 1819–1924. | |
| Palitana | Thakur, 9 | 745 km² 1891: 49, 1941: 62 |
1941: 821000 | 74 K, 401 I, 7 G | An important Jain sanctuary , Mount Satrunjaya , is located in the country. |
|
|
Raja (until 1869), Maharaja, 13 | 6625 km² 1891: 225, 1931: 212 |
1941: 1.16 million | 165 K, 1165 I, 36 G. | Gegr. 1732. Protectorate 1807. Loyal 1857. |
|
|
Maharaja, 15 | 1891: 3766, 1941: 2293 km² 1891: 79, 1941: 76 |
1941: 5500 | 327 K, 454 I, 4 G | Gegr. in the 16th century by Rawat Bhikaji, with the capital Deolia. Protectorate Treaty 1818. Population loss 1891–1901 (hunger and epidemics): 41% |
|
|
Maharaja Bahadur, 17 | 1891: 13980, 1941: 15330 km² 1891: 1.46 million (50% Hindus) |
2423 K, 4147 I, 109 G. | Gegr. 1761, protectorate 1809. Raja Bhupinder Singh was one of the most active opponents of the Federation in the negotiations for constitutional reform 1930-5 and one of the most autocratic Indian princes. See also: Patiala and East Punjab States Union . | |
|
|
Maharaja, 9 | 6192 km² 257 |
1941: 1.2 million | Protectorate 1803. | |
|
|
Rana, 11 | 1640 km² 1891: 71, 1941: 139 |
1941: approx. 2.5 million | 14 K, 236 I, 113 G | 1808 Agreement to fight pirates. In the following year British control of the three ports. The Raja was the second Indian ever to be granted an audience in the Vatican by Benedict XV. , Maharaja Natvarsinhji Bahadur led the Indian cricket team on its tour of England in 1932. |
|
|
Tondiman Raja, 11th | 1891: 3560, 1941: 3041 km² 1891: 302, 1901: 380, 1941: 401 |
16 K, 136 I, 27 G | Ancient state tradition that emerged from the Vijayanagara Empire. From 1350 under the Pallava dynasty. 1801 under British control, the Raja became a puppet, but remained at least nominally independent with the introduction of a permanent settlement in 1803 that fixed property taxes . The actually agreed tribute of one elephant per year was never delivered until the obligation was lifted in 1839. | |
| Radhanpur | Nawab Sahib, 11th | 2967 km² (1943: 5201 km²) 1941: 70 (173 villages), 1943: 100644 |
1941: approx. 800,000 | Babi dynasty ruled from the time of Humayun. Didn't pay tribute but received Rs. 1712 from 18 surrounding villages. 1943 Connection of numerous miniature states. | |
|
|
Rawat (1871–80: Nawab, 1886: Raja), 11 | 1891: 1690, 1941: 2481 km², 1891: 118, 1941: 135 |
1941: 100000 | 300 K, 360 I, 6 G | 1681 emerged from the division of Umatwara into Rajgarh and Narsinghgarh. Part of the Bhopawar Agency, later Kathiawar Agency. The Raja converted to Islam in 1871. The capital (24 ° 1 'N. 76 ° 44' E) is not to be confused with the homonymous (27 ° 14 ', 76 ° 38' E) Alwar resp. Bikaner (28 ° 39 'N, 75 ° 24' E). |
|
|
Thakur Sahib, 9 | 1891: 727 km² 1872: 36.770, 1881: 46, 1891 and 1901: 50, 1941: 75 |
1891: approx. 300,000, tribute 21,321 Rs. | 40 K, 310 I, 8 G | 1807 protectorate. At the suggestion of Colonel Richard Harte Keatinge , VC (1825-1904), the Rajkumar College for the princely sons of the Bombay Presidency was founded in the main town in 1870 . |
|
|
Raja, 11 (later 13) | 3914 km² 1872: 120, 1881: 114, 1891 and 1901: 171, 1941: 206 |
Tribute to Baroda from 1823: Rs 50001; 1941: approx. 250,000 | 77 K, 443 I, 23 G (1904: 111 total + 239 police) | Gohel dynasty since 1470. Submission in October 1821, after a dispute about the successor. Main town Nandod . Rewa Kantha Agency . 1884–97 under compulsory administration due to mismanagement. Own post until 1886. Badly affected by famine in 1896-8 and 1899-1902. |
|
|
Nawab (from 1737), 13 | 2427 km² 1872: 507, 1881: 541, 1891: 551, 1901: 533 |
1903: 3.5 million (of which 1.9 property tax) | 598 K, 2417 I, 28 G. | Founded as Aonla in 1719, later called Rohilkhand . British interventions in 1774 (transfer of the capital to Rampur) and 1794. Vassal in 1801, loyal in 1857 with subsequent enlargement of territory. Central India Agency, from 1936 Gwalior Agency. The capital Rampur City (28 ° 49 'N, 79 ° 2' E) should not be confused with the capital of the same name in the Bengali dwarf state of Rairakhol , which in 1901 had 1,400 inhabitants. |
|
|
Raja Maharaja (1921), 13 | 1880 (? 2300) km² 1881: 87, 1891: 89, 1901: 83 (16% Bhils); 1941: 107 |
1903: approx 50,000 (plus 67,000 inches, 34,000 tributes) | 134 K, 246 I, 13 G (of which 1903 5 usable) | Founded in 1652 under Ratan Singh, Protectorate on Jan. 5, 1819. Malwa Agency. Boundary and area unclear as it is closely interwoven with Sailana. Between 1902-4, around 2000 plague deaths annually The currency until 1897 was the Bahm Shahi rupee, minted in Partabgarh, own copper coins. |
|
|
Maharaja, 17 | 33540 km² 1891: 1.5 million, 1901: 1.32 (12% Gond, 15% Kol ), 1941: 1.59 |
1902: 290,000 (including 135,000 property tax), 1941: 6 million | 691 K, 3135 I, 55 G | Gegr. by Bilagar Deo (= Biag Deo) around 1057. Protection treaties 1812 and 1813. Coal and lime mining. In the rural district of Theonthai, the population decrease due to famine in 1891–1901 was 41%. Bagga shahi copper coins (56 = 1 R) were minted in the 19th century . |
|
|
Nawab, Jan. | 108 km² 1891: 19 (in 21 villages), 1941: 22 |
1891: 200000, 1941: 397000 | 5 K, 52 I, 4 G (60 police officers) | Dynasty (Habshi Sidis of Danda-Rajapur and Janjira ) descendants of Muslim Abyssinian sailors in the service of Aurangzeb . The founding date (sidelines of Janjira) is 6 June 1791. Fragmented territory mainly in the Surat district; Protectorate 1813, Surat Agency. 1835–64 under direct British administration. "Capital" Sachin (21 ° 4 'N, 72 ° 59' E) 1901: 997 inhabitants. The Raja was against the Federation in 1931. |
|
|
Raja, 11th | 291 km² 1891: 29 (¼ tribals), 1941: 35 |
1941: 300000 | 21 K, 152 I, 3 G | Gegr. by Jai Singh 1730. British guards 1819 who bore the Sindh tribute of Rs 46,000 since 1860. Territory closely intertwined with Ratlam, from which it secessionized. |
| Samthar | Raja, 11th | 459 km² 1881: 39, 1891: 41, 1901: 33 (−17% starvation), 1941: 33 |
1891: 150,000, 1941: 350,000 (of which 200,000 from ceded lands) | 290 K, 2275 I, 46 G (1903 Life Guard 12 K, 40 I) | Secession from Dattia at the end of the 18th century. Alliance rejected in 1804; Recognized as a separate state by the British in 1817 after submission. Raja as chief judge, executive in the hands of a vizier. First land surveys in 1855/7 and 1860-2. Until around 1873 currency based on the Nana Shahi rupee was struck in Jhansi and Datia. Railway line from 1888. Saltpetre extraction. |
|
|
Raja, 9 | 2930 km² 1941: 258 |
1941: 160,000 | State railway from Sangli to Miraj , just under 10 km. At the beginning of the 20th century, a constitutional monarchy with a four-person cabinet and legislative assembly. | |
|
|
Maharaja, 9 | 1016 km² 1941: 84 |
1941: 436,000 | ||
|
|
Sir Desai, 9th | 2386 km² 1872: 191, 1881: 192, 1901: 217 |
1903: 430,000 | 12 K, 400 I, 34 G (1904 total 324 men, 1 British officer) | Part of Bijapur from around 1450 . 1554 first independent under Mang Savant, finally under Khem Savant Bhonsla (r. 1627–40). Territorial gains in the 17th century. The friendship treaty signed in 1730 was the first to be signed with a Marathi prince. Succession battles 1803-12, in which pirates made use of the ports. Port of Vengrula ceded to the British in 1812, Protectorate 1819. From 1838 to 1861 under direct administration. According to surveying, the property tax revenue rose from 180,000 to 270,000 Rs in 1895-7. Main town Wari (= Vari). |
|
|
Rajahiraja, 9 | 1045 km² 1941: 54 |
1941: 381,000 | The state was established in 1706 and after the Marath Wars, Shahpura became a British protectorate. On March 25, 1948, Rajasthan joined the Union, and on April 7, 1949, it joined India. From 1914 to 1948 Shahpura maintained a state post. Initially, very simply designed postage stamps were issued, but from 1932 fiscal stamps could be used for franking. | |
|
|
Maharaja, 15 | 7107 km² 1891: 30, 1951: 161 |
approx. 5000 militia men | Occupied for the first time by British forces in the war against Nepal in 1814 (expulsion of the Gurkhas). 1835 cession of the Darjeeling region for Rs 3000 annual pension for the Raja. 1890 British-Chinese agreement that established a protectorate. No military protection agreed. Political agent on site since the Tibet expedition of 1904 . Capital Gangtok . Massive immigration of Nepalese in the 20th century, who made the indigenous Lepchas and Bhutias a minority. Annexed by India in 1975. | |
| Sirmur (= Sirmaur, Sirmour) | Raja (Maharaja 1918), 13 | 2700 km² 1891: 112, 1901: 135, 1941: 148 |
1901: 600,000, 1935–40: ø 867,000 | 100 K, 408 I, 10 G | New capital Sirmur, founded as Nahan in 1095, 1621. Occupied by Nepalese 1803-15, after its expedition by Sir David Ochterlony's expedition, protectorate as part of the Shimla Hills (Ambala Division). The regiment of the 2nd King Edward VII's Own Gurkha Rifles was known as the Sirmoor Rifles . Own mail until December 31, 1901. |
|
|
Maharaoh, 15 | 7791 km² 1891: 142, 1941: 216 |
199 K, 532 I, 8 G | In the country is the sacred mountain of the Rajputs, Mount Abu . There assignment of territory in 1845 for a sanatorium of the colonial army . Hunger-related population loss 17.79%. The state was a center of the non-cooperation campaign of 1921/22, which found many supporters, especially among the Bhils. Divided in 1951. | |
|
|
Raja, 11th | 521 km² 1941: 28 |
1941: 271000 | ||
| Sonepur (Orissa) | Maharaja, 9 | 2347 km² |
|||
|
|
Raja, 11th | 1011 (? 1083) km² 52 |
1912: 30,000 Rs. | 12 K, 12 I, 4 G | State tradition since 765th Dynasty, according to legend, descended from the Pandavas of Mahabharata . Historically from the Bengali Sena. First contract after the Nepal War in 1815 . Under British protectorate since Oct. 24, 1846. The treaty (as well as that of Chamba and Mandi) expressly forbids ceding of territory, killing of newborns, slave trade and the burning of widows or lepers. |
| Sunth | Raja, 9 | 1016 km² 59 |
1872: 22,000, of which 6,108 tribute | 98 K, 226 I, 4 G | Named after the conqueror in 1055. The British fought back an invasion of Sind in 1819 and took the country under protection. |
|
|
Raja, 11th | 1891: 10784, 1941: 11610 km² 1891: 199, 1941: 470 |
1941: 1.85 million | Capital Narendnagar | |
|
|
Nawab, 17th | 6473 km² 1891: 338, 1941: 317 |
1941: 2.1 million | 510 C, 2081 I, 77 G. | Exclave within the Central India Agency. |
|
|
Maharaja, 19 | 1891: 17363, 1901: 18295, 1941: 19642 km² 1891: 2.4 million (20% Christians); 1901: 2.9 million, 1931: 5.1 million |
for defense from 1805: 800000; 1941: 26.8 million | 61 K, 1442 I, 6 G | First friendship treaty in 1723, extended in 1795; Protectorate in 1805, which led to the Velu Thampi Dalawa rebellion , which was crushed in 1809. Two-chamber parliament since 1932. In 1938 the Travancore State Congress was founded, which carried the politics of the Congress into the state and dominated as a party until 1956. Coin shelf with own embossing (made by the British from 1873) until 1948. Currency: 16 cash = 1 chukram , 1 row = 28 chukram. Post sovereignty until 1948, then stamp issues until 1950 after the merger with Cochin . |
|
|
Maharana, 19th | 32743 (without vassals) km² 1891 (with vassals): 1.49 million, 1901: 1.02 (deaths over 40%), 1931: 1.56 |
1941: 6.5 million | 5560 K, 19344 I, 464 G From 1881 the income from Mewar Merwara was completely ceded to the British to cover defense costs (50,000 Rs for Bhil Corps, 16,000 Rs for Merwara Corps). |
Major vassals: Chani, Jawas, Jura, Madri, Oghna, Panarwa, Para, Patia, Sarwan and Thana. Supported the British in the Maratha War in 1803 , but requests for protection in 1805 were rejected. British protectorate only on January 13, 1818, with far-reaching defense obligations. Political control through the Mewar Residency , which included Udaipur, Banswara, Dungarpur and Partabgarh. Focus on nationalist agitation in the 1920s. Coin shelf, from 1851 own mints with the inscription (in Nagari ) Dosti Landan (“Friend of London”) and on the lapel Chitrakuta Udaipur. Mintings took place in Calcutta from 1932. |
| Vizianagram (Vizagapatam, Madras) | Maharaja (from 1890), "Durbar Salut" since 1876 |
1901: 2.9 million |
Location of one of the first British trading posts. Actually part of the Madras presidency. Other titles of the ruler from the Mughal period : Maharaja Sahiba Meharban Mushpaku, Kadaradan Karampharmayi Mokhalesan Maharaja Mitza, Manya Sultan Garu Bahadur. The Raja, under British influence since 1757, was a large landowner ( Zamindar ) in other states as well. Manganese mining since 1891. | ||
|
|
Thakur Sahib, 9 | 609 km² 1881: 43, 1891: 42, 1901: 35 (−18%) |
1901: 375,000, including 28,692 tribute | 49 K, 280 I, 9 G; 1901: 163, of which 39 K | Main town Wadhwan (22 ° 42 'N, 71 ° 44' E) and 31 villages. Not to be confused with the dwarf state in the Dangs . Own post and stamps until 1893. |
|
|
Raj Sahib, 9 (11) | 1068 km² 1891: 30, 1931: 44 |
1941: 727000 | 73 K, 312 I, 15 G |
Other persons entitled to salute
- The Aga Khan , as head of the Ismaili Muslims: 11
Some heads of dynasties whose countries had become part of British India, the so-called political pensioners, were given the right to a personal salute on site:
- Nawab of Murshidabad , formerly ruler of Greater Bengal, about today's Bangladesh, Bihar, Orissa and West Bengal: 19
- Nawab of Arkot until the state was re-established as a principality
- Zamindar of Manyam (French India): 4
In 1966, Pakistani President Muhammed Ayub Khan saluted the following rulers:
In Hadramaut (South Arabia) the rulers:
-
 Sultanate of Shihr and Mukalla (11 rounds since 1903)
Sultanate of Shihr and Mukalla (11 rounds since 1903) -
 The " Kathiri State of Seiyun"
The " Kathiri State of Seiyun"
The rulers of five of the seven sheikdoms of Trucial Oman in the Arabian Peninsula, administratively managed as part of the Bombay Presidency, then part of the Persian Gulf Residency until 1937 , had the right to a three shot salute. The goods:
Groupings
The British controlled the princes with residents (for larger countries) and agencies ( agencies ), smaller groups of countries. The respective British “advisors” had the last word in case of doubt and did not hesitate to bring rulers who were too independent to reason.
Subordinate directly to the viceroy:
- Hyderabad
- Mysore
- the Gujarat and Baroda Agency. It was merged in 1944 with the Western India States Agency created in 1924 to form the Baroda, Western India and Gujarat States Agency .
- Kashmir and Jammu
- Gwalior, spun off from the Central India Agency in 1921 .
- Baluchistan Agency, consisted of three states: Kalat (with Makran) as well as Kharan and Las Bela.
- Rajputana Agency (main town Mt. Abu ) with 21 countries was divided into four agencies. It originally consisted of 18 states and 2 domains. (Initially it was divided into six smaller agencies and three residencies):
-
Central India Agency (since 1854) under one agent had 97 countries under it, divided into:
- Central India Agency # Bundelkhand Agency (until 1931)
- Central India Agency # Bagelkhand Agency (1871–1931) with: Rewa (1931 in Indore), Maihar, Nagode, Sohawal, Jaso, Kothi, Baraunda, Paldeo, Kamta-Rajaula, Taraon, Pahra, Bhaisaunda
- Indore Residency
- Gwalior Residency (1886-1921)
- Madras States, of which there were five, namely Banganapalle, Cochin, Pudukkottai, Sandur, and Travancore. Until October 1, 1923 they were under the governor of Madras.
- Western India States Agency formed in 1924 from the Kathiawar, Kutch and Palanpur Agencies. Kathiawar now comprised only 134 tiny states.
- United Deccan States : Akalkot, Aundh, Bhor, Jamkhandi, Jath, Kuraundvad Senior, Kuraundvad Junior, Miraj Senior and Junior, Mudhol, Phaltan, Ramdurg, Sangli, Savantvadi, Savanur and Wadi, and two others.
-
Chota Nagpur States and Orissa Tributary States were merged to form the Eastern States Agency , created in 1933 , which became the Eastern States Union in 1947 :
- Later Orissa states Gangpur, Bonai, Mayurbhanj were (until 1 January 1949), Bamra, Keonjhar, rairakhol, Sonpur, Athmallik, Pal Lahara, Talcher, Patna, Boudh, Dhenkanal, indole, Daspalla, Narasinghapur, Barhamba, Athgarh , Tigiria, Nayagarh, Ranpur and Kalahandi
- In May 1948 to Bihar: Kharsawan and Sareikella
- Chang Bhakar, Korea, Surguja, Jashpur, Udaipur, Raigarh, Sarangarh, Kawardha, Khairagarh, Nandgaon, Kanker and Bastar became part of Madhya Pradesh .
- United Provinces of Agra and Oudh with three countries, including the Bhopal Agency (1818–1947).
- Punjab States Agency had 13 states as of 1929
Cooch Behar and Tripura were under the governor-general from 1922, before they had been administered by Bengal. The North-West Frontier Agencies were placed under the political supervision of the respective district commissioners as tribal areas. Sikkim officially enjoyed full British protection from 1917.
Checked by local authorities from:
- Governor of Assam: Manipur and 24 minor chiefdoms of the Khasia and Jaintia Hills.
- Governor of Punjab, represented by the district administrator for Ambala: Dujana, Kalsi and Pataudi. From the original 18 Shimla Hill States , the Punjab States Agency was created in 1901 , after enlargement renamed the Punjab Hill States Agency in 1936 .
In addition to the ones mentioned, the following administrative units existed, which were dissolved or renamed as part of administrative restructuring:
- Malwa Agency founded in 1895: Jaora, Ratlam, Sitamau, Sailana, and parts of Gwalior, Tonk, Indore. 1925 merged with the Bhopawar Agency (larger states: Bakhatgarh, Barwani, Dhar, Ali Rajpur, Jhabua, Jobat, Mathwar, Kathiwara, Ratanmal) to form the Malwa and Southern States Agency . Renamed back to Malwa Agency soon afterwards .
- Gilgit Agency , from 1877
- Kathiawar Agency (until 1924) on the peninsula of the same name comprised 193 mostly very small states, 14 of which had the right to their own jurisdiction. The famine years 1891–1902 led to a population loss of at least 15%.
- Mahi Kantha Agency (until 1924) with Idar, Dedhrota, Derol, Pal, Danta, Malpur, Mansa, Mohanpur, Varsora, Pethapur, Ranasan, Punadra, Khadal, Ghorasar, Katosan, Maguna, Palej, Virsoda, Ilol, Amliyara, Satlasana, Sathamba, Moyad, Vagpur, etc. a. In 1891–1901 the population fell by 41%.
- North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA), formerly called North-East Frontier Tracts and today forms the state of Arunachal Pradesh .
- 61 mostly small states belonged to the Rewa Kantha Agency , the largest being Rajpipla.
See also
Large territorial states, without salute authorization:
literature
- Archibald Adams: The Western Rajputana States. A Medico-Topographical and General Account Of Marwar, Sirohi, Jaisalmir. Junior Army & Navy Stores, London 1899, Text Archive - Internet Archive .
- Directorate of the Chamber's Special Organization: The British Crown & the Indian States. An Outline Sketch Drawn up on Behalf of the Standing Committee of the Chamber Of Princes. King, London 1929.
- Jagdish C. Dua: Illustrated Encyclopaedia & Who's Who of Princely States in Indian Sub-Continent. Kaveri Books, New Delhi 2000, ISBN 81-7479-036-5 .
- The Fifth Report from the Select Committee on the affairs of the East India Company. 1812, Calcutta 1837, ( digitized version ).
- Thomas H. Holland (Ed.): Provincial Geographies of India. 4 volumes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1913-1923.
- William Lee-Warner: The Native States of India; Macmillan and Co., London 1910, Text Archive - Internet Archive .
- Roper Lethbridge: The Golden Book of India. A Genealogical and Biographical Dictionary of the Ruling Princes, Chiefs, Nobles, and other Personages, titled or decorated of the Indian Empire. Macmillan and Co., London 1893, Text Archive - Internet Archive .
- Vanaja Rangaswami: The Story of Integration. A New Interpretation in the Context of the Democratic Movements in the Princely States of Mysore, Travancore and Cochin, 1900-1947. Manohar, New Delhi 1981, (Also: Delhi, University, Dissertation, 1978: The Democratic Movement in the British Indian States of Mysore, Travancore, and Cochin, 1900–1948. ).
- John Sutherland: Sketches of the Relations Subsisting Between the British Government in India and the Different Native States. Huttmann, Calcutta 1837, Textarchiv - Internet Archive .
swell
The 1891 census data were taken as a basis for area and population, because this was the first in the modern methodology. Statistical data on the individual countries in the sources nevertheless differ greatly from one another in some cases. Where numbers for 1891 were not available, numbers from 1901 were used. The intervening decade was the time of the greatest famine in Indian history. In individual districts, the population loss was 60-70%. In the Deccan and the West in particular, it was not until the 1930s that the level of 1891 was reached again. The information for 1931/41 comes from Dua (2000), who reprinted a work published around 1942 without citing the source.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c lt. Golden Book of India; 1893
- ↑ a b c Michel stamp catalog Europa-Übersee . Leipzig 1934, pp. 1102-1139
- ↑ texts
- ↑ 39 & 40 Vict., C. 10. cf. [: en: Royal Titles Act 1876]
- ↑ a b conversion factor 2.58. According to Golden Book, 1893, not always reliable due to a lack of sufficient cadastral data
- ↑ 1891 census, or 1901. additionally different years of the Imperial Gazetteer
- ↑ a b or tribute, payable to the British. "For defense" means payable to the British for troops, not the cost of their own troops.
- ↑ a b Status 1891: K = cavalry, I = infantry, G = guns. (Own troops, mostly only body or honor guard, of the Rajas). Most of the guns were muzzle-loaders and were obsolete by 1900. according to the Golden Book of India; 1893
- ↑ a b c d e Parmeshwari Lal Gupta: Coins . 4th edition. New Delhi 2000, ISBN 81-237-1887-X ; Cape. "Princely States"
- ↑ by the Pakistani President
- ↑ with vassal state Kusalgarh
- ↑ splintered but larger than the Kingdom of Württemberg
- ↑ a b c d e f g Statistics shows an increase in 1891-1901 only because in 1901 the tribals not counted before were also counted . Real population decrease (starved!) Approx. 20%. Census of India, Vol.XXV (Rajputana Reports)
- ↑ Geography of India (1909) gives only 101,000 inhabitants for 1901.
- ↑ John Malcolm in the English language Wikipedia
- ↑ Including Berar . That is more than three times the size of the Kingdom of Bavaria , or slightly larger than the FRG (1949–1989).
- ↑ About 1½ million starved to death in 1899/01 alone. Imperial Gazetteers of India - Provincial Series: Hyderabad State; Calcutta 1909, p. 49.
- ↑ on obligations in detail: British Crown & the Indian States (1929), p. 227ff.
- ↑ on this (1903): 2988 European and 5549 Indian occupation troops. Gazetteers (1909), p. 70.
- ↑ cf. Bawa Satinder Singh; Raja Gulab Singh's Role in the First Anglo-Sikh War; Modern Asian Studies, Vol. 5, No. 1 (1971), pp. 35-59
- ^ New Cambridge History of India; Indian Princes and their states, chap. 5 "Princes as Men ..."
- ^ Native States (1875), pp. 85-88.
- ↑ Chakrabarti, Jadab Chandra; The Native States of India; London 1896
- ↑ cf. Stuart Cary Welch (Ed.); The legitimation of kingly authority in Kotah. Gods, Kings and Tigers: The Art of Kotah; Munich 1997
- ↑ 1891 census, or 1901. additionally different years of the Imperial Gazetteer (*)
- ↑ British Crown & the Indian States (1929), pp. 77-82.
- ↑ Biography of the Rajas (1930s): Satadru Sen; The Loyal Insurgency: Empire, Identity and KS Ranjitsinhji; Manchester 2004
- ↑ cf. Imperial Gazetteer of India; Vol. XXV (Sa-Si) 1908, pp. 365-370.
- ↑ a b C. SK Singh; Bhils' Participation in Politics in Rajasthan in the 1920's; Social Scientist, Vol. 13, No. 4 (Apr. 1985), pp. 31-43
- ↑ Lee-Warner (1910), p. 142.
- ↑ cf. Reginald H. Hooker: Modes of Census-Taking in the British Dominions . In: Journal of the Royal Statistical Society , Vol. 57, No. 2 (Jun., 1894), pp. 298-368
- ↑ cf. FC Danvers: A Review of Indian Statistics . In: Journal of the Royal Statistical Society , Vol. 64, No. 1 (Mar., 1901), pp. 31-72
- ↑ Full texts of the census data partly on archive.org