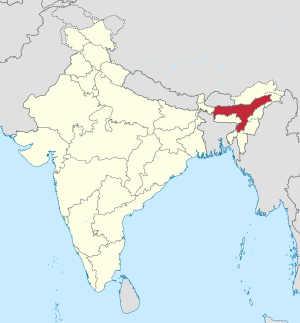
Assam
| status | State |
| Capital | Dispur |
| surface | 78,438 km² |
| Residents | 31,169,272 (2011) |
| Population density | 397 inhabitants per km² |
| languages | Asamiya ; Bengali , Bodo (associated official languages at regional level) |
| governor | Jagdish Mukhi |
| Chief Minister | Sarbananda Sonowal ( BJP ) (since 2016) |
| Website | assam.gov.in |
| ISO code | IN-AS |
Assam ( Assamese : অসম [ ɔxɔm ], Asam ) is an Indian state with an area of 78,438 km² and 31.2 million inhabitants (2011 census). The capital and seat of government is Dispur , a suburb of Guwahati , the largest city in the state. The main languages spoken are Assamese (Asamiya) and Bengali (Bengali) in addition to numerous small languages of the Tibetan-Burmese language family.
geography
Position and extent
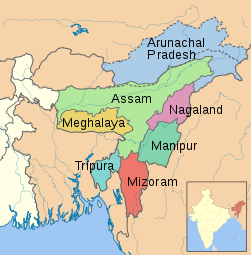
Assam is located in northeast India and is one of the so-called seven sister states , which are only connected to the rest of the country by a narrow corridor. Neighboring states are Arunachal Pradesh in the northeast, Nagaland and Manipur in the east, Mizoram , Tripura and Meghalaya in the south and West Bengal in the west. In the northwest is the state border with Bhutan , in the southwest and south Assam has two border sections with Bangladesh . The area of the state is 78,512 square kilometers. It occupies a middle position among the states of India and is about the size of the Czech Republic .
Most of Assam belongs to the Brahmaputra river valley , which lies between the Himalayas in the north and the mountains of Meghalaya , North Cachar and Nagaland in the south. The Brahmaputra has its source in Tibet and, after having crossed the Himalayas in a deep gorge, enters the Assam river plain. Here it reaches a width of ten kilometers in places. The Brahmaputra Valley is about 1000 kilometers long and 80 to 100 kilometers wide. In the south of Assam are the Bareil Mountains and beyond them the Barak Valley . The 40 to 50 kilometer wide river valley of the Barak is isolated from the rest of Assam by the mountains and is geographically a continuation of the river plains of East Bengal .
Cities
By far the largest city of Assam is Guwahati (formerly Gauhati) with a good 960,000 inhabitants (2001 census). The capital of Assam is Dispur , a suburb of Guwahati.
(Status: 2011 census)
| city | Residents | city | Residents | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Guwahati | 962.334 | 8th | Bongaigaon | 67,322 |
| 2 | Silchar | 178,865 | 9 | Dhubri | 63,388 |
| 3 | Dibrugarh | 145,488 | 10 | Diphu | 61,797 |
| 4th | Jorhat | 126,736 | 11 | North Lakhimpur | 59,814 |
| 5 | Nagaon | 121,628 | 12 | Karimganj | 56,854 |
| 6th | Tinsukia | 116,322 | 13 | Goalpara | 53,430 |
| 7th | Tezpur | 75,540 | 14th | Sivasagar | 50,781 |
population
Demographics

According to the 2011 Indian census, Assam has 31,169,272 inhabitants. Between 2001 and 2011 the population increased by 16.9 percent. The growth rate thus corresponds to the average for India of 17.6 percent in the same period. The population density of Assam is 397 inhabitants per square kilometer, which is close to the overall Indian average of 382 inhabitants per square kilometer. A large part of the population is concentrated in rural areas: only 14.1 percent of Assam's population live in cities. The degree of urbanization is thus significantly lower than the national average of 31.2 percent. With a literacy rate of 73.2 percent, Assam ranks in the middle of the Indian states and is close to the mean value for India (74.0 percent). In the period from 2010 to 2014, the average life expectancy was 63.9 years (the Indian average was 67.9 years). The fertility rate was 2.17 children per woman (as of 2016) while the Indian average was 2.23 children in the same year.
A not inconsiderable minority of the population of Assam belong to a number of indigenous peoples. Although they mainly differ in less linguistic-cultural in economic and social terms of the majority population, these ethnic groups are often called " tribal peoples " ( tribals called). The 2001 Indian census classified 12.4 percent of the population as scheduled tribes . The largest group is formed by the Bodo , who settle in the plains of the lower Brahmaputra valley in western Assam and make up around 40 percent of the tribal population of Assam. The remaining tribal peoples live in the mountainous areas to the east and south of Assam. The largest of these are the Miri , Mikir , Rabha , Kachari , Lalung , Dimasa and Deori . The two districts Dima Hasao and Karbi Anglong , in which the tribal people make up the majority of the population, and the Bodo areas ( Bodoland ) have an autonomous status.
A large number of immigrants from other parts of India and from Bangladesh live in Assam . Above all, the illegal immigration of Muslim Bengali from Bangladesh has led to an increasing degree of xenophobia among the long-established population of Assam, who fear foreign infiltration and the creeping Islamization of Assam. This conflict has repeatedly expressed itself in severe pogroms against Muslim Bengali.
Population development
Assam census population (within today's boundaries) since the first Indian census in 1951.
| Census year | population |
|---|---|
| 1951 | 8,029,100 |
| 1961 | 10,837,700 |
| 1971 | 14.625.157 |
| 1981 | 18,041,250 |
| 1991 | 22,414,320 |
| 2001 | 26,638,600 |
| 2011 | 31.169.272 |
languages
| Languages in Assam | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| language | percent | |||
| Assamese | 48.38% | |||
| Bengali | 28.92% | |||
| Hindi | 6.73% | |||
| Bodo | 4.54% | |||
| Sadan / Sadri | 2.29% | |||
| Miri / Mishing | 1.98% | |||
| Nepali | 1.91% | |||
| Karbi (Mikir) | 1.64% | |||
| Other | 3.61% | |||
| Distribution of languages (2011 census) Language families: |
||||
In much of what is now the state, Assamese is the native language of the population. This is especially true for the valley areas. Part of the state originally belonged to the British province of Bengal. After independence, a small part of the Bengali-speaking area remained with Assam. However, many speakers of Bengali are immigrants from Bangladesh. In the mountain regions of Assam there are numerous peoples who mostly use a Tibetan-Burman language. Assamese, Bengali and speakers of Tibetan Burman languages are therefore regionally the mother tongue of the local residents.
The official language of Assam is Assamese . Assamese is one of the Indo-Aryan languages and is thus related to the languages of northern India and also distantly to most of the languages spoken in Europe. Of the Indo-Aryan languages, Assamese has penetrated the furthest east. It is spoken as a mother tongue by half of Assam's residents.
Bengali (28 percent), Hindi (6 percent) and Nepali (2 percent) are particularly widespread among the immigrant population . Bengali is also the traditional majority language in the Barak Valley, which has historically and culturally strong affinities to East Bengal. In the three districts there, Cachar , Karimganj and Hailakandi , it has a status as an associated official language alongside Assamese.
The tribal people of Assam speak a variety of languages, most of which belong to the Tibetan-Burmese language family. The largest of these languages is the Bodo , the language of the ethnic group of the same name. It is spoken by 5 percent of the population of Assam as their mother tongue and is an associated official language in the Bodo areas alongside Assamese. The tribal peoples of eastern Assam speak a variety of smaller Tibetan Burmese languages. The most important are Miri , Karbi , Garo , Rabha and Dimasa . The historically significant Ahom language , which served as court and literary language in the Ahom empire, has been extinct since the 19th century, but small Tai languages are still spoken in parts of Assam .
Religions
The majority of Assam's residents are Hindus . According to the 2011 census, they make up 62 percent of the state's population. Their share is thus lower than the Indian average. On the other hand there is a large minority of Muslims . With 34 percent, Assam has the highest Muslim population of all Indian states, after the union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh . In several districts of Assam, Muslims make up the majority of the population. There is also a Christian minority of just under 4 percent. The Christian population is particularly high among the tribal peoples. In the Dima Hasao district, which is largely inhabited by indigenous peoples, over a quarter of the residents profess Christianity. The distribution to the individual religious communities is shown in the following table:
| year | Buddhists | Christians | Hindus | Jainas | Muslims | Sikhs | Other | not specified | Total | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| number | % | number | % | number | % | number | % | number | % | number | % | number | % | number | % | number | % | |
| 2011 | 54,993 | 0.18 | 1,165,867 | 3.74 | 19.180.759 | 61.47 | 25,949 | 0.08 | 10,679,345 | 34.22 | 20,372 | 0.07 | 27,118 | 0.09 | 50,873 | 0.16 | 31.169.272 | 100.00% |
| Source: 2011 census result | ||||||||||||||||||
history
Beginnings and Colonial History

Assam has been under the rule of the Ahom dynasty since 1228 . The Ahom were a conqueror people from the area of today's Thailand, who initially adhered to the Buddhist faith, but later, over the centuries, assimilated with the subjugated Assamese majority population, absorbed into it and adopted Hinduism. Due to its relatively remote location, Assam went through a different development from the rest of India. For example, the country was never under the rule of Muslim rulers and never belonged to the Mughal empire .
In 1826 the British East India Company took over Assam from the Burmese after the First Anglo-Burmese War . Administratively, the new area was annexed to the Bengal Presidency , which among other things also had the consequence that many British-Bengali officials and workers from all over India came to the country for the newly established tea plantations. Even before the British takeover, there had been recurring conflicts between the inhabitants of the Brahmaputra level ( 'plains people' ) and the inhabitants of the mountains ( 'hills people' ). The former were Hindus and spoke mostly Assamese, the latter belonged to Tibetan-Burmese tribal peoples who adhered to their local religions . Under British colonial rule, another level of ethno-religious conflict emerged - that between the autochthonous inhabitants of Assam (the Assamese and tribal peoples) and immigrants from other parts of India. Initially, the immigrants were predominantly Bengali Hindus, but later, increasingly, Bengali Muslims also immigrated to Assam. In 1874 the area was administratively separated from the Bengal Presidency and elevated to the status of a North-East Frontier Province. After the partition of Bengal in 1905 , it was again added to the newly created province of East Bengal . After the division had to be reversed due to the ongoing protests, the Assam province was re-created in 1911.
After independence

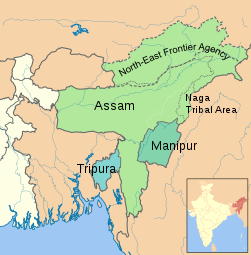
After the partition of India in the course of independence from the British in 1947, after a referendum on July 6, 1947, the Sylhet area, which previously belonged to the province of Assam, became part of the new East Pakistan . The rest of Assam joined the Indian Union and formed the state of Assam since 1950. Assam was a decidedly multi-ethnic state. The Assamese-speaking population was only about 60%. The constitution of the Republic of India , which came into force in 1950, provided for a special administration for the tribal areas in Assam. This was regulated in Appendix 6 ( 6th Schedule ) of the constitution. A distinction was made between “A” and “B” tribal areas ( Part A , Part B ). The A tribal areas were referred to as "autonomous districts", but had roughly the same status as the other districts of Assam and, for example, also elected members of the parliament of Assam and the all-India parliament in elections. The B tribal areas, which included the area of the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) and the Naga tribal area , were directly subordinate to the Governor of Assam as the representative of the Indian President and also had no parliamentary representation in an Indian parliament. In the constitution it was explicitly stated that the Indian central government should have the right to change the borders of the tribal areas at its own discretion, or, for example, to outsource individual tribal areas from Assam.
In the 1960s and 1970s, the Assamese government pursued a policy of "Assamization". The Assamese language should become the only state language and should be taught as the only language in schools and universities. Against this resistance arose from the other peoples of Assam. Little by little, large parts of the tribal areas of Assam were separated and elevated to union territories and later to separate federal states. In 1962 Nagaland (from Naga Tribal Area and Naga Hills district ), 1972/87 Arunachal Pradesh (from the NEFA area), 1972 Meghalaya (from Garo Hills and United Khasi & Jaintia Hills district ) and 1972/86 Mizoram ( from Lushai Hills district ). Another problem was that since the 1950s, Bengali from East Pakistan (from 1971 Bangladesh ) have been immigrating illegally across the green border to Assam. It is estimated that around 2 million Bangladeshis immigrated between 1950 and 1980. When it became known that many of these immigrants had also entered the electoral register illegally, the long-established Assamese and tribal peoples felt that they would soon become a minority in their own country. From 1979 to 1985 the so-called Assam Movement took place in the state , an ethnic-nationalist mass movement led by Assamese student organizations. The Assam movement boycotted elections, blocked the infrastructure, hindered the state organs and, in some cases, took violent action against the Muslim minority. There were thousands of deaths due to ethno-religious violence. The unrest took only their far-reaching end when in 1985 the Assam Agreement ( Assam accord ) between the leaders of Assam Movement and the Indian central government under Rajiv Gandhi was closed. The Assam movement turned into a political party ( Asom Gana Parishad ) and its leaders were promised the deportation of most of the illegally immigrated Bengali.
Due to the complicated ethnic conditions, Assam has been a reservoir for various separatist organizations for decades (see Separatist Organizations in Northeast India ). The Bodoland region has long been one of the main trouble spots .
- Territorial division of Northeast India since 1951
The state of Assam in 1951. The North-East Frontier Agency and the Naga Tribal Area had a special status, but were formally part of Assam (the territory claimed by the People's Republic of China)
The People's Republic of China claims most of the territory of the former North-East Frontier Agency , which until 1972 belonged to Assam (today's state of Arunachal Pradesh ). In 1962 Assam was directly affected by the Indo-Chinese border war . Chinese armed forces advanced as far as the banks of the Brahmaputra, but after a short time withdrew again across the border.
politics
Political system
The legislature of the state of Assam consists of a unicameral parliament , the Assam Legislative Assembly . The 126 members of parliament are elected by direct election every five years . 16 seats are reserved for members of the indigenous tribes population ( Scheduled Tribes ) and eight for members of disadvantaged castes ( Scheduled Castes ). The parliament has its seat in Dispur , a suburb of Guwahati . The Chief Minister of Assam is elected by Parliament. But is appointed by the President of India Governor (at the head of the State Governor ). Its main tasks are to appoint the Chief Minister and to entrust him with the formation of the government. Assam's highest court is the Gauhati High Court , based in Guwahati. In addition to Assam, his area of responsibility also includes the states of Arunachal Pradesh , Mizoram and Nagaland .
Assam has 14 members in the Lok Sabha , the lower house of the Indian parliament, and seven in the Rajya Sabha , the Indian upper house.
Parties
| Distribution of seats after the 2016 general election |
|
|---|---|
| BJP | 60 |
| INC | 26th |
| AGP | 14th |
| AIUDF | 13 |
| BPF | 12 |
| Independent | 1 |
| total | 126 |
For a long time, Assam's policy was shaped by the national congress party (INC) on the one hand and a number of regional parties on the other. The Congress Party has provided most of Assam's governments since independence. The most important regional party is the Asom Gana Parishad (AGP). The party has outgrown the Assam movement , which between 1979 and 1985 was partly violently directed against the immigration of mostly Muslim Bengalis to Assam. After the signing of an agreement with the Indian central government ended the agitation, the AGP was founded in 1985, which won the parliamentary elections in the same year and ruled the state until 1989 and again from 1996 to 2001. Since then, however, the AGP has lost much of its support and now only plays a marginal role. While the AGP represents xenophobic and Assamese nationalist positions, the All India United Democratic Front (AIUDF), founded in 2005, sees itself as representing the interests of Muslims and the other minorities of Assam. She has successfully managed to unite many Muslim voices. The third regional party, the Bodoland People's Front (BPF), on the other hand, emerged from the Bodoland movement, which advocates an autonomous status for the Bodo people .
In the local parliamentary elections in 2011, the Congress party, which had ruled since 2001, was re-elected for the second time. With 78 out of 126 seats in parliament, it won an absolute majority. The second strongest force was the AIUDF with 18 MPs, followed by the BPF with 12 seats and the AGP with ten seats. The supraregional Hindu nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) played only a subordinate role in Assam's parliament with five members. Also represented in parliament was the All India Trinamool Congress (AITC), a congress spin-off that has its base in neighboring West Bengal. There were also two independent MPs.
In the all-Indian parliamentary elections in 2014 , the BJP, which has not played a major role in the state, achieved a surprise success due to the favorable mood throughout the country in Assam: it won seven of 14 constituencies of Assam. Of the remaining constituencies, three each went to the Congress Party and the AIUDF and one to an independent candidate.
In the election to the federal state parliament in 2016, the BJP was able to continue its upward trend and with 29.5% of the vote won almost half of the parliamentary seats. In terms of share of the vote, the Congress party remained the strongest party (31.0%), but won only 26 of 125 constituency seats. On May 24, 2016, Sarbananda Sonowal was sworn in as the state's first chief minister to be a member of the BJP. He formed a coalition government made up of the BJP, AGP and BPF. However, the AGP left this coalition on January 7, 2019 due to differences of opinion about the planned amendment to the Citizenship Bill 2016 .
economy
With a per capita gross domestic product of 44,263 rupees (968 US dollars ) in 2015, Assam was ranked 26th out of 29 Indian states. Assam is one of the poorest and most underdeveloped states in India. Reasons for the underdevelopment are a remote inland location, poor infrastructure and regular political and social unrest. Agriculture is of particular economic importance to the state.
Between 2005 and 2006, 31.4% of the population was malnourished, the fourth highest rate among any Indian state.
Assam tea
Almost half of Indian tea production is produced in Assam. Assam is known for the strong, tart Assam tea . The largest contiguous tea cultivation fields in the world are located in the region. In German-speaking countries, Assam tea is known as the main component of East Frisian tea.
Administrative division
The state of Assam was divided into 27 districts in 2011 (population and population density according to the 2011 census). The five districts created in 2015 are Biswanath (formed from Sonitpur), Charaideo (formed from Sivasagar), Hojai (formed from Nagaon), South Salmara-Mankachar (formed from Dhubri) and West Karbi Anglong (formed from Karbi Anglong). Majuli (formed from Jorhat) was added in 2016 as the 33rd district and so far the newest.
| ISO 3166–2 abbreviations |
District | Administrative headquarters | Area (km²) |
Population (2011) |
Population density ( inhabitants / km² ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BK | Baksa | Mushalpur | 2.008 | 953.773 | 475 |
| BA | Barpeta | Barpeta | 2,679 | 1,693,190 | 632 |
| BS | Biswanath | Biswanath Chariali | 1,783 | 612.491 | 344 |
| BO | Bongaigaon | Bongaigaon | 1,724 | 732.639 | 425 |
| CA | Cachar | Silchar | 3,783 | 1,736,319 | 459 |
| CD | Charaideo | Sonari | 1,068 | 458.615 | 429 |
| CH | Chirang | Kajalgaon | 1,975 | 481.818 | 244 |
| THERE | Darrang | Mangaldai | 1,849 | 908.090 | 491 |
| DM | Dhemaji | Dhemaji | 3,230 | 688.077 | 213 |
| DB | Dhubri | Dhubri | 1,664 | 1,948,632 | 1,171 |
| DI | Dibrugarh | Dibrugarh | 3,378 | 1,327,748 | 393 |
| NC | Dima Hasao | Haflong | 4,853 | 213,529 | 44 |
| GP | Goalpara | Goalpara | 1,825 | 1,008,959 | 553 |
| GG | Golaghat | Golaghat | 3,506 | 1,058,674 | 302 |
| HA | Hailakandi | Hailakandi | 1,326 | 659.260 | 497 |
| HJ | Hojai | Hojai | 1,456 | 931.218 | 640 |
| JO | Jorhat | Jorhat | 2,849 | 1,091,295 | 383 |
| KR | Kamrup | Guwahati | 3,480 | 1,517,202 | 436 |
| KM | Kamrup Metropolitan | Guwahati | 627 | 1,260,419 | 2.010 |
| KA | Karbi Anglong | Diphu | 10,379 | 965.280 | 93 |
| KR | Karimganj | Karimganj | 1,808 | 1,217,002 | 673 |
| KK | Kokrajhar | Kokrajhar | 3,668 | 1,040,644 | 280 |
| LA | Lakhimpur | North Lakhimpur | 2,277 | 889.010 | 457 |
| Majuli | Garamur | 787 | 167,304 | 213 | |
| MA | Marigaon | Marigaon | 1,550 | 957.853 | 618 |
| NG | Nagaon | Nagaon | 3,975 | 2,826,006 | 711 |
| NL | Nalbari | Nalbari | 1.009 | 769.919 | 763 |
| SI | Sivasagar | Sivasagar | 2,669 | 1,150,253 | 431 |
| SO | Sonitpur | Tezpur | 5,277 | 1,925,975 | 365 |
| SM | South Salmara-Mankachar | Hatsingimari | 568 | 555.114 | 98 |
| TI | Tinsukia | Tinsukia | 3,795 | 1,316,948 | 347 |
| UD | Udalguri | Udalguri | 1,676 | 832.769 | 497 |
| WK | West Karbi Anglong | Hamren | 3,073 | 295,358 | 96 |
Attractions
The Kaziranga National Park , which was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1985, is located in Assam .
Web links
- Official website of the government of Assam
- Rajen Barua: On the Origins of the Names 'Oxom' and 'Assam'. (PDF; 93 kB)
Individual evidence
- ^ Government of India, National Commissioner Linguistic Minorities: 42nd Report, July 2003 to June 2004 ( Memento of February 20, 2009 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Assam (India): Districts & Cities - Population Statistics, Charts and Map. Retrieved December 29, 2018 .
- ^ Census of India 2001: Provisional Population Tables and Annexures ( Memento of January 10, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) and Provisional Population Totals - India - Rural-Urban Distribution. (PDF; 8.1 MB)
- ^ Indian States by Life Expectancy 2010-2014. Retrieved March 19, 2018 .
- ^ Fertility Rates. Retrieved March 19, 2018 .
- ↑ Census of India 2001: Assam. Data highlights: The Scheduled Tribes. (PDF; 39 kB)
- ^ Thomas Benedikter: North East India: Experimental field for regional autonomy. Northeast India's autonomous districts between minority protection and secession, suedasien.info, August 2, 2009.
- ^ Population of Indian States | Indian states population 1901-2011 - StatisticsTimes.com. Retrieved March 19, 2018 .
- ↑ Census of India 2011: Census of India, population by mother tongue .
- ↑ Stephen Morey: The Tai Languages of Assam, Canberra 2005.
- ↑ a b Assam Results Status. Indian Election Commission, accessed May 19, 2016 .
- ↑ Sandeep Phukan: For Sarbananda Sonowal's Oath, PM Modi And 14 Chief Ministers In Assam: 10 Facts. NDTV, May 24, 2016, accessed on May 25, 2016 .
- ↑ BJP loses another ally: Asom Gana Parishad quits NDA over Citizenship (Amendment) Bill, having threatened to do so in past. firstpost.com, January 7, 2019, accessed February 19, 2019 .
- ^ Comparing Indian States and Countries by GDP per capita - StatisticsTimes.com. Retrieved March 18, 2018 .
- ↑ International Institute for Population Sciences- IIPS / India, Macro International: India National Family Health Survey (NFHS-3) 2005-06 . 2007 ( dhsprogram.com [accessed March 18, 2018]).
- ↑ Census of India 2011, results from City Population
- ^ NIC Policy on format of e-mail address. (pdf) May 13, 2013, accessed on January 16, 2015 (English).
Coordinates: 26 ° 24 ' N , 93 ° 0' E