Pipe bomb

Pipe bomb is the general name for an explosive device with an elongated metal shell which, during the reaction of the ingredients, is pressurized to such an extent that it bursts, causing the gas to expand explosively into the environment.
construction
Pipe bombs can contain various explosive substances, e.g. B. black powder or ecrasite .
The pipe is ruptured by high pressure. This can be done by a chemical reaction taking place inside the sealed tube, during which a gas is released. This can be through combustion, or a gas is created from a suspension. This category is not about explosives in the strict sense, as the substances do not detonate on their own. In order to achieve a devastating effect, metallic shells (pipe pieces) are used.
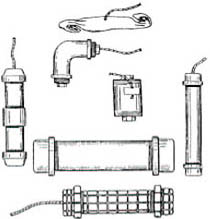
The bomb itself usually consists of a metal tube with two threads, a so-called " nipple ", which is closed at both ends with a blind cap ("stopper") and contains the filler. The detonator is usually inserted through a hole in the pipe.
Misfires
Due to the non-industrial quality of the individual components of the pipe bomb (especially the explosives), there is always a real risk of a premature explosion during construction and transport of the bomb. The bomb can e.g. B. by shock, shock, heat, friction, electrical discharge (static electricity) etc. are triggered prematurely. On the other hand, a pipe bomb cannot ignite correctly and thus can not produce an immediate explosion. This can e.g. This may be the case, for example, if the pressure build-up inside the pipe does not proceed as planned, because leaks (e.g. the thread or the connection for the igniter) can cause the expanding gas to escape prematurely and the pressure is not high enough to close the pipe bust. The bomb can also be completely tight, but the pressure of the expanding gases inside can be too low to blow up the bomb shell. In this case the result is a pipe bomb which is under high internal pressure, which has not yet exploded, but can do so at any time.
Safety distance
If a bomb is found, safety distances should be observed until it is defused. The necessary minimum safety distance depends on the location of the bomb and its (presumed) explosive power. For safety reasons, the explosive power of the bomb is estimated as if its entire volume had been filled with TNT. Typical pipe bombs contain an amount of explosives equivalent to about 2 kg of TNT.
| Mass of the explosive (TNT equivalent) |
Safety distance in buildings |
Safe distance outside of buildings |
|---|---|---|
| 2 kg | 20 m | 250 m |
| 2.3 kg | 21 m | 259 m |
An attempt should always be made to evacuate all persons further than the safety distance outside of buildings .
Known missions
Due to their relatively simple production, pipe bombs are mostly used by terrorists, simple criminals or other people who do not have access to high-quality explosives and more complex technologies. Sometimes the construction and use of pipe bombs, without harmful intentions, is also pursued as a leisure activity.
Multiple use over long periods of time
- 1936–1939, Spanish Civil War
- 1940–1945, World War II , in preparation for the possible German invasion of Great Britain , members of the British Home Guard learn how to make and use pipe bombs
- Since the 1990s, Northern Ireland conflict , hundreds of pipe bomb attacks, carried out by various groups involved, e.g. B. Loyalist paramilitaries, Red Hand Defenders (RHD), Orange Volunteers (OV), Irish Republican paramilitaries ( Provisional Irish Republican Army , Continuity Irish Republican Army , Real Irish Republican Army ), Republican Action Against Drugs (RAAD). Due to the meanwhile widespread knowledge also increasingly used by criminals in southern Ireland.
Well-known individual cases and small series
- May 4, 1886, bomb attack during the Haymarket Riots in Chicago, Illinois, USA, 18 dead, unknown number of injured
- September 26, 1980, Oktoberfest attack in Munich, Germany, 13 dead, 211 injured
- May 10, 1988, 1992–1994, department store blackmail by Arno Funke (alias “Dagobert”), no dead, 1 injured
- 1993–1997, several attacks by Franz Fuchs
- since August 21, 1994, Italian unabomber
- July 27, 1996, Bomb attack at the 1996 Olympic Games in Atlanta, USA, 2 dead, 111 injured
- April 20, 1999, Columbine High School rampage , Littleton, USA
- July 27, 2000, explosives attack in Düsseldorf , Germany, 1 dead, 10 injured
- December 11, 2010, suicide bombing in Stockholm 2010 , Stockholm, Sweden, 1 dead (the assassin himself), 2 injured by an additional car bomb
- December 10, 2012, explosives found at Bonn Central Station 2012 , Bonn, Germany, no dead, no injured
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Ekkehard M. Kasper, Markus M. Luedi, Pascal O. Zinn, Peter AD Rubin, Clark Chen: Retained transorbital foreign body with intracranial extension after pipe bomb explosion . In: Surgical Neurology International . tape 1 , 2010, ISSN 2229-5097 , p. 94 , PMID 21246061 , PMC 3019363 (free full text) - ( surgicalneurologyint.com ). doi : 10.4103 / 2152-7806.74241 (currently unavailable) .
- ↑ a b c d Bomb Threat Stand-Off Distances. (PDF) Office of the Director of National Intelligence.
- ^ A b Hans-Dieter Nüßler: First use of dangerous goods. ecomed-Storck, 2013, ISBN 978-3-86897-141-5 , p. 381.
- ^ Georgia College Girl Arrested for Alleged Pipe Bomb 'Hobby'. abcnews.go.com, 2012 (English).
- ↑ Texas House candidate says probation for pipe bomb stems from blowing up tree stumps . In: The Texas Tribune . 2018 (English, texastribune.org ): “Growing up, I blew up tree stumps recreationally”
- ^ Campbell McCutcheon: Small Arms Training III other Weapons - 8 - Home-made Grenades . In: The Home Guard Manual 1941 . Amberley Publishing Limited, 2012, ISBN 978-1-4456-1103-7 , pp. 77 ( books.google.com ).
- ^ John Davison Lawson, Robert Lorenzo Howard: American State Trials. A Collection of the Important and Interesting Criminal Trials which Have Taken Place in the United States, from the Beginning of Our Government to the Present Day - with Notes and Annotations . tape 12 . Thomas Law Book Company, 1919, pp. 64 ( Textarchiv - Internet Archive ).
- ↑ mak: Oktoberfest assassination attempt - new investigations required after 30 years. In: Spiegel Online from September 12, 2010.
- ↑ J. Jüttner: The Dagobert case - "We were like two boxers". In: Spiegel Online , March 12, 2012.
- ^ Letter bomb bomber Franz Fuchs is dead. In: Spiegel Online , February 26, 2000.
- ↑ Traces of death, dead traces . In: Der Spiegel . No. 30 , 2001 ( online ).
- ^ Konrad Litschko: Arrest 16 years after the attack: "Extremely plausible". In: The daily newspaper . 1st February 2017.
- ↑ telegraph.co.uk
- ↑ (aar / ulz / dpa / Reuters): bomb alarm. Bag blown up in Bonn Central Station . Spiegel Online , December 10, 2012.