Snake eels
| Snake eels | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

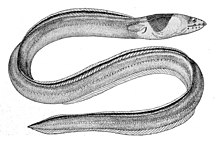
Ringed snake eel ( Myrichthys colubrinus ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Ophichthidae | ||||||||||||
| Rafinesque , 1815 |
The snake eels (Ophichthidae) are a family from the order of the eel-like . It consists of about 300 species in 52 genera . The name comes from the Greek : ophis means snake and ichthys means fish.
Snake eels live in subtropical and tropical seas in coastal regions, over sandy bottoms or in coral reefs . Some species also go into estuaries.
features
Snake eels are similar to moray eels : they are elongated, the number of their vertebrae is between 110 and 270, the pectoral fins are very small or absent, as is the caudal fin , whose function is taken over by the long dorsal and anal fins that reach far back . The tip of the tail is reinforced with bones in many species and enables the fish to dig themselves backwards into the sand very quickly. The mouth of the snake eel is terminal or strongly subordinate . The teeth of the individual species are very different: in addition to conical fangs, blunt teeth also appear in order to grind hard-shelled prey. In contrast to the moray eels, whose nostrils are at eye level, the nostrils of the snake eels are far in front above the tip of the snout and end in tubes that are bent downwards. Snake eels are eleven centimeters to 1.7 meters long.
Way of life
Most species are nocturnal. During the day they hide in the sand, often only the head looks out, at night the robbers go foraging for food. The animals are not so tied to their hiding place as morays.
Snake eels eat fish or crustaceans , some specialize in cephalopods . The prey is tracked down gustatory (via the sense of taste).
The reproduction of snake eels is largely unknown. Some species have been observed to form groups and swim to the surface to spawn.
Tribal history and systematics
The fossil snake eel Goslinophis is known from the northern Italian Monte Bolca Formation, which arose from Tethys deposits in the Eocene .
Snake eels belong to the eel-like family and, together with eight other families, belong to the suborder Congroidei. Almost all members of this suborder, including the snake eels, lack the scales. The frontal bone has grown together.
Subfamily Ophichthinae
The members of this subfamily often have stripes or spots, and some have a uniform color. The tail is without a caudal fin and is hard or fleshy. The genera Apterichtus , Cirricaecula and Ichthyapus are completely without fins, others lack pectoral , dorsal or anal fin .
- Genus Rhinophichthus McCosker, 1999
- Rhinophichthus penicillatus McCosker, 1999
- Tribe of Bascanichthyini
- Genus Allips McCosker, 1972
- Allips concolor McCosker, 1972
- Genus Bascanichthys Jordan & Davis, 1891
- Bascanichthys bascanium Jordan, 1884
- Bascanichthys bascanoides Osburn & Nichols, 1916
- Bascanichthys ceciliae Blache & Cadenat, 1971
- Bascanichthys congoensis Blache & Cadenat, 1971
- Bascanichthys cylindricus Meek & Hildebrand, 1923
- Bascanichthys deraniyagalai Menon, 1961
- Bascanichthys fijiensis Seale, 1935
- Bascanichthys filaria Günther, 1872
- Bascanichthys gaira Moreno et al., 2016
- Bascanichthys inopinatus McCosker, Böhlke & Böhlke, 1989
- Bascanichthys kirkii Günther, 1870
- Bascanichthys longipinnis Kner & Steindachner, 1867
- Bascanichthys myersi Herre, 1932
- Bascanichthys panamensis Meek & Hildebrand, 1923
- Bascanichthys paulensis Storey, 1939
- Bascanichthys pusillus Seale, 1917
- Bascanichthys scuticaris Goode & Bean, 1880
- Bascanichthys sibogae Weber, 1913
- Genus Caralophia Böhlke, 1955
- Caralophia loxochila Böhlke, 1955
- Genus Dalophis Rafinesque, 1810
- Dalophis boulengeri Blache, Cadenat & Stauch, 1970
- Dalophis cephalopeltis Bleeker, 1863
- Dalophis imberbis Delaroche, 1809
- Dalophis multidentatus Blache & Bauchot, 1972
- Dalophis obtusirostris Blache & Bauchot, 1972
- Genus Ethadophis Rosenblatt & McCosker, 1970
- Ethadophis akkistikos McCosker & Böhlke, 1984
- Ethadophis byrnei Rosenblatt & McCosker, 1970
- Ethadophis epinepheli Blache & Bauchot, 1972
- Ethadophis foresti Cadenat & Rou, X1964
- Ethadophis merenda Rosenblatt & McCosker, 1970
- Genus Gordiichthys Jordan & Davis, 1891
- Gordiichthy's combibus McCosker & Lavenberg, 2001
- Gordiichthys ergodes McCosker, Böhlke & Böhlke, 1989
- Gordiichthys irretitus Jordan & Davis, 1891
- Gordiichthys leibyi McCosker & Böhlke, 1984
- Gordiichthys randalli McCosker & Böhlke, 1984
- Genus Leptenchelys Myers & Wade, 1941
- Leptenchelys vermiformis Myers & Wade, 1941
- Genus Phaenomonas Myers & Wade, 1941
- Phaenomonas cooperae Palmer, 1970
- Phaenomonas longissima Cadenat & Marchal, 1963
- Phaenomonas pinnata Myers & Wade, 1941
- Genus Allips McCosker, 1972
- Tribe Callechelyini
- Genus Aprognathodon Böhlke, 1967
- Aprognathodon platyventris Böhlke, 1967
- Genus Callechelys Kaup, 1856
- Callechelys bilinearis Kanazawa, 1952
- Callechelys bitaeniata Peters, 1877
- Callechelys catostoma Schneider & Forster, 1801
- Callechelys cliffi Böhlke & Briggs, 1954
- Callechelys eristigma McCosker & Rosenblatt, 1972
- Callechelys galapagensis McCosker & Rosenblatt, 1972
- Callechelys guineensis Osório, 1893
- Callechelys leucoptera Cadenat, 1954
- Callechelys lutea Snyder, 1904
- Callechelys marmorata Bleeker, 1853
- Callechelys muraena Jordan & Evermann, 1887
- Callechelys papulosa McCosker, 1998
- Callechelys randalli McCosker, 1998
- Callechelys springeri Ginsburg, 1951
- Callechelys striata Smith, 1957
- Genus Letharchus Goode & Bean, 1882
- Letharchus aliculatus McCosker, 1974
- Letharchus rosenblatti McCosker, 1974
- Letharchus velifer Goode & Bean, 1882
- Genus Leuropharus Rosenblatt & McCosker, 1970
- Leuropharus lasiops Rosenblatt & McCosker, 1970
- Genus Paraletharchus McCosker, 1974
- Paraletharchus opercularis Myers & Wade, 1941
- Paraletharchus pacificus Osburn & Nichols, 1916
- Genus Xestochilus McCosker, 1998
- Xestochilus nebulosus Smith, 1962
- Genus Aprognathodon Böhlke, 1967
- Ophichthini tribe
- Genus Aplatophis Böhlke, 1956
- Aplatophis chauliodus Böhlke, 1956
- Aplatophis zorro McCosker & Robertson, 2001
- Genus Brachysomophis Kaup, 1856
 Sterngucker-Schlangenaal ( Brachysomophis cirrocheilos )
Sterngucker-Schlangenaal ( Brachysomophis cirrocheilos )- Brachysomophis atlanticus Blache & Saldanha, 1972
- Stargazer snake eel ( Brachysomophis cirrocheilos ) Bleeker, 1857
- Brachysomophis crocodilinus Bennett, 1833
- Brachysomophis henshawi Jordan & Snyder, 1904
- Brachysomophis longipinnis McCosker & Randall, 2001
- Brachysomophis porphyreus Temminck & Schlegel, 1846
- Brachysomophis umbonis McCosker & Randall, 2001
- Genus Echelus Rafinesque, 1810
- Echelus myrus Linnaeus, 1758
- Echelus pachyrhynchus Vaillant, 1888
- Echelus uropterus Temminck & Schlegel, 1846
- Genus Echiophis Kaup, 1856
- Echiophis brunneus Castro-Aguirre & Suárez de los Cobos, 1983
- Echiophis creutzbergi Cadenat, 1956
- Echiophis intertinctus Richardson, 1848
- Echiophis polyspondylus McCosker & Ho, 2015
- Echiophis punctifer Kaup, 1860
- Genus Elapsopis Kaup, 1856
- Elapsopis cyclorhinus Fraser-Brunner, 1934
- Elapsopis versicolor Richardson, 1848
- Genus Evips McCosker, 1972
- Evips percinctus McCosker, 1972
- Genus Herpetoichthys Kaup, 1856
- Herpetoichthys fossatus Myers & Wade, 1941
- Genus Hyphalophis McCosker & Böhlke, 1982
- Hyphalophis devius McCosker & Böhlke, 1982
- Genus Kertomichthys McCosker & Böhlke, 1982
- Kertomichthys blastorhinos Kanazawa, 1963
- Genus Leiuranus Bleeker, 1853
- Leiuranus semicinctus Lay & Bennett, 1839
- Genus Lethogoleos McCosker & Böhlke, 1982
- Lethogoleos andersoni McCosker & Böhlke, 1982
- Genus Malvoliophis Whitley, 1934
- Malvoliophis pinguis Günther, 1872
- Genus Myrichthys Girard, 1859
- Myrichthys aspetocheiros McCosker & Rosenblatt, 1993
- Myrichthys bleekeri Gosline, 1951
- White-spotted snake eel ( Myrichthys breviceps ) Richardson, 1848
- Ringed snake eel (
- Genus Aplatophis Böhlke, 1956
- Myrichthys maculosus Cuvier, 1816
- Myrichthys magnificus Abbott, 1860
- Myrichthys ocellatus Lesueur, 1825
- Myrichthys pantostigmius Jordan & McGregor, 1899
- Myrichthys pardalis Valenciennes, 1839
- Myrichthys tigrinus Girard, 1859
- Myrichthys xysturus Jordan & Gilbert, 1882
- Mystriophis crosnieri Blache, 1971
- Mystriophis rostellatus Richardson, 1848

- Ophichthus altipennis Kaup, 1856
- Ophichthus apachus McCosker & Rosenblatt, 1998
- Ophichthus aphotistos McCosker & Chen, 2000
- Ophichthus apicalis Anonymous [Bennett], 1830
- Ophichthus arneutes McCosker & Rosenblatt, 1998
- Ophichthus asakusae Jordan & Snyder, 1901
- Ophichthus bicolor McCosker & Ho, 2015
- Saddle Snake Eel ( Ophichthus bonaparti ) Kaup, 1856
- Ophichthus brachynotopterus Karrer, 1982
- Ophichthus brasiliensis Kaup, 1856
- Ophichthus brevicaudatus Chu, Wu & Jin, 1981
- Ophichthus celebicus Bleeker, 1856
- Ophichthus cephalozona Bleeker, 1864
- Ophichthus cruentifer Goode & Bean, 1896
- Ophichthus cylindroideus Ranzani, 1839
- Ophichthus echeloides D'Ancona, 1928
- Ophichthus episcopus Castelnau, 1878
- Ophichthus erabo Jordan & Snyder, 1901
- Ophichthus evermanni Jordan & Richardson, 1909
- Ophichthus exourus McCosker, 1999
- Ophichthus fasciatus Chu, Wu & Jin, 1981
- Ophichthus frontalis Garman, 1899
- Ophichthus garretti Günther, 1910
- Ophichthus genie McCosker, 1999
- Ophichthus gomesii Castelnau, 1855
- Ophichthus grandoculis Cantor, 1849
- Ophichthus hyposagmatus McCosker & Böhlke, 1984
- Ophichthus karreri Blache, 1975
- Ophichthus kunaloa McCosker, 1979
- Ophichthus kusanagi Hibino et al., 2019
- Ophichthus leonensis Blache, 1975
- Ophichthus limkouensis Chen, 1929
- Ophichthus longipenis McCosker & Rosenblatt, 1998
- Ophichthus lupus Hibino et al., 2019
- Ophichthus macrochir Bleeker, 1853
- Ophichthus macrops Günther, 1910
- Ophichthus maculatus Rafinesque, 1810
- Ophichthus madagascariensis Fourmanoir, 1961
- Ophichthus manilensis Herre, 1923
- Ophichthus marginatus Peters, 1855
- Ophichthus mecopterus McCosker & Rosenblatt, 1998
- Ophichthus megalops Asano, 1987
- Ophichthus melanoporus Kanazawa, 1963
- Ophichthus melope McCosker & Rosenblatt, 1998
- Ophichthus menezesi McCosker & Böhlke, 1984
- Ophichthus mystacinus McCosker, 1999
- Ophichthus oligosteus Hibino et al., 2019
- Ophichthus omorgmus McCosker & Böhlke, 1984
- Ophichthus ophis Linnaeus, 1758
- Ophichthus parilis Richardson, 1848
- Ophichthus polyophthalmus Bleeker, 1864
- Ophichthus puncticeps Kaup, 1860
- Ophichthus regius Richardson, 1848
- Ophichthus remiger Valenciennes, 1837
- Ophichthus rex Böhlke & Caruso, 1980
- Ophichthus roseus Tanaka, 1917
- Ophichthus rotundus Lee & Asano, 1997
- Ophichthus rufus Rafinesque, 1810
- Ophichthus rugifer Jordan & Bollman, 1890
- Ophichthus rutidoderma Bleeker, 1853
- Ophichthus rutidodermatoides Bleeker, 1853
- Ophichthus serpentinus Seale, 1917
- Ophichthus shaoi McCosker & Ho, 2015
- Ophichthus singapurensis Bleeker, 1864-1865
- Ophichthus spinicauda Norman, 1922
- Ophichthus stenopterus Cope, 1871
- Ophichthus tchangi Tang & Zhang, 2002
- Ophichthus tetratrema McCosker & Rosenblatt, 1998
- Ophichthus triserialis Kaup, 1856
- Ophichthus tsuchidae Jordan & Snyder, 1901
- Ophichthus unicolor Regan, 1908
- Ophichthus urolophus Temminck & Schlegel, 1846
- Ophichthus woosuitingi Chen, 1929
- Ophichthus yamakawai Hibino et al., 2019
- Ophichthus zophochir Jordan & Gilbert, 1882
- Ophisurus macrorhynchos Bleeker, 1853
- Ophisurus serpens Linnaeus, 1758
- Phyllophichthus macrurus McKay, 1970
- Phyllophichthus xenodontus Gosline, 1951
- Pisodonophis boro Hamilton, 1822
- Pisodonophis cancrivorus Richardson, 1848
- Pisodonophis copelandi Herre, 1953
- Pisodonophis daspilotus Gilbert, 1898
- Pisodonophis hijala Hamilton, 1822
- Pisodonophis hoeveni Bleeker, 1853
- Pisodonophis hypselopterus Bleeker, 1851
- Pisodonophis semicinctus Richardson, 1848
- Pisodonophis zophistius Jordan & Snyder, 1901
- Quassiremus ascensionis Studer, 1889
- Quassiremus evionthas Jordan & Bollman, 1890
- Quassiremus nothochir Gilbert, 1890
- Quassiremus polyclitellum Castle, 1996
- Scytalichthys miurus Jordan & Gilbert, 1882
- Suculentophichthus nasus Fricke, Golani & Appelbaum-Golani, 2015
- Xyrias guineensis Blache, 1975
- Xyrias multiserialis Norman, 1939
- Xyrias revulsus Jordan & Snyder, 1901
- Genus Apterichtus Duméril, 1806
- Apterichtus anguiformis Peters, 1877
- Apterichtus ansp Böhlke, 1968
- Apterichtus caecus Linnaeus, 1758
- Apterichtus dunalailai McCosker & Hibino, 2015
- Apterichtus equatorialis Myers & Wade, 1941
- Apterichtus flavicaudus Snyder, 1904
- Apterichtus gracilis Kaup, 1856
- Apterichtus gymnocelus Böhlke, 1953
- Apterichtus hatookai Hibino et al., 2014
- Apterichtus jeffwilliamsi McCosker & Hibino, 2015
- Apterichtus kendalli Gilbert, 1891
- Apterichtus keramanus Machida, Hashimoto & Yamakawa, 1997
- Apterichtus klazingai Weber, 1913
- Apterichtus malabar McCosker & Hibino, 2015
- Apterichtus monodi Rou, X 1966
- Apterichtus moseri Jordan & Snyder, 1901
- Apterichtus mysi McCosker & Hibino, 2015
- Apterichtus nariculus McCosker & Hibino, 2015
- Apterichtus orientalis Machida & Ohta, 1994
- Apterichtus succinus Hibino et al., 2016
- Genus Caecula Vahl, 1794
- Caecula pterygera Vahl, 1794
- Genus Cirrhimuraena Kaup, 1856
- Cirrhimuraena calamus Günther, 1870
- Cirrhimuraena cheilopogon Bleeker, 1860
- Cirrhimuraena chinensis Kaup, 1856
- Cirrhimuraena inhacae Smith, 1962
- Cirrhimuraena oliveri Seale, 1910
- Cirrhimuraena orientalis Nguyen, 1993
- Cirrhimuraena paucidens Herre & Myers, 1931
- Cirrhimuraena playfairii Günther, 1870
- Cirrhimuraena tapeinoptera Bleeker, 1863
- Genus Cirricaecula Schultz in Schultz, Herald, Lachner, Welander & Woods, 1953
- Cirricaecula johnsoni Schultz, 1953
- Cirricaecula macdowelli McCosker & Randall, 1993
- Genus Hemerorhinus Weber & de Beaufort, 1916
- Hemerorhinus heyningi Weber, 1913
- Hemerorhinus opici Blache & Bauchot, 1972
- Genus Ichthyapus Brisout de Barneville, 1847
- Ichthyapus acuticeps Barnard, 1923
- Ichthyapus omanensis Norman, 1939
- Ichthyapus ophioneus Evermann & Marsh, 1900
- Ichthyapus selachops Jordan & Gilbert, 1882
- Ichthyapus vulturis Weber & de Beaufort, 1916
- Genus Lamnostoma Kaup, 1856
- Lamnostoma kampeni Weber & de Beaufort, 1916
- Lamnostoma mindora Jordan & Richardson, 1908
- Lamnostoma orientalis McClelland, 1844
- Lamnostoma polyophthalma Bleeker, 1853
- Lamnostoma taylori Herre, 1923
- Genus Stictorhinus Böhlke & McCosker, 1975
- Stictorhinus potamius Böhlke & McCosker, 1975
- Genus Yirrkala Whitley, 1940
- Yirrkala calyptra McCosker, 2011
- Yirrkala chaselingi Whitley, 1940
- Yirrkala fusca Zuiew, 1793
- Yirrkala gjellerupi Weber & de Beaufort, 1916
- Yirrkala insolitus McCosker, 1999
- Yirrkala kaupii Bleeker, 1858
- Yirrkala lumbricoides Bleeker, 1864
- Yirrkala macrodon Bleeker, 1863
- Yirrkala maculata Klausewitz, 1964
- Yirrkala maculatus Chu, Wu & Jin, 1981
- Yirrkala misolensis Günther, 1872
- Yirrkala moluccensis Bleeker, 1864
- Yirrkala moorei McCosker, 2006
- Yirrkala tenuis Günther, 1870
- Yirrkala timorensis (Günther, 1870)
Subfamily Myrophinae
The members of this subfamily are uniformly colored. Often the back is darker. The fin rays of the caudal fin are small, but still connected to the dorsal and anal fin . Pectoral fins may be present or absent.
- Genus Skythrenchelys Castle & McCosker, 1999
- Skythrenchelys lentiginosa Castle & McCosker, 1999
- Skythrenchelys zabra Castle & McCosker, 1999
- Genus Sympenchelys Hibino et al., 2015
- Sympenchelys taiwanensis Hibino et al., 2015
- Benthenchelyini tribe
- Genus Benthenchelys Fowler, 1934
- Benthenchely's cartieri Fowler, 1934
- Benthenchelys indicus Castle, 1972
- Benthenchelys pacificus Castle, 1972
- Genus Benthenchelys Fowler, 1934
- Tribe myrophini
- Genus Ahlia Jordan & Davis, 1891
- Ahlia egmontis Jordan, 1884
- Genus Asarcenchelys McCosker, 1985
- Asarcenchelys longimanus McCosker, 1985
- Genus Glenoglossa McCosker, 1982
- Glenoglossa wassi McCosker, 1982
- Genus Mixomyrophis McCosker, 1985
- Mixomyrophis longidorsalis Hibino et al., 2014
- Mixomyrophis pusillipinna McCosker, 1985
- Genus Muraenichthys Bleeker, 1853
- Muraenichthys elerae Fowler, 1934
- Muraenichthys gymnopterus Bleeker, 1853
- Muraenichthys iredalei Whitley, 1927
- Muraenichthys macrostomus Bleeker, 1865
- Muraenichthys philippinensis Schultz & Woods, 1949
- Muraenichthys schultzei Bleeker, 1857
- Muraenichthys sibogae Weber & de Beaufort, 1916
- Muraenichthys thompsoni Jordan & Richardson, 1908
- Muraenichthys velinasalis Hibino & Kimura, 2015
- Genus Myrophis Lütken, 1852
- Myrophis anterodorsalis McCosker, Böhlke & Böhlke, 1989
- Myrophis cheni Chen & Weng, 1967
- Myrophis lepturus Kotthaus, 1968
- Myrophis microchir Bleeker, 1865
- Myrophis platyrhynchus Breder, 1927
- Myrophis plumbeus Cope, 1871
- Myrophis punctatus Lütken, 1852
- Myrophis vafer Jordan & Gilbert, 1883
- Genus Neenchelys Bamber, 1915
- Neenchelys andamanensis Hibino et al., 2015
- Neenchelys buitendijki Weber & de Beaufort, 1916
- Neenchelys daedalus McCosker, 1982
- Neenchelys diaphora Ho et al., 2015
- Neenchelys gracilis Ho & Loh, 2015
- Neenchelys microtretus Bamber, 1915
- Neenchelys nudiceps Tashiro et al., 2015
- Neenchelys pelagica Ho et al., 2015
- Neenchelys retropinna Smith & Böhlke, 1983
- Neenchelys similis Ho et al., 2015
- Genus Pylorobranchus McCosker & Chen, 2013
- Pylorobranchus hearstorum McCosker, 2014
- Pylorobranchus hoi McCosker et al., 2013
- Genus Pseudomyrophis Wade, 1946
- Pseudomyrophis atlanticus Blache, 1975
- Pseudomyrophis frio Jordan & Davis, 1891
- Pseudomyrophis fugesae McCosker, Böhlke & Böhlke, 1989
- Pseudomyrophis micropinna Wade, 1946
- Pseudomyrophis nimius Böhlke, 1960
- Genus Schismorhynchus McCosker, 1970
- Schismorhynchus labialis Seale, 1917
- Genus Schultzidia Gosline, 1951
- Schultzidia johnstonensis Schultz & Woods, 1949
- Schultzidia retropinnis Fowler, 1934
- Genus Scolecenchelys Ogilby, 1897
- Scolecenchelys acutirostris Weber & de Beaufort, 1916
- Scolecenchelys australis Macleay, 1881
- Scolecenchelys borealis Machida & Shiogaki, 1990
- Scolecenchelys brevicaudata Hibino & Kimura, 2015
- Scolecenchelys breviceps Günther, 1876
- Scolecenchelys castlei McCosker, 2006
- Scolecenchelys chilensis McCosker, 1970
- Scolecenchelys cookei Fowler, 1928
- Scolecenchelys erythraeensis Bauchot & Maugé, 1980
- Scolecenchelys godeffroyi Regan, 1909
- Scolecenchelys gymnota Bleeker, 1857
- Scolecenchelys japonica Machida & Ohta, 1993
- Scolecenchelys laticaudata Ogilby, 1897
- Scolecenchelys macroptera Bleeker, 1857
- Scolecenchelys nicholsae Waite, 1904
- Scolecenchelys okamurai Machida & Ohta, 1996
- Scolecenchelys profundorum McCosker & Parin, 1995
- Scolecenchelys puhioilo McCosker, 1979
- Scolecenchelys robusta Hibino & Kimura, 2015
- Scolecenchelys tasmaniensis McCulloch, 1911
- Scolecenchelys vermiformis Peters, 1866
- Scolecenchelys xorae Smith, 1958
- Genus Ahlia Jordan & Davis, 1891
literature
- Joseph S. Nelson : Fishes of the World , John Wiley & Sons, 2006, ISBN 0-471-25031-7
- Kurt Fiedler: Textbook of Special Zoology, Volume II, Part 2: Fish . Gustav Fischer Verlag Jena, 1991, ISBN 3-334-00339-6
- Hans A. Baensch / Robert A. Patzner: Mergus Sea Water Atlas Volume 6 Non-Perciformes (Non-Perciformes) , Mergus-Verlag, Melle, ISBN 3-88244-116-X
- Dieter Eichler / Robert F. Myers: Korallenfische Indopazifik , Jahr-Verlag GmbG & Co., ISBN 3-86132-225-0
Web links
- Snake eels on Fishbase.org (English)
- Integrated Taxonomic Information System Ophichthidae