Secernentea
| Secernentea | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
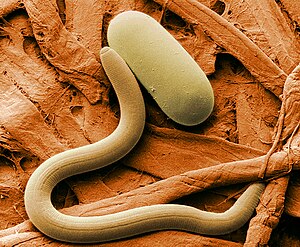
Heterodera glycines with an egg, a parasite of the soybean |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Secernentea | ||||||||||||
| Lorenzen , 1981 | ||||||||||||
| Subclasses | ||||||||||||
The Secernentea form a monophyletic group of roundworms (Nematoda). In the more recent systematics, the roundworms are viewed as a separate strain of the animal kingdom, in which the Secernentea represent one of the two classes alongside the Adenophorea .
features
The main distinguishing feature of the Secernentea from the group of Adenophorea is the presence of tail sensillae (phasmids or phasmidial organs) in most species. In some species these sensillae are absent, but it is assumed that they have regressed in the course of evolution. Further distinguishing features are the lateral excretion canals and the absence of the caudal and epidermal glands in the Secernentea. The males only have one testicle.
The internal systematic classification of the Secernentea is mainly based on the structure of the esophagus . The Rhabditia have a three-part esophagus which is narrowed in the middle part. In the Diplogasteria this part of the digestive tract has an anterior, muscular and a posterior, glandular part. The Spiruria have a bottle-shaped esophagus.
Way of life
The wild species of Secernentea can be found in fresh water or in the ground. They feed as saprophages , diatom eaters or predatory . However, many species also live as parasites of plants and animals. They cause damage to crops in agriculture or are considered pathogens in animals and humans. The species of the genus Zalophora live like endoparasites in the intestines of bipedes , but feed on other roundworms in a predatory manner.
Among the parasites of humans belonging hookworms with Necator americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale , the roundworms with the roundworm of man ( Ascaris lumbricoides ) and the pinworm ( Enterobius vermicularis ), the filarial as Mangifera , Onchocerca volvulus and Loa loa and the Guinea worm ( Dracunculus medinensis ).
Species that parasitize the roots of crops include the beetroot ( Heterodera schachtii ), the soybean cyst nematode ( Heterodera glycines ) and the golden nematode ( Globodera rostochiensis ), which sucks on potato roots. The eggs of these roundworms can survive in the soil within cysts for up to 10 years.
Systematics

Orders with selected species:
- Class Secernentea
- Subclass Diplogasteria
- Subclass Rhabditia
- Subclass Spiruria
- Order Ascaridida
- Order Camallanida
- Order Drilonematida
- Order Oxyurida
- Order Rhigonematida (formerly in Tylenchida)
- Order Spirurida
The consideration of the Tylenchida as a separate subclass is discussed.
Individual evidence
- ^ David J. Hunt, Dave Moore: Rhigonematida from New Britain diplopods. 2. The genera Rhigonema Cobb, 1898 and Zalophora Hunt, 1994 (Rhigonematoidea: Rhigonematidae) with descriptions of three new species. Nematology, 1, 3, pp. 225-242, 1999
literature
- Sievert Lorenzen: Design of a phylogenetic system for free-living nematodes. Publications of the Institute for Marine Research in Bremerhaven, Supplement 7, Verlag Leuwer, Bremen 1981
- Winfried Ahne, Hans-Georg Liebich, Manfred Stohrer, Eckhard Wolf : Zoology: Textbook for students of veterinary medicine and agricultural sciences. With the assistance of Horst Erich König. Schattauer, FK Verlag, Stuttgart and New York 2000, pp. 214-217 ISBN 978-3-7945-1764-0
- Horst Börner: Plant diseases and plant protection. 8th edition, Springer, Berlin and Heidelberg 2009, pp. 137–163 ISBN 978-3-540-49067-8
Web links
- Secernentea systematics