Game notation
As game notation refers to recording methods for board games by character, word or descriptive phrases. With them, a game can be understood as completely as possible. Game notations are widespread, especially in competitive strategic board games . They are used there, especially since the advent of computer databases, for preparation and follow-up.
description
Game notations have developed particularly in popular brain teaser games such as go , chess or checkers . Each move is marked with a unique position, and in chess with the figure. There are basically two closely related types of game notation. On the one hand, the game notation, in which the course of the game can be traced. On the other hand, the position notation, in which a certain score is described.
recording
In general, there are several ways of recording a game. In chess it is common for the players to write down their games themselves after a long period of reflection . If you run out of time , the referee will take care of it . In go-sport, on the other hand, this task is almost always performed by a referee or another player. In the meantime, electronic recording devices have also been developed in which the moves and, with a corresponding digital chess clock , the time are transferred to a computer file. In computer games, this is output directly as a file.
Notation variants
Rectangular game plan
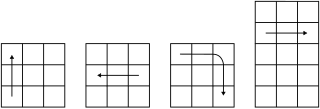
In western countries in particular, the notation on the chessboard and similar game boards is most widespread. The notations are designed according to a matrix . From left to right, the white player marks the columns from A to H (chess), J (10-square queen) or T (Go). The rows are numbered from 1 to 8, 10 or 19 from bottom to top. A field is called a combination of letter and number, according to its coordinate. Moves are noted in such a way that the start and the target field are indicated, in clear cases only the target field. In games with pieces that move differently , such as chess, a short name for the game figure is added for better readability. In placement games such as Go, there is also another possible notation, the kifu , which is described below.
Polygonal game plan
In addition to rectangular game boards, the matrix notation is also adapted in a modified form for other game boards.
- In the mill game , the nodes of the mill board are interpreted as a 7x7 chessboard and the columns from a to g and the rows from 1 to 7 are named according to the games mentioned above. Accordingly, 25 of the 49 possible combinations are missing.
- In the case of abalone , which is played on a hexagonal field, the notation is similar to the game of chess. Here, however, the lines are not at right angles to one another, but instead intersect at a 60 ° angle. The rows run horizontally parallel to the white baseline and are designated from A to I from there to the black baseline. The columns run from bottom right to top left. These are numbered from 1 to 9 starting with the left side as seen by the white player. Due to the hexagonal structure of the game board, rows and columns are of different lengths. This size varies between 5 and 9 for both.
The moves of the game are recorded in two ways. If the stones are drawn in a line, this is noted as the movement of the last stone. If these are pulled across each other, this is noted as the movement of the two outer stones. A position notation is done by notation of the fields occupied by white or black.
I O O O O O
H O O O O O O
G · · O O O · ·
F · · · · · · · ·
E · · · · · · · · ·
D · · · · · · · · 9
C · · X X X · · 8
B X X X X X X 7
A X X X X X 6
1 2 3 4 5
- Similar to Abalone, the fields of the Sternhalma are marked with the crossed 17x17 diagonals. Here you start with a on the left diagonal, which consists of only one field, and end with q on the right. The star point closest to the starting player is assigned a 1. The one furthest away is 17. Here, too, the individual diagonals and columns are of different lengths and not all possible combinations are possible with notations.
Round trip games
- The moves in backgammon are noted in such a way that the counting goes backwards for each player. Field 24 of one player is therefore field 1 of the other, field 23 is field 2, field 22 is field 3, etc. A stone on the bar is noted as "bar" or field 25, stones removed are "off" or on the field 0. If an opponent's stone is captured, this is noted with a "*". If two or more stones are moved together in a double, the number is written after them in brackets.
- Similar to backgammon, the game is noted in Mancala and its variants. Your own six bowls are numbered consecutively from left to right. The bowl from which the stones were removed is noted. Since these stones are then placed in the neighboring bowls, the move is completely noted. A position notation is made by noting the bowls, including both winning switches, with the stones they contain.
Placement games
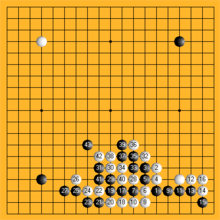
A separate form of notation, the kifu, was developed for Go , which is particularly popular in Asia . This is a hybrid of game and position notation. Since Go is a placement game, it is sufficient to simply enter the number of moves in the field on an image of the game board in order to note both the entire game and the end position.
This system can in principle to all placement games such as Gomoku , Connect Four , Space mill or Tic-Tac-Toe to be adapted. In addition to the game notation options in which the lines / columns of the move are noted or only the columns for Four Wins, the kifu principle can also be used here, in which only the end position appears and each stone is marked with its move number. A special feature of Raummühle and its related games such as 3-D-Tic-Tac-Toe results from the three-dimensionality . This is reproduced in the notation in that the nxn basic grid is again divided into n parts column by column and is graphically highlighted for better visual recognition.
Rubik's Cube
As a three-dimensional game device, the Rubik's Cube makes special demands on the game notation . Over the years, two basic ways of recording the solutions have become established. A graphic notation and a letter notation.
The graphical forms of notation use either three-dimensional cube representations or a 3 × 3 top view of the front with arrows that show the rotation of the cube faces. The latter options have the disadvantage that operations of the middle and rear cube level (seen from the front) are difficult to represent, e.g. B. by an additional settlement of the top. One advantage of this notation, however, is that rotations of the other median planes can be represented as single lines.
| abbreviation | page | |
|---|---|---|
| German | engl. | |
| V | Front) | front |
| H | B (ack) | back |
| R. | R (ight) | right |
| L. | L (eft) | Left |
| O | U (p) | above |
| U | D (own) | below |
| x | x | Rotation of the whole cube when looking at the right side |
| y | y | Rotation of the whole cube when looking at the top |
| z | z | Rotation of the whole cube when looking at the front side |
With the letter notation, each move combination for the die is assigned a letter.
A letter always means a 90 ° clockwise rotation, a 'or −1 counterclockwise relative to the page currently being viewed. For example, rotating the bottom 90 ° clockwise (D) is exactly the opposite of rotating the top 90 ° clockwise (U). Lower case letters referring to pages mean the rotation of two planes when viewed from the corresponding side; for r z. B. the right and parallel middle plane.
Example: The following combination tilts two curb stones and leaves all others unchanged:
- K 1 = B 'R2 B2 RB' R 'B' R2 FDBD 'F'
Here, B 'means a rotation of the rear side by 90 ° counterclockwise, R2 a rotation of the right side by 180 ° and R a rotation of the right side by 90 ° clockwise.
Card games
In card games , the notation is usually done in such a way that the playing cards are recorded in the hand in the form of positional notation and the throws are noted according to a game notation.
Author games
Authors' games represent a particular challenge for notation systems . Due to the variety of possible moves compared to classic strategy games, game recordings must be significantly more extensive.
Remote game
A special variant of games is based on the possibility of notation. The so-called remote game. The remote game is based on the fact that the spatially separated players send each other their moves by letter, postcard, telephone or email. They then receive the answer from their opponent in the same way. Due to the long duration between the moves, which can take several days, a significantly deeper game analysis is achieved than in face-to-face games with sometimes only a few minutes to think about. The analytical ability of computers is now also heavily used in long-distance games , which would be absolutely prohibited in direct duels.
One type of remote game that has become particularly popular in recent years are online games . However, these differ in two respects from the classic game types mentioned above. On the one hand, the transmission takes place much faster than, for example, by post. Thus, the reflection time is the same as that of the game on site. On the other hand, the trains are only transmitted via the Internet in a computer-readable form and implemented by a game program in a form that can be interpreted by humans, for example in the simulation of a specific game situation on a board.
In chess in particular, distance games have a long tradition as correspondence chess . Competitions in this discipline have been held against each other since 1804. The International Correspondence Chess Federation , founded in 1924, has held world championships since 1947, which in the past took up to 5 years due to the long transmission time by post. Nowadays it is held alternately as a traditional post tournament and as an email tournament.
meaning
Especially in the professional tournament moderately powered Puzzle take databases game notations a high priority. On the one hand, they serve to analyze games that have already been played. They are also used to prepare for an upcoming game. The strengths and weaknesses of an opponent and his style of play are analyzed in order to be able to develop counter-strategies.
In chess this has been practiced with particular intensity since the founding of the chess informator in 1966. Since the 1980s, this has been further intensified by the advent of chess databases and computer chess . It is now common practice that all tournament games by top chess players are available in databases. The largest commercially available chess database " Chessbase " contains several million games.
File formats
Over the years, various file formats have evolved into game notation. The standard file format in chess is the portable game notation . In the Go area, the more flexible Smart Game Format is used, which can display other games in addition to chess and Go. In addition, there are other file formats for game notation with the Forsyth-Edwards notation , the GBR code and others. Various file formats such as the Portable Bridge Notation have been developed for the bridge card game.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Archived copy ( Memento of the original from January 14, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.