Signy Island
| Signy Island | ||
|---|---|---|
| Signy station at Factory Cove | ||
| Waters | Weddell Sea | |
| Archipelago | South Orkney Islands | |
| Geographical location | 60 ° 42 ′ 41 ″ S , 45 ° 38 ′ 8 ″ W | |
|
|
||
| length | 6 km | |
| width | 4.5 km | |
| surface | 19.3 km² | |
| Highest elevation |
Tioga Hill 278 m |
|
| Residents | uninhabited | |
| main place | ( Signy station ) | |
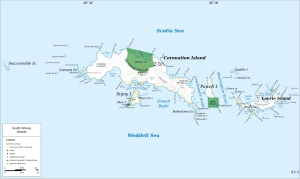
| Map of the South Orkney Islands | ||
Signy Island is a sub-Antarctic island in the Southern Orkney Islands . It is located immediately south of the central part of Coronation Island , separated from it by the 1.6 km wide Normanna Strait. The 1.2 km² Moe Island is located in front of it in the southwest . Signy Island is 6 kilometers long, up to 4.5 kilometers wide and rises up to 278 meters above the sea surface. Its area is 19.3 km². About half of the island is covered by an ice cap . The largest of several glaciers calves directly into the sea in the area of Clowes Bay in the south. In the summer, large areas of moss and some grasses are exposed, and many freshwater pools and lakes are created.
history
The island was discovered in 1823 by Matthew Brisbane (1787–1833) and appears on a map created by James Weddell from 1825, at that time without a name. In the summer of 1912–1913, the Norwegian captain Petter Sørlle (1884–1933) explored the island with the whaler Paal . Sørlle named the island after his wife, Signy Sørlle. From 1920-21, the Norwegian whaling company Tønsbergs Hvalfangeri A / S built a whaling station on Signy that worked until 1926 during the summer months. Borge Bay, the best anchorage in the South Orkney Islands, was used by the Company's factory ships until 1930 . In the 1920s, 3,500 whales were killed here, mostly fin , blue and humpback whales .
In 1947 the United Kingdom established the Signy-Station research station here , which initially served mainly as a meteorological station. It later grew into one of the UK's premier biological research stations. Since 1996 the station has only been manned during the Antarctic summer.
Flora and fauna
The island consists largely of metamorphic rock . It is home to a wide variety of animal and plant life. In addition to around 50 moss , 12 liverwort and 120 lichen species, there are also two flowering plants : the Antarctic Schmiele ( Deschampsia antarctica ) and the Antarctic pearlwort ( Colobanthus quitensis ).
17 different species of birds, including three types of penguins, breed on the island . The Signy Island is therefore designated by BirdLife International as an Important Bird Area (AQ019). Three species of seals , the Antarctic fur seal , the Weddell seal and the southern elephant seal , have their young here. In addition, leopard seals and crab eaters are regularly sighted on ice floes in the waters around Signy Island.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Signy Island (AQ019) in the Data Zone at BirdLife International, accessed on July 22, 2018 (English).
- ^ John Stewart: Antarctica - An Encyclopedia . Vol. 2, McFarland & Co., Jefferson and London 2011, ISBN 978-0-7864-3590-6 , p. 1414
- ^ William James Mills: Exploring Polar Frontiers - A Historical Encyclopedia . tape 2 . ABC-CLIO, 2003, ISBN 1-57607-422-6 , pp. 607 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
Web links
- Information on the research station on Signy Iceland on the website of the British Antarctic Survey (English)