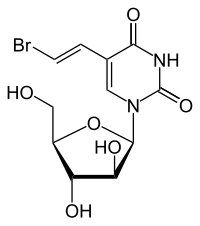
Sorivudine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Sorivudine | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 11 H 13 BrN 2 O 6 | |||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 349.13 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Sorivudine is an anti -viral drug from the Japanese company Nippon Shoji , which was used to treat herpes zoster infections (shingles), herpes simplex type 1 and Epstein-Barr virus . Several deaths in patients treated simultaneously with sorivudine and fluorouracil sparked a pharmaceutical scandal in Japan in 1994. The commercial preparation Usevir ® is no longer on the market in Japan.
application
Sorivudine is an inhibitor of the fluorouracil- degrading enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), which can lead to the lethal accumulation of fluorouracil administered at the same time.
Sorivudine, like brivudine , is broken down in the body into the metabolite bromovinyluracil (BVU).
Deaths
The deaths of 16 sorivudine-treated patients sparked a drug scandal in Japan in 1994 . Three patients had already died during the clinical trials of sorivudine. Since Sorivudine inventor Nihon Shoji had submitted misleading and inaccurate data to the Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare (MHW), Sorivudine was approved. It was later revealed that Nihon Shoji employees sold off their shares before the link between sorivudine and the deaths was reported in the press.
See also
Web links
- Drugs containing 5-fluorouracil or 5-fluoropyrimidine derivatives for systemic use, interaction with brivudine and phenytoin, step-by-step plan procedure stage II. BfArM , April 10, 2007, accessed on May 2, 2017 .
literature
- RB Diasio: Sorivudine and 5-fluorouracil; a clinically significant drug-drug interaction due to inhibition of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase . In: Br J Clin Pharmacol . tape 46 , no. 1 , July 1998, pp. 1–4 , doi : 10.1046 / j.1365-2125.1998.00050.x , PMC 1873978 (free full text).
- H. Gurdon: Japan bans shingles drug after deaths . In: The BMJ . tape 309 , September 1994, p. 627 , doi : 10.1136 / bmj.309.6955.627 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ ABDA database (as of December 4, 2009).
- ^ Brian Woodall, Aki Yoshikawa: Japan's Failure in Pharmaceuticals: Why Is the World Saying "No" to Japanese Drugs? ( August 31, 2000 memento on the Internet Archive ) Georgia Institute of Technology, Yoshikawa Stanford University, March 1997.
