Pointed-headed bushfish
| Pointed-headed bushfish | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
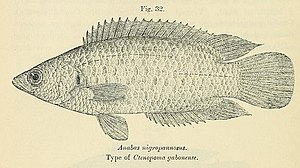
Pointed-headed bushfish ( Ctenopoma nigropannosum ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Ctenopoma nigropannosum | ||||||||||||
| Reichenow , 1875 |
The pointed-headed bushfish ( Ctenopoma nigropannosum ) is an African freshwater fish from the bushfish family that is found in most of the Congo Basin , in the Kouilou and Ngongo-Noumbi in the Republic of the Congo and in the Chiloango on the border between Cabinda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo . There are reports of an occurrence in the Ogooué in Gabon, but these have not yet been confirmed and may also be based on confusion with Ctenopoma gabonense .
features
The pointy-headed bushfish has a spindle-shaped body, which is relatively slender for bush fish, is covered with comb scales and has a pointed mouth, and reaches a maximum length of 15.5 to 17 cm. The body length is about three times the body height and head length. The fish are dark brown, gray-brown or gray in color and show up to nine only faintly visible stripes on the sides of the body that have a width of a scale length. On the tail stalk, which is twice as high as it is long, there is an oval dark spot that is clearly visible in juvenile fish and younger adults, but disappears more and more in older specimens. The pelvic fins are transparent, the unpaired fins are dark. The gill membranes visible in the indentation of the gill cover are often black. The edges of the gill cover and the angle of the preoperculum are sawn. The dorsal fin is supported by 17 to 20, rarely also by 21 hard rays and 10 to 12, rarely by 9 or 13 soft rays and the anal fin by 8 to 9, rarely by 10 hard rays and 10 to 12, rarely by 9 or soft rays. The pectoral fins have 12 to 15 rays. The caudal fin is rounded. The pelvic fins do not reach the beginning of the anal fin. The mouth extends below the center of the eye. Palatine teeth are present. On the lower branch of the first gill arch there are 6 to 7 very short gill rakes .
- Dandruff formula : SL 2-4 / 29-32 (15-20 / 6-16) / 7-9
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Melanie Stiassny, Guy Teugels & Carl D. Hopkins: The Fresh and Brackish Water Fishes of Lower Guinea, West-Central Africa, Volume 2 , ISBN 978-9074752213 , page 361 u. 363.
- ↑ a b Ctenopoma nigropannosum on Fishbase.org (English)
- ^ George Albert Boulenger (1916): Catalog of the fresh-water fishes of Africa in the British Museum (Natural History) . Page 55 and 56.