Swazilink
| Swazilink | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Route length: | 599 km | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gauge : | 1067 mm ( cape track ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Swazilink is a projected railway connection through South Africa and Eswatini , which is supposed to relieve the Richards Bay Coal Line from general freight traffic. The project is carried out jointly by Transnet and Eswatini Railways . The opening was planned for 2019 or 2020. To date (as of 2020), however, the project has not yet got beyond the planning and preparation phase and construction has not yet started.
task
The new connection is intended to disentangle freight traffic on the Richards Bay Coal Line from Ermelo to Richards Bay , which was opened in 1976, while the freight trains that do not transport coal will be routed via this alternative route. The Richards Bay Coal Terminal could export 91 million tons of coal annually, but the railways are currently only able to deliver 76 million tons to the port. If the general freight trains were discontinued, the coal line could transport 91 to 100 million tons of coal, while other freight from the provinces of Gauteng and Mpumalanga would reach the port of Richards Bay via the Swazilink .
The line construction project is designed for an annual freight transport of 15 million tons and is to be implemented with a budget of between 15 and 17 billion rand .
Preparations
In mid-2011, plans to build a new rail link from the Mpumalanga area via Swaziland to Richards Bay were announced. At a press conference of the Southern African Rail Association in Midrand announced in 2011 the director of Eswatini Railways (until 2018 still Swazi Rail) that by means of a feasibility study of a new rail link between Swaziland and South Africa will investigate the construction, with the proposed new line as Western Link referred has been. The project study should be completed by the end of 2014 and the environmental impact assessment has started. The official start of the project was announced in early 2012. In the course of the preparatory work, different routes were considered. In August 2014 an agreement in principle was signed with the landowners for the route area of the new line. Construction was scheduled to start in 2016 and construction will take three years.
course
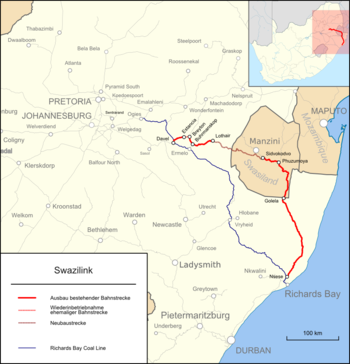
The Swazilink begins in a new marshalling yard to be built near Davel , which will be used to switch trains from electric to diesel traction. The trains from the north drive through a return loop from the south into the station, so it that the yard without changing direction back toward the north exit to where the route first runs parallel to the Richards Bay Coal Line before the carbon sheet with a Überwerfung crosses . The Swazilink follows the old route from Springs to Ermelo to Buhrmannskop. The section from Estancia to the confluence of the Breyten line , which has not been in operation for several years, has to be rebuilt. From Buhrmannskop, the Swazilink follows the branch line to Lothair , where the 146 km long new line begins, which crosses the border at Nerston to Eswatini and is to join the existing line from Matsapha at Sidvokodvo , which connects the Swazilink to the port of Richards Bay, 345 km away leads. At Phuzumoya , a 154-kilometer route branches off to the port of Maputo in Mozambique .
The line is to be built for an axle load of 26 tons and operated with diesel locomotives .
Swaziland line or Swaziland route
The Swaziland line or Swaziland route is the name given to the north-south railway connection from Komatipoort via Eswatini to the Golela border crossing and on to Durban . It has been continuously navigable since 1986 and is mainly used to transport phosphate raw materials and magnetite from the Phalaborwa region to the port of Richards Bay .
Web links
- Pieter Botha, Barend Smit: Environmental Impact Assessment: The Proposed Upgrade and new Construction related to the Development of the Swaziland Rail Link Project, From Davel to Nerston in Mpumalanga . Aurecon Ltd., Lynnwood Manor, 2014. Available online at www.transnet.net (English, PDF).
- Candice Durr, Pieter Botha, Barend Smit: Environmental Assessment Report for the Environmental Impact Assessment: The Proposed Upgrade and new Construction related to the Development of the Swaziland Rail Link Project, from the Sandlane border, through Sidvokodvo to the Lavumisa border . Lynnwood Manor 2014, online at www.sea.org.sz (English, PDF).
- Tebogo Sebego, Barend Smit: Swaziland Rail Link Project - Resettlement Action Plan . Lynnwood Manor, 2014, online at www.sea.org.sz , (English, PDF) PDF document p. 4.
Individual evidence
- ^ Environmental Impact Assessment: The Proposed Upgrade and new Construction related to the Development of the Swaziland Rail Link Project, From Davel to Nerston in Mpumalanga. (PDF) Aurecon, May 9, 2014, accessed October 4, 2015 (English).
- ↑ Terence Creamer: Transnet says take-or-pay contracts offer volume 'cover' in weak commodity climate. Retrieved October 4, 2015 .
- ↑ Keith Barrow: Transnet Invests in heavy-haul capacity . News from January 25, 2012 on www.railjournal.com (English)
- ^ Ceremony launches Swazilink rail project . News from January 12, 2012 on www.railwaygazette.com (English)
- ↑ Keith Barrow: Transnet Invests in heavy-haul capacity . News from January 25, 2012 on www.railjournal.com (English)
- ^ Transnet buys trains and launches Swazilink . News from January 13, 2012 on www.supplymanagement.com (English)
- ↑ Transnet Mulls new Richards Bay line . on www.miningmx.com (English)
- ^ New TFR route through Swaziland. In: Railways Africa. Retrieved October 11, 2015 (en-ZA).
- ^ Proposed new Swazi Rail line feasibility. In: Railways Africa. Retrieved October 11, 2015 .
- ^ SA, Swaziland in major rail investment . Announcement of January 13, 2012 on www.southafrica.info ( Memento of the original of January 26, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (English)
- ↑ Malusi Gigaba, Minister of Public Enterprises: Swazilink media launch and SOD-Turning ceremony . January 12, 2012. at www.dpe.gov.za (English)
- ↑ Transnet inks MoU with landowners for Swazi rail link project. In: Engineering News. Retrieved October 11, 2015 .
- ↑ Commodity exporters brave bloodbath to protect market. In: Moneyweb. Retrieved October 11, 2015 (American English).
- ^ Transnet buys trains and launches Swazilink . News from January 13, 2012 on www.supplymanagement.com (English)
- ^ Proposed New Swazi Rail Line Feasibility . News from June 4, 2014 on www.railwaysafrica.com (English)
- ↑ Terence Creamer: R17bn Swazi, SA rail link to open new coal capacity . on www.miningweekly.com (English)
- ^ Coal system: development plan (d) Komatipoort to Richards Bay. (PDF) (No longer available online.) In: Long-term Planning Framework 2014. Transnet, p. 51 , archived from the original on December 28, 2014 ; accessed on October 10, 2015 (English, quote: "Keep existing diesel system."). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ R17bn Swazi, SA rail link to open new coal capacity. In: Mining Weekly. Retrieved October 10, 2015 .
- ^ Coal system - demand and current capacity (d) Komatipoort to Richards Bay. (PDF) (No longer available online.) In: Long-term Planning Framework 2014. Transnet, p. 49 , archived from the original on December 28, 2014 ; accessed on October 10, 2015 (English, quote: "This line carries magnetite and rock phosphate to Richards Bay via Swaziland .."). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Inter-provincial arterial lines. Kaapmuiden - Mica and beyond to Tzaneen and Groenbult . on www.safiri.co.za (English)