Tellurium tetraiodide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
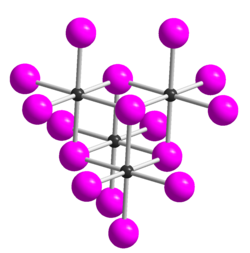
__ Te 4+ __ I - Te 4 I 16 unit in the crystal structure of TeI 4 |
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tellurium tetraiodide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Tellurium (IV) iodide |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Part 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
gray to black solid with a pungent odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 635.22 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
5.403 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
280 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Decomposes in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Tellurium tetraiodide is an inorganic chemical compound of tellurium from the group of iodides .
Extraction and presentation
Tellurium tetraiodide can be obtained by reacting telluric acid with hydrogen iodide .
It can also be obtained by reacting tellurium and iodine , whereby tellurium diiodide and tellurium monoiodide can also be formed depending on the reaction conditions.
properties
Tellurium tetraiodide is an iron-gray solid that decomposes slowly in cold water and rapidly in warm water to form tellurium dioxide and hydrogen iodide . It is stable even in moist air and decomposes when heated, releasing iodine . It is soluble in hydriodic acid with formation of H [TeI5] and somewhat soluble in acetone . 5 modifications of tellurium tetraiodide are known, all of which are made up of tetrameric molecules. The δ-form is the thermodynamically most stable form. This derives (as well as the α-, β- and γ-form) structurally from the ε-form from which a structure of Kuban has -type as four linked via halide bridges TeI 3 + I - describe units composed leaves. The individual shapes differ in that a part 3 corner of the cube is shifted.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h data sheet Tellurium (IV) iodide, 99% (metals basis) from AlfaAesar, accessed on December 17, 2013 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Georg Brauer , with the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a. (Ed.): Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry . 3rd, revised edition. tape I . Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , pp. 435 .
- ^ JJ Zuckerman: Inorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Halogens . John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 0-470-14538-2 , pp. 59 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Erwin Riedel, Christoph Janiak: Inorganic Chemistry . Walter de Gruyter, 2011, ISBN 3-11-022567-0 , p. 461 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 , p. 632.



