Terbium (IV) oxide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||
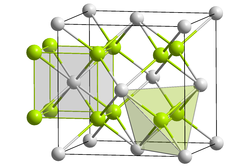
| __ Tb 4+ __ O 2− | ||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Terbium (IV) oxide | |||||||||
| other names |
Terbium dioxide |
|||||||||
| Ratio formula | TbO 2 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
dark red solid |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 190.92 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Terbium (IV) oxide is a chemical compound of terbium from the group of oxides .
Extraction and presentation
Terbium (IV) oxide cannot be obtained by reacting lower terbium oxides with oxygen . The compound could be obtained for the first time by reacting terbium (III, IV) oxide with atomic oxygen at 350 ° C. Later it could be represented by the decomposition of terbium oxides in aqueous solutions.
properties
Terbium (IV) oxide is a dark red solid. It has a crystal structure of fluorite and decomposes in air at temperatures at 350 ° C.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d H. Harry Julius Emeleus, AG Sharpe: ADVANCES IN INORGANIC CHEMISTRY AND RADIOCHEMISTRY . Academic Press, 1977, ISBN 978-0-08-057869-9 , pp. 73 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.