Calcium fluoride
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
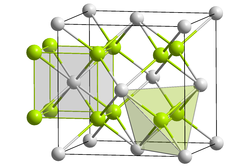
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| __ Ca 2+ __ F - | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Calcium fluoride | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | CaF 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, odorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 78.08 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
3.18 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
1423 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
2500 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (15 mg l −1 at 18 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4338 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
1 mg m −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Calcium fluoride (also calcium fluoride , actually calcium difluoride) is the calcium salt of hydrofluoric acid .
properties
Calcium fluoride forms colorless crystals that are sparingly soluble in water, alcohol and dilute acids with the widespread fluorite lattice . Naturally occurring calcium fluoride is called fluorite or fluorspar and is mostly colored yellow, green, blue, brown, beige or purple due to impurities. It has a high permeability for ultraviolet and infrared radiation . Alkaline solutions do not attack calcium fluoride. There is no reaction with hydrogen and oxygen even under red heat.
Reactions
- Calcium fluoride and sulfuric acid release hydrogen fluoride.
- Calcium cations and fluoride anions always form the poorly soluble calcium fluoride.
Occurrence and extraction

Fluorspar is mined in large quantities, several million tons per year, in surface and underground mining. Since it with other minerals such as barytes (barium sulfate BaSO 4 , galena PbS and quartz SiO 2 is associated), has the 30-60% CaF 2 containing raw ore to be processed before an industrial utilization. For this purpose, the ore extracted is mechanically crushed and then concentrated up to 98% by (multi-stage) flotation . A distinction is made as a commercial form
- Crystal spar with more than 99% CaF 2
- Acid spar with more than 97% CaF 2
- Ceramic spar with more than 95% CaF 2
- Hut spar with more than 85% CaF 2
- Metal spar with 75–82% CaF 2
Pure calcium fluoride is obtained by reacting hydrogen fluoride or hexafluorosilicic acid with calcium carbonate , since precipitated calcium fluoride has a gelatinous consistency in the absence of calcium carbonate and is therefore difficult to clean.
use
Along with the fluorides from phosphoric acid production, calcium fluoride is the most important raw material for fluorine production . According to the fluorspar qualities mentioned above, calcium fluoride is used for the following applications:
- Crystal spar for grinding lenses and optical glasses
- Acid spar for the production of hydrogen fluoride
- Ceramic spar for the production of glass and enamel
- Slag as a flux and slag in metallurgy
Other uses:
- Catalyst for the production of calcium cyanamide
- Because of their permeability to ultraviolet and infrared light, single crystals are used as lenses in instrumental analysis and in the manufacture of electronic circuits.
- Because of its optical properties, calcium fluoride lenses are used in apochromatic lenses in high-quality objectives and telescopes .
- Due to the mutual compensation of the change in the refractive index and the thermal expansion , thermal lenses are only weakly pronounced. For this reason, calcium fluoride is used as a window for laser beams with high power density.
- Standard mineral of the Mohs hardness scale (hardness 4).
Precautions
Hydrogen fluoride is released on contact with strong acids . This is extremely poisonous and extremely corrosive.
proof
Etching test: Put CaF 2 with a little concentrated sulfuric acid in a test tube. The wetting of the glass surface changes because hydrofluoric acid HF is formed.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on calcium fluoride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 20, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Korth Crystals: Calcium Fluoride , accessed December 9, 2015.
- ^ H. Kojima, S. G. Whiteway, C. R. Masson: Melting points of inorganic fluorides . In: Canadian Journal of Chemistry . 46 (18), 1968, pp. 2968-2971, doi : 10.1139 / v68-494 .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-245.
- ↑ G. Brauer (Ed.), Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry 2nd ed., Vol. 1, Academic Press 1963, pp. 233-4.

