Barium fluoride
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
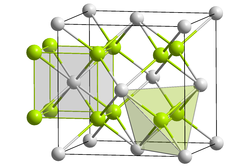
| __ Ba 2+ __ F - | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Barium fluoride | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | BaF 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to white, odorless, crystalline solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 175.33 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
4.89 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
1355 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
2260 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
little in water (1.2 g l −1 at 25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4744 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
1 mg m −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−1207.1 kJ / mol |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Barium fluoride is a chemical compound of barium and is one of the fluorides . It is a colorless crystalline solid.
Occurrence
Barium fluoride occurs naturally in the form of the rare mineral Frankdicksonite .
Extraction and presentation
If its solubility product is exceeded, barium fluoride precipitates when aqueous solutions containing barium and fluoride are concentrated.
properties
Like calcium and strontium fluoride, barium fluoride crystallizes in the cubic fluorite structure . In addition to the structure that is stable under normal conditions, two high-pressure modifications are known in which the barium is coordinated nine or eleven times.
Above 3 GPa pressure, the orthorhombic lead (II) chloride structure forms, in which the other barium halides also crystallize. Another phase change occurs at 12 GPa. Above this pressure, the hexagonal Ni 2 In structure is the most stable.
In the gas phase, contrary to the predictions of the VSEPR model , barium fluoride molecules are not linear, but angled at an angle of 126 °. Relativistic effects are responsible for this .
use
Barium fluoride single crystals are optically transparent over a wide range from 150 nm in the ultraviolet to 15 μm in the infrared . This can be used for optical devices. Like other fluorides, barium fluoride is a flux used in the production of light metals , alloys and in the enamel industry.
If barium fluoride is doped with lanthanoids , it can be used as a material for fiber lasers .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on barium fluoride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ^ H. Kojima, SG Whiteway, CR Masson: Melting points of inorganic fluorides . In: Canadian Journal of Chemistry . 46 (18), 1968, pp. 2968-2971, doi : 10.1139 / v68-494 .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-245.
- ↑ Not explicitly listed in Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , but with the indicated labeling it falls under the group entry barium salts, with the exception of barium sulphate, salts of 1-azo-2-hydroxynaphthalenyl aryl sulphonic acid, and of salts specified elsewhere in this Annex in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-6.
- ^ Mineralienatlas: Frankdicksonit
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1241.
- ↑ JM Leger, J. Haines, A. Atouf, O. Schulte: High-pressure x-ray- and neutron-diffraction studies of BaF 2 : An example of a coordination number of 11 in AX2 compounds. In: Phys. Rev. 1995, B 52, pp. 13247-13256, doi : 10.1103 / PhysRevB.52.13247 .
- ↑ Luis Seijo, Zoila Barandiarán, Sigeru Huzinaga: Ab initio model potential study of the equilibrium geometry of alkaline earth dihalides: MX2 (M = Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba; X = F, Cl, Br, I). In: J. Chem. Phys . 1991, 94, p. 3762 (1991), doi : 10.1063 / 1.459748 .
- ↑ a b entry on barium fluoride. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 13, 2014.

