Barium bromide
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
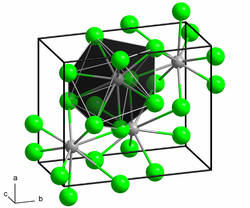
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| __ Ba 2+ __ Br - | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Barium bromide | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | BaBr 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 297.13 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
3.58 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
847 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
good in water (1041 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
0.5 mg m −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
-757.3 kJ / mol |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Barium bromide is a chemical compound of barium and is one of the bromides . It is a colorless solid with a high melting point.
history
Barium bromide plays a role in the discovery of radioactivity and nuclear fission . Since barium and radium compounds have similar properties, it is not easy to separate them. One possibility is the fractional crystallization of suitable salts. Initially, Marie Curie used the chlorides for this. However, these only allow a slow and therefore complex separation. The bromides enable significantly better separations with higher enrichment rates.
This enrichment became important when Otto Hahn discovered nuclear fission , when the product obtained from irradiating uranium with neutrons was initially mistaken for radium. It was only through the unexpected reaction during fractional crystallization that he and Fritz Straßmann realized that it was radioactive barium isotopes and not radium and that a nuclear fission must have taken place.
Extraction and presentation
Water-containing barium bromide dihydrate precipitates out when aqueous solutions containing barium and bromide are concentrated. Above 120 ° C the crystal water is released and the waterless salt is formed.
Further possibilities for the production of barium bromide are the reaction of barium sulfide or barium carbonate with hydrobromic acid .
properties
Like barium chloride and barium iodide, barium bromide crystallizes in the lead (II) chloride structure .
In the gas phase, contrary to the predictions of the VSEPR model , barium bromide molecules are not linear, but angled at an angle of 146 °. Relativistic effects are responsible for this .
use
Except for the separation of barium and radium, which is of little importance due to the dangers posed by radioactive radium, barium is used for the production of chemicals for photography and for the production of other bromides.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Data sheet Barium bromide anhydrous, beads, −10 mesh, 99.999% trace metals basis from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 17, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on barium bromide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Not explicitly listed in Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , but with the indicated labeling it falls under the group entry barium salts, with the exception of barium sulphate, salts of 1-azo-2-hydroxynaphthalenyl aryl sulphonic acid, and of salts specified elsewhere in this Annex in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-6.
- ^ Marie Curie: Radium and the New Concepts in Chemistry . Nobel Prize Speech, Stockholm, December 11, 1911.
- ↑ a b Günther Hermann: Five decades ago: From the transurans to nuclear fission . In: Angewandte Chemie . 1990, 102, 5, pp. 469-496, doi : 10.1002 / ange.19901020504 .
- ↑ a b c Pradyot Patnaik: Handbook of inorganic chemicals. McGraw-Hill Professional, 2003, p. 81, ISBN 978-0-070-49439-8 .
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1241.
- ↑ Luis Seijo, Zoila Barandiarán, Sigeru Huzinaga: Ab initio model potential study of the equilibrium geometry of alkaline earth dihalides: MX2 (M = Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba; X = F, Cl, Br, I). In: J. Chem. Phys . 1991, 94, p. 3762, doi : 10.1063 / 1.459748 .

