Tetrapropylammonium perruthenate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 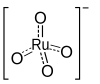
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Tetrapropylammonium perruthenate | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 28 NO 4 Ru | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
dark green solid |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 351.43 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
160 ° C |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Tetrapropylammonium perruthenate ( TPAP or TPAPR ) is a chemical compound that is described by the formula (C 3 H 7 ) 4 N RuO 4 . Sometimes referred to as the Ley Griffith reagent, this compound is mainly used in organic syntheses. The salt consists of the tetrapropylammonium cation and the perruthenate anion (RuO 4 - , ruthenate (VII)). Ruthenium tetraoxide is a very aggressive oxidant , but the derivative RuO 4 - which has been reduced by one step - is a mildly oxidizing agent for converting alcohols into aldehydes .
This oxidizing agent can also be used to oxidize primary alcohols to carboxylic acids . However, this requires a catalyst and a cooxidant with the addition of two equivalents of water . Here, the alcohol is first oxidized to the aldehyde and this is then further oxidized to the carboxylic acid.
TPAP, while expensive, can be used in catalytic amounts. The catalytic cycle is maintained by the stoichiometric addition of cooxidants such as N -methylmorpholine- N -oxide or molecular oxygen.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b data sheet tetrapropylammonium perruthenate from AlfaAesar, accessed on February 9, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Tetrapropylammonium perruthenate data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 03, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Steven V. Ley, Joanne Norman, William P. Griffith, Stephen P. Marsden: Tetrapropylammonium Perruthenate, Pr 4 N + RuO 4 - , TPAP: A Catalytic Oxidant for Organic Synthesis. In: Synthesis , 1994, p. 639, doi : 10.1055 / s-1994-25538 .
- ↑ Z. Xu, CW Johannes, AF Houri, DS La, DA Cogan, GE Hofilena, AH Hoveyda: Applications of Zr-Catalyzed Carbomagnesation and Mo-Catalyzed Macrocyclic Ring Closing Metathesis in Asymmetric Synthesis. Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Sch 38516 (Fluvirucin B1). In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, p. 10302.
- ^ Roman Lenz and Steven V. Ley: Tetra-n-propylammonium perruthenate (TPAP) -catalysed oxidations of alcohols using molecular oxygen as a co-oxidant. In: J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 . 1997, p. 3291, doi : 10.1039 / C39870001625 .

