Transports Internationaux Routiers
Transports Internationaux Routiers ( TIR ; French for 'international road transport') is a customs transit procedure for the temporary import or transit of goods. The associated customs document is always a TIR carnet .
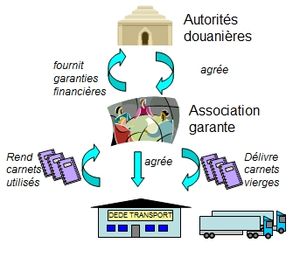
The abbreviation is placed on signs on trucks that transport goods using the TIR method. The freight compartments of the vehicles are sealed . This means that no opening is possible on the way without this being noticed during an inspection. The Carnet minimizes the administrative work involved in customs controls , as only the starting and destination countries are involved in customs clearance. This makes the handling of transit traffic much easier.
TIR Carnets are issued by the Geneva- based International Road Transport Union (IRU - International Road Transport Union / Union Internationale des Transports Routiers).
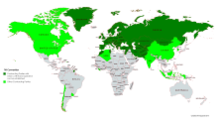
The first TIR agreement was signed between several European countries in 1949. The current legal basis of the TIR procedure is the Convention on the International Transport of Goods with Carnet TIR of November 14, 1975 with currently 68 contracting states, including the member states of the European Union . In practice, the transit procedure with Carnet TIR is only available in 58 guaranteeing countries with corresponding national associations (as of October 15, 2013).
Japan is a party to the 1959 TIR Convention, but not to the 1975 TIR Convention; Therefore, the 1959 TIR Convention remains the legal basis of the TIR procedure for all contracting parties to the 1959 TIR Convention in relation to Japan, even if the latter states are also contracting parties to the 1975 TIR Convention and therefore the 1975 TIR Convention is the legal basis of the TIR procedure is. (As of October 15, 2013).
Board with the inscription "TIR" on road vehicles
A black rubber band is also stretched diagonally across these two TIR boards to show that no TIR transport is being carried out.
"Road vehicles or trucks that carry TIR transport must have a rectangular [...] board marked 'TIR' on the front and back." The boards with a blue background must be 250 mm by 400 mm, the letters TIR in large Latin Block letters must be white and 200 mm high and their lines at least 20 mm wide. “These boards must be placed in such a way that they are clearly visible; they must be detachable or attached or designed in such a way that they can be turned over, covered or folded or in some other way indicate that no TIR transport is being carried out. "
Comments that are not legally binding for the contracting parties to the TIR Convention, but are of importance for the interpretation, harmonization and application of the Convention, also state: “TIR panels must be […] stable panels. Stickers are not recognized as TIR boards. ”The color RAL 5017 is intended for the blue background of the TIR board .
Other customs agreements on carnets
While the Customs Convention on the International Transport of TIR Carnets (TIR Convention) is used to allow the transit of goods by States without in transit countries (ie countries through which the goods pass is transported) duties on the goods paid for the customs agreement on the ATA carnet for the temporary import of goods (ATA Convention) of Brussels of 6 December 1961 serves to avoid the payment of customs duties for goods that are only intended for temporary use, but not for consumption introduced a limited time in a destination country, and in good time before expiry of the residence time that is to be executed fully and again.
See also
Web links
- Translation. Customs agreement for the international transport of goods with TIR carnets (TIR agreement). Completed in Geneva on November 14, 1975. Approved by the Federal Assembly on September 27, 1977. Swiss instrument of ratification deposited on February 3, 1978. Entered into force for Switzerland on August 3, 1978. (Status on January 1, 2015) In addition, the Scope . Both in: The Federal Council. Swiss government portal . Federal Chancellery .
-
TIR , eTIR and the TIR Handbook . All in: unece.org . United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE ).
TIR manual . Edition from 2005. Online at: unece.org . United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) (also contains the complete wording of the TIR Convention from 1975 in the outdated version of September 19, 2004; PDF file, 1.9 MiB). - TIR. Global, seamless and certain . About TIR. Global, seamless and certain . History [of the IRU]. All in: iru.org . IRU (English).
- Contracting parties to the TIR Convention . As of 15 October 2013. In: zoll.de . General Customs Directorate (PDF file; 17 KiB).
- TIR (Transports Internationaux Routiers, international road freight transport) . In: ec.europa.eu . European Commission (German).
- Carnet TIR , its fundamentals ( general fundamentals , locked vehicles and containers and security ) as well as TIR in NCTS . All in: zoll.de . General Customs Directorate .
- TIR Carnet - TIR procedure . In: ezv.admin.ch . Federal Customs Administration FCA.
Individual evidence
- ↑ About the TIR System ( Memento from September 12, 2015 in the Internet Archive ). In: iru.org . IRU. (English).
-
↑ translation. Customs agreement for the international transport of goods with TIR carnets (TIR agreement). Completed in Geneva on November 14, 1975. Approved by the Federal Assembly on September 27, 1977. Swiss instrument of ratification deposited on February 3, 1978. Entered into force for Switzerland on August 3, 1978. (Status on January 1, 2015) In: The Federal Council. Swiss government portal . Federal Chancellery , accessed and received on September 1, 2016 (earlier versions linked in the navigation column on the right; a list of the scope here ).
The original version of November 14, 1975 can be found online here (Federal Republic of Germany):
Law on the Customs Convention of November 14, 1975 on the International Transport of Goods with TIR Carnets (TIR Convention 1975). May 21, 1979 . In: Bundesgesetzblatt , year 1979, part II, no. 23, issued in Bonn on May 29, 1979, pp. 445–564 , accessed and received on September 2, 2016 (PDF file, 8.79 MiB; Convention for the Federal Republic of Germany entered into force on June 20, 1983, see here on pp. 446–447).
or here (European Union):
Customs Agreement on the International Transport of Goods with TIR Carnets (TIR Agreement) , accessed on September 4, 2016 In: Official Journal No. L 252 of September 14, 1978 pp. 2-65. Online in: EUR-Lex . European Union ( implementing regulation here , accessed on September 4, 2016 ). For the history of changes, see: Date of changes and the date they came into effect for the Federal Republic of Germany in juris , accessed and received on September 4, 2016. Consolidated version from 2009 including a list of links to the other changes that came into force for the European Union afterwards , accessed on September 4, 2016 , but missing this change, in EUR-Lex.
-
↑ a b c Detailed view of the State Treaty on Customs Agreement of November 14, 1975 on the international transport of goods with TIR Carnets (TIR Agreement) (with attachments) of the State Treaty database . In: eda.admin.ch . Federal Department of Foreign Affairs FDFA, last update November 27, 2017, accessed and received on February 23, 2018.
Contracting parties to the TIR Convention . Linked in the list of contracting parties - TIR . In: zoll.de . General Customs Directorate , November 24, 2017, accessed and received on February 23, 2018 (PDF file; 17 kB). -
↑ Law on the Customs Convention of January 15, 1959 on the International Transport of Goods with TIR Carnets (TIR Convention). 19 June 1961 . In: Bundesgesetzblatt , Born 1961, Part II, No. 30, published in Bonn on June 24, 1961, pp. 649–741 , accessed and received on September 4, 2016 (PDF file; 5.4 MiB). The Convention came into force for the Federal Republic of Germany on January 21, 1962, see: Announcement on the Entry into Force of the Customs Convention on the International Transport of Goods with TIR Carnets (TIR Convention). 11 December 1961 . In: Bundesgesetzblatt , born in 1962, Part II, No. 1, published in Bonn on January 12, 1961, p. 8 , accessed and received on September 4, 2016 (PDF file; 47 KiB).
Translation. Customs agreement for the international transport of goods with TIR carnets (TIR agreement). Completed in Geneva on January 15, 1959. Approved by the Federal Assembly on March 10, 1960. Swiss instrument of ratification deposited on July 7, 1960. Entered into force for Switzerland on October 5, 1960. (Status on September 28, 2007) In: The Federal Council. Swiss government portal . Federal Chancellery , called and received on September 5, 2016 ( list of the scope here , whereby it should be noted that, in the relationships between the contracting parties for which the TIR Agreement of November 14, 1975 came into force, the latter in accordance with its Art 56 The former overrides and replaces it). - ↑ a b Article 16 of the Customs Convention on the International Transport of Goods with TIR Carnets (TIR Convention, 1975) [TIR Convention as of September 19, 2004 (other provisions partly out of date)]. In: TIR manual . Edition from 2005. pp. 36–240, here p. 60. Online in: unece.org . United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) , pp. 44–248 of the PDF document, here p. 68 of the PDF document, accessed and received on September 1, 2016 (PDF file; 1.9 MiB).
- ↑ Appendix 5 to the Customs Convention on the International Transport of Goods with TIR Carnets (TIR Convention, 1975) [TIR Convention as of September 19, 2004 (other provisions partly out of date)]. In: TIR manual . Edition from 2005. pp. 36–240, here p. 181. Online in: unece.org . United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) , pp. 44–248 of the PDF document, here p. 189 of the PDF document, accessed and received on September 1, 2016 (PDF file; 1.9 MiB).
- ↑ TIR manual . Edition from 2005. p. 36. Online at: unece.org . United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) , p. 44 of the PDF document, accessed and received on September 13, 2016 (PDF file; 1.9 MiB).
- ↑ Commentary on Article 16 of the Customs Convention on the International Transport of Goods with TIR Carnets (TIR Convention, 1975) [TIR Convention as of September 19, 2004 (some articles or annexes no longer up to date)]. In: TIR manual . Edition from 2005. pp. 36–240, here p. 61. Online in: unece.org . United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) , pp. 44–248 of the PDF document, here p. 69 of the PDF document, accessed and received on September 1, 2016 (PDF file; 1.9 MiB).
- ↑ Commentary on Annex 5 to the Customs Convention on the International Transport of Goods with TIR Carnets (TIR Convention, 1975) [TIR Convention as of September 19, 2004 (some articles or annexes no longer up to date)]. In: TIR manual . Edition from 2005. pp. 36–240, here p. 181 Online in: unece.org . United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) , pp. 44–248 of the PDF document, here p. 189 of the PDF document, accessed and received on September 13, 2016 (PDF file; 1.9 MiB).