Trichostatin A
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
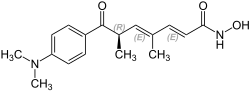
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Trichostatin A | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 17 H 22 N 2 O 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 302.37 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in ethanol and DMSO |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Trichostatin A (TSA) is a fungal antimycotic from the bacterium Streptomyces platensis and selectively blocks class I and class II histone deacetylases (HDAC) in mammals; but not HDAC Class III / Sirtuins .
TSA also blocks the eukaryotic cell cycle during the onset of cell division .
TSA can be used to alter gene expression by inhibiting the removal of acetyl groups on histones ( histone deacetylases , HDAC). This improves the ability of the transcription factors to dock onto DNA promoter areas .
Since histone deacetylases, which inhibit the expression of tumor-suppressing genes, are often active in cancer cells , trichostatin A has potential as a cancer drug. One theory about the mechanism of action of TSA states that the antibiotic upregulates the expression of apoptosis genes, thus reducing the likelihood of cancer cells surviving. Other theories see TSA as an inducer of cell differentiation , which causes the growth of otherwise dedifferentiated and thus divisible cancer cells to stop.
Trichostatin A has hardly been used in clinical studies to date.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c sheet trichostatin A, ≥98% (HPLC), from at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on 28 May 2012 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Information on trichostatin A at AppliChem
- ↑ Vanhaecke T., Papeleu P., Elaut G., Rogiers V .: Trichostatin A - like Hydroxamate Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Therapeutic Agents: Toxicological Point of View . In: Current Medicinal Chemistry . tape 11 , no. 12 , 2004, p. 1629-1643 , doi : 10.2174 / 0929867043365099 , PMID 15180568 .
- ↑ Vigushin DM, Ali S, Pace PE, Mirsaidi N, Ito K, Adcock I, Coombes RC: Trichostatin A is a histone deacetylase inhibitor with potent antitumor activity against breast cancer in vivo . In: Clin Cancer Res. Volume 7 (4) , April 2001, p. 971-6 , PMID 11309348 .
- ↑ Daryl C Drummond, Charles O Noble, Dmitri B Kirpotin, Zexiong Guo, Gary K Scott, Christopher C Benz: Clinical development of histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer agents . In: Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology . tape 45 , 2005, p. 495-528 , doi : 10.1146 / annurev.pharmtox.45.120403.095825 , PMID 15822187 .
- ↑ Sharmila Shankar, Rakesh K. Srivastava: Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Mechanisms and Clinical Significance in Cancer: HDAC Inhibitor-Induced Apoptosis . In: Programmed Cell Death in Cancer Progression and Therapy (= Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology ). tape 615 . Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht 2008, ISBN 978-1-4020-6553-8 , pp. 261-298 , doi : 10.1007 / 978-1-4020-6554-5_13 , PMID 18437899 .
- ↑ ClinicalTrials.gov: Trichostatin A
